Abstract
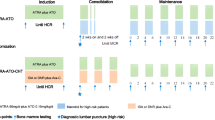
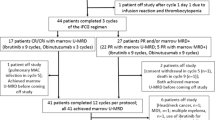
A prospective multicenter study was performed to investigate the clinical and molecular results of intensified double induction therapy including high-dose cytarabine (ara-C) in combination with ATRA in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), followed by consolidation and 3 years maintenance therapy. Fifty-one patients, diagnosed and monitored from December 1994 to June 1999, were evaluated. The median age was 43 (16–60) years. The morphologic diagnosis was M3 in 40 (78%) and M3v in 11 (22%) patients. In 15 (30%) patients the initial white blood cell counts were ⩾5 × 109/l. The cytogenetic or molecular proof of the translocation t(15;17) was a mandatory prerequisite for eligibility. The diagnosis was confirmed by karyotyping in 46 and by RT-PCR of the PML/RARα transcript in 45 cases. The rate of complete hematological remission was 92% and the early death rate 8%. Monitoring of minimal residual disease by RT-PCR of PML/RARα (sensitivity 10−4) showed negativity in 29 of 32 (91%) evaluable cases after induction, in 23 of 25 (92%) after consolidation, and in 27 of 30 (90%) during maintenance, after a median time of 2, 4 and of 18 months after diagnosis, respectively. After a median follow-up of 27 months, the estimated actuarial 2 years overall and event-free survival were both 88% (79, 97), and the 2 years relapse-free survival 96% (90, 100). The high antileukemic efficacy of this treatment strategy is demonstrated by a rapid and extensive reduction of the malignant clone and by a low relapse rate. The results suggest that the intensity of the induction chemotherapy combined with ATRA is one of the factors which may have a critical influence on the outcome of APL. A randomized trial should assess the value of an induction therapy including ATRA and high-dose ara-C in comparison to standard-dose ara-C.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fenaux P, Le Deley MC, Castaigne S, Archimbaud E, Chomienne C, Link H, Guerci A, Duarte M, Daniel MT, Bowen D, Huebner G, Bauters F, Fegueux N, Fey M, Sanz M, Löwenberg B, Maloisel F, Auzanneau G, Sadoun A, Gardin C, Bastion Y, Ganser A, Jacky E, Dombret H, Chastang C, Degos L and the European APL 91 Group . Effect of all-trans retinoic acid in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Results of a multicenter randomized study Blood 1993 82: 3241–3249
Tallman MS, Andersen JW, Schiffer CA, Appelbaum FR, Feusner JH, Ogden A, Shepherd L, Willman C, Bloomfield CD, Rowe JM, Wiernik PH . All-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia New Engl J Med 1997 337: 1021–1028
Kanamaru A, Takemoto Y, Tanimoto M, Murakami H, Asou N, Kobayashi T, Kiriyama K, Ohmoto E, Sakamaki H, Tsubaki K, Hiraoka A, Yamada O, Oh H, Saito K, Matsuda S, Minato K, Ueda T, Ohno R and the Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group . All-trans retinoic acid for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1995 85: 1202–1206
Frankel SR, Eardley A, Heller G, Berman E, Miller WH, Dmitrowsky E, Warrell RP . All-trans retinoic acid for acute promyelocytic leukemia. Results of the New York Study Ann Intern Med 1994 120: 278–286
Warrell RP, Maslak P, Eardley A, Heller G, Miller WH, Frankel SR . Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans retinoic acid: an update of the New York experience Leukemia 1994 8: 929–933
Fenaux P, Castaigne S, Dombret H, Archimbaud E, Duarte M, Morel P, Lamy T, Tilly H, Guerci A, Maloisel F, Bordessoule D, Sadoun A, Tiberghien P, Fegueux N, Daniel MT, Chomienne C, Degos L . All-trans retinoic acid followed by intensive chemotherapy gives a high complete remission rate and may prolong remissions in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: a pilot study on 26 cases Blood 1992 80: 2176–2181
Huang M, Ye Y, Chen S, Chai S, Lu JX, Lin Z, Gu L, Wang Z . Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1988 72: 567–572
Chen ZY, Xue YQ, Zhang R, Tao RF, Xia XM, Li C, Wang W, Zu WY, Yao XZ, Ling BJ . A clinical and experimental study on all-trans retinoic acid-treated acute promyelocytic leukemia patients Blood 1991 78: 1413–1419
Bernard J, Weil M, Boiron M, Jacquillat C, Flandrin G, Gemon MF . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: results of treatment by daunorubicin Blood 1973 41: 489–496
Head D, Kenneth JK, Weick J, Files JC, Ryan D, Foucar K, Montiel M, Bickers J, Fishleder A, Miller M, Spier C, Hanson C, Bitter M, Braziel R, Mills G, Welborn J, Williams W, Hewlett J, Willman C, Appelbaum F . Effect of aggressive daunomycin therapy on survival in acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1995 86: 1717–1728
Mandelli F, Diviero D, Avvisati G, Luciano A, Barbui T, Bernasconi B, Broccia G, Cerri R, Falda M, Fioritoni G, Leoni F, Liso V, Petti MC, Rodeghiero F, Saglio G, Vegna ML, Visani G, Jehn U, Willemze R, Muus P, Pelicci PG, Biondi A, Lo Coco F, for the Gruppo Italiano Mallatie Ematologiche Maligne dell'Adulto and Associazione Italina di Ematologia ed Oncologia Pediatrica Cooperative Groups . Molecular remission in PML/RARα-positive acute promyelocytic leukemia by combined all-trans retinoic acid and idarubicin (AIDA) therapy Blood 1997 90: 1014–1021
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM, Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, Chen Y, Li Z, Fang ZW, Wang YT, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, chen SJ, Chen Z, Wang ZY . Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). II. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients Blood 1997 89: 3354–3360
Estey E, Thall PF, Pierce S, Kantarjian H, Keating M . Treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia without cytarabine J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 483–490
Sanz MA, Martín G, Rayón C, Esteve J, Gonzáles M, Díaz-Mediavilla J, Bolufer P, Barragán E, Terol MJ, Gónzales JD, Colomer D, Chillón C, Rivas C, Gómez C, Ribera JM, Bornstein R, Róman J, Calasanz MJ, Arias J, Álvarez C, Ramos F, Debén G for the PETHEMA Group . A modified AIDA protocol with anthracycline-based consolidation results in high antileukemic efficacy and reduced toxicity in newly diagnosed PML/RARa-positve acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1999 94: 3015–3021
Büchner T, Hiddemann W, Wörmann B, Löffler H, Gassmann W, Haferlach T, Fonatsch C, Haase D, Schoch C, Hossfeld D, Lengfelder E, Aul C, Heyll A, Maschmeyer G, Ludwig WD, Sauerland MC, Heinecke A . Duble induction strategy for acute myeloid leukemia. The effect of high-dose cytarabine with mitoxantrone instead of standard-dose cytarabine with daunorubicin and 6-thioguanine. A randomized trial by the German AML Cooperative Group Blood 1999 93: 4116–4124
Haferlach T, Gassmann W, Löffler H, Jürgensen C, Noack J, Ludwig WD, Thiel E, Haase D, Fonatsch C, Becher R, Schlegelberger B, Nowrousian MR, Lengfelder E, Eimermacher H, Weh HJ, Braumann D, Maschmeyer G, Koch P, Heinecke A, Sauerland MC and Büchner T for the AML Cooperative Group . Clinical aspects of acute myeloid leukemias of the FAB types M 3 and M 4 Eo Ann Hematol 1993 66: 165–170
Lengfelder E, Reichert A, Hehlmann R, Löffler H, Fonatsch C, Schoch C, Staib P, Seifarth W, Sauerland MC, Heinecke A, Wörmann B, Hiddemann W, Büchner T, for the German Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cooperative Group (AMLCG) . Effects of high dose cytarabin as part of double induction strategy in acute promyelocytic leukemia and results of combination with all-trans retinoic acid Blood 1997 90: (Suppl. 1) 330a
Rowley JD, Golomb HM, Dougherty C . 15/17 transloction, a consistent chromosomal change in acute promyelocytic leukaemia Lancet 1977 1: 549–550
Kakizuka A, Miller WH, Umesono K, Warrell RP, Frankel SR, Murty VV, Dimitrovky E, Evans RM . Chromosomal translocation t(15; 17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RARα with a novel putative transcription factor, PML Cell 1991 66: 663–674
De The H, Lavau C, Marchio A, Chomienne C, Degos L, Dejean A . The PML-RARα fusion mRNA generated by the t(15; 17) translocation in acute promyelocytic leukemia encodes a functionally altered RAR Cell 1991 66: 675–684
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C . Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias Br J Haematol 1976 33: 451–458
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C . A variant form of hypergranular promyelocytic leukemia Ann Intern Med 1980 92: 261
Tallman MS, Kwaan HC . Reassessing the hemostatic disorder associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1992 79: 543–553
Frankel SR, Eardley A, Lauwers G, Weiss M, Warrell RP . The ‘retinoic acid syndrome’ in acute promyelocytic leukemia Ann Intern Med 1992 117: 292–296
Tallman MS, Andersen JW, Schiffer CA, Appelbaum FR, Feusner JH, Ogden A, Shepherd L, Rowe JM, Francois C, Larson RS, Wiernik PH . Clinical description of 44 patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia who developed the retinoic acid syndrome Blood 2000 95: 90–95
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T . Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY 1989
Cross NC, Hughes TP, Lin F, O'Shea P, Bungey J, Marks DI, Ferrant A, Martiat P, Goldman JM . Minimal residual disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukaemia in first chronic phase: Correlations with acute graft-versus-host disease Br J Haematol 1993 84: 67–74
Hochhaus A, Lin F, Reiter A, Skladny H, Mason PJ, van Rhee F, Shepherd PC, Allan NC, Hehlmann R, Goldman JM, Cross NC . Quantification of residual disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients on interferon-α therapy by competitive polymerase chain reaction Blood 1996 87: 1549–1555
Sanger F, Nicklein S, Coulson A . DNA sequencing with chain termination inhibitors Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1976 74: 5463–5467
Büchner TH, Urbanitz D, Hiddemann W, Rühl H, Ludwig WD, Fischer H, Aul HC, Vaupel HA, Kuse R, Zeile G, Nowrousian MR, König HJ, Walter M, Wendt FC, Sodomann H, Hossfeld DK, von Paleske A, Löffler H, Gassmann W, Hellriegel KP, Fülle HH, Lunscken CH, Emmerich B, Pralle H, Pees HW, Pfreundschuh M, Bartels H, Koeppen KM, Schwerdtfeger R, Donhuijsen-Ant R, Mainzer K, Bonfert B, Köppler H, Zurborn KH, Ranft K, Thiel E, Heinecke A . Intensified induction and consolidation with or without maintenance chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Two multicenter studies of the German AML Cooperative Group J Clin Oncol 1985 3: 1583–1589
Fenaux P, Chastang C, Chevret S, Sanz M, Dombret H, Archimbaud E, Fey M, Rayon C, Huguet F, Sotto J, Gardin C, Makhoul PC, Travade P, Solary E, Fegueux N, Bordessoule D, San Miguel J, Link H, Desablens B, Stamatoullas A, Deconinck E, Maloisel F, Castaigne S, Preudhomme C, Degos L . A randomized comparison of all transretinoic acid (ATRA) followed by chemotherapy and ATRA plus chemotherapy and the role of maintenance therapy in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1999 94: 1192–1200
Burnett AK, Grimwade D, Solomon E, Wheatley K, Goldstone AH . Presenting white blood cell counts and kinetics of molecular remission predict prognosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all-trans retinoic acid: results of the randomized MRC trial Blood 1999 93: 4131–4143
Estey EH, Keating MJ, McCredie KB, Bodey GP, Freireich EJ . Phase II trial of mitoxantrone in refractory acute leukemia Cancer Treat Rep 1983 67: 389–390
Arlin ZA, Dukart G, Schoch I, Reisman A, Moore J, Silver RA, Cassileth P, Bertino J, Gams R . Phase I–II trial of mitoxantrone in acute leukemia: an interim report Invest New Drugs 1985 3: 213–217
Willemze R, Zwaan FE, Coplin G, Keunig JJ . High-dose cytosine arabinoside in the mangement of refractory acute leukemia Scand J Haematol 1982 29: 141–146
Herzig RH, Wolff SN, Lazarus HM, Phillips GS, Karanes C, Herzig GP . High dose cytosine arabinoside therapy for refractory leukemia Blood 1983 62: 361–369
Hiddemann W, Kreutzmann H, Straif K, Ludwig WD, Mertelsmann R, Donhuijsen-Ant R, Lengfelder E, Arlin Z, Büchner TH . High-dose cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone: a highly effective regimen in refractory acute myeloid leukemia Blood 1987 69: 744–749
Büchner TH, Barlogie B, Asseburg U, Hiddemann W, Kamanabroo D, Göhde W . Accumulation of S-phase cells in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia by cytosine arabinoside Blut 1974 28: 299–300
Kantarjian HM, Keating MJ, Walters RS, Smith TL, McCredie K, Freireich EJ . Role of maintenance chemotherapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia Cancer 1987 59: 1258–1263
Diviero D, Rossi V, Avvisati G, De Santis S, Pistilli A, Pane F, Saglio G, Martinelli G, Petti MC, Santoro A, Pellici PG, Mandelli F, Biondi A, Lo Coco F for the GIMEMA and AIEOP Cooperative Groups . Early detection of relapse by prospective reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis of the PML/RARα fusion gene in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia enrolled in the GIMEMA-AIEOP multcenter ‘AIDA’ trial Blood 1998 92: 784–789
Licht JD, Chomienne C, Goy A, Chen A, Scott AA, Head DR, Michaux JL, Wu Y, DeBlasio A, Miller WH Jr . Clinical and molecular characterization of a rare syndrome of acute promyelocytic leukemia associated with translocation t(11; 17) Blood 1995 85: 1083–1094
Redner RL, Rush EA, Faas S, Rudert WA, Corey SJ . The t(5; 17) variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia expresses a nucleophosmin-retinoic acid receptor fusion Blood 1996 87: 882–886
Scott AA, Head DR, Kopecky KJ, Appelbaum FR, Theil KS, Grever MR, Chen IM, Whittacker MH, Griffith BB, Licht JD, Waxman S, Whalen MM, Bankhurst AD, Richter LC, Grogan TM, Wilman CL . HLA-DR−, Cd33+, CD56+, CD16− myeloid/natural killer cell acute leukemia: a previously unrecognized form of acute leukemia potentially misdiagnosed as French–American–British acute myeloid leukemia-M3 Blood 1994 84: 244–255
Chou WC, Tang JL, Yao M, Lee FY, Lin MT, Wang CH, Shen MC, Chen YC, Tien HF . Clinical and biological characteristics of acute promyelocytic leukemia in Taiwan. A high relapse rate in patients with high initial and peak white blood cell counts during all-trans retinoic acid treatment Leukemia 1997 11: 921–928
Runde V, Aul C, Landen H, Dokekias A, Fillet G, Schneider W . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: clinical findings and therapeutic results in 30 patients Haematol Blood Transfus 1990 33: 346–350
De Botton S, Dombret H, Sanz M, San Miguel J, Cxaillot D, Zittoun R, Gardemblas M, Stamatoulas A, Condé E, Guerci A, Gardin C, Geiser K, Cony Makhoul D, Reman O, de la Serna J, Lefrere F, Chomienne C, Chastang C, Degos L, Fenaux P, and the European APL Group . Incidence, clinical features, and outcome of all trans retinoic acid syndrome in 431 cases of newly diagnosaed acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1998 92: 2712–2718
Lo Coco F, Diviero D, Pandolfi PP, Biondi A, Rossi V, Avvisati G, Rambaldi A, Arcese W, Petti MC, Meloni G, Mandelli F, Grignani F, Masera G, Barbui T, Pellici PG . Molecular evaluation of residual disease as a predictor of relapse in acute promyelocytic leukemia Lancet 1992 340: 1437–1438
Miller WH Jr, Kakizuka A, Frankel SR, Warrell RP Jr, DeBlasio A, Levine K, Evans RM, Dmitrovsky E . Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for the rearranged retinoic acid receptor alpha clarifies diagnosis and detects minimal residual disease in acute promyelocytic leukemia Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 2694–2698
Huang W, Sun GL, Li XS, Cao Q, Lu Y, Jang GS, Zhang FQ, Chai JR, Wang ZY, Waxman S, Chen Z, Chen SJ . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: clinical relevance of two major PML-RARα isoforms and detection of minimal residual disease by retrotranscriptase/polymerase chain reaction to predict relapse Blood 1993 82: 1264–1269
Miller WH, Levine K, DeBlasio A, Frankel SR, Dmitrovsky E, Warrell RP Jr . Detection of minimal residual disease in acute promyelocytic leukemia by a reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay for the PML/RARα fusion mRNA Blood 1993 82: 1689–1694
Fukutani H, Naoe T, Ohno R, Yoshida H, Kiyoi H, Miyawaki S, Morishita H, Sano F, Kamibayashi H, Matsue K, Miyake T, Hasegawa S, Ueda Y, Kato Y, Kobayashi H, Shimazaki C, Kobayashi M, Kurane R, Sakota H, Masaki K, Wakayama T, Tohyama K, Nonaka Y, Natori H and the Leukemia Study Group of the Ministry of Health and Welfare (Kouseisho) . Prognostic significance of the RT-PCR assay of PML-RARA transcripts in acute promyelocytic leukemia Leukemia 1995 9: 588–593
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Prof Dr Wolfgang Köpcke, University of Münster, for his biostatistical advice. We are grateful to the clinicians who entered their patients into this trial. The following institutions participated. Medizinische Klinik II, Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen (T Ittel); Humaine Klinikum Bad Saarow (W Schulze), Krankenhaus Neukölln, Berlin (A Grüneisen); Universitätsklinikum Charité, Berlin (A Trittin); Robert-Rössle-Klinik, Humboldt-Universität, Berlin (W-D Ludwig); Knappschaftskrankenhaus Bochum (W Schmiegel); Zentralkrankenhaus Bremen (H Rasche, U Kubica); Evangelische Diakonissenanstalt Bremen (K Pflüger); Klinik I für Innere Medizin, Universität zu Köln (V Diehl, P Staib); Krankenhaus Düren (J Karow); Medizinische Klinik Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf (C Aul, A Heyll); Medizinische Klinik II, St Johannes-Hospital Duisburg (M Westerhausen, C Schadeck-Gressel); St-Antonius-Hospital Eschweiler (R Fuchs, A Thomalla); Klinik für Knochenmarktransplantation, Universitätsklinikum Essen (U Schaefer, D Beelen); Westdeutsches Tumorzentrum, Universitätsklinikum Essen (M Nowrousian); Evangelisches Krankenhaus Essen-Werden (W Heidt, C Tirier); Zentrum Innere Medizin, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen (W Hiddemann, B Wörmann, D Haase, C Schoch); Katholisches Krankenhaus Hagen (H Eimermacher); Städtisches Krankenhaus Halle-Dölau (U Haak); Klinikum Hannover-Siloah (H Kirchner); Allgemeines Krankenhaus Altona, Hamburg (K Mainzer, D Braumann); Evangelisches Krankenhaus Hamm (L Balleisen, D Grote-Metke); Städtische Kliniken Kassel (W Hirschmann, B Eggeling); II. Medizinische Klinik, Klinikum der Christian-Albrechts-Universität Kiel (H Löffler, W Gassmann, T Haferlach); Medizinische Klinik II, Klinikum Krefeld (K Becker, M Planker); Städtisches Krankenhaus Süd, Lübeck (H Bartels); Klinikum Ludwigshafen (M Uppenkamp, M Baldus); III. Medizinische Klinik Mannheim der Universität Heidelberg (R Hehlmann, E Lengfelder); Krankenhaus Maria Hilf, Mönchen-Gladbach (HW Reis, B Trenn); Städtisches Krankenhaus München-Neuperlach (M Garbrecht, H Schäfer); Klinikum Osnabrück (J Hartlapp, T Hegge); Paracelsus-Klinik Osnabrück (O Koch); I. Medizinische Klinik, Klinikum der Universität Regensburg (R Andreesen, A Reichle); Medizinische Universitätsklinik Ulm (L Bergmann). The NB4 cell line was provided by the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmBH, Braunschweig.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lengfelder, E., Reichert, A., Schoch, C. et al. Double induction strategy including high dose cytarabine in combination with all-trans retinoic acid: effects in patients with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leukemia 14, 1362–1370 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401843
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401843
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: A History over 60 Years—From the Most Malignant to the most Curable Form of Acute Leukemia
Oncology and Therapy (2019)
-
Acute promyelocytic leukemia: where did we start, where are we now, and the future
Blood Cancer Journal (2015)
-
Two cycles of risk-adapted consolidation therapy in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Results from the SAL-AIDA2000 trial
Annals of Hematology (2015)
-
What is the Standard Regimen for Patients with Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia?
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2014)
-
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: Do We Have a New Front-Line Standard of Treatment?
Current Oncology Reports (2013)