Abstract
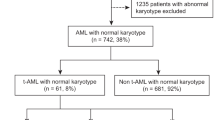
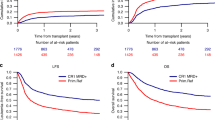
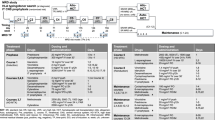
To improve the basis for the stratification of patients with refractory and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) univariate and multivariate analyses of prognostic factors were performed in 254 patients (median age 50 years, range 18–74) undergoing S-HAM salvage chemotherapy during two consecutive prospective trials of the German AML Cooperative Group. In a multivariate analysis, duration of the first complete remission (CR) was the only factor associated with time to treatment failure (P = 0.0223). Disease-free survival was influenced by a short duration of the first CR of less than 6 months (P = 0.0001), WBC (P = 0.0018), blast count (P = 0.0037), and neutrophil count (P = 0.0119). The achievement of CR was related to the hemoglobin level only (P = 0.0457), the early death rate was related to age only (P = 0.0109), and survival was related to the bilirubin level only (P = 0.0166). In the subgroup of 104 patients in whom additional karyotype analyses were performed prior to first-line therapy unfavorable chromosome abnormalities were associated with a lower CR rate (univariate analysis, P = 0.0342; CR 24% vs 53%) and were the only factor related to survival. These analyses warrant the further evaluation of the impact of cytogenetic abnormalities on the outcome of patients with advanced AML in order to improve the characterization according to duration of first CR and to WBC of distinct subgroups of patients with differing prognoses as a basis for stratification in future trials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russell NH . Biology of acute leukaemia Lancet 1997 349: 118–122
Bloomfield CD, Lawrence D, Byrd JC, Carroll A, Pettenati MJ, Tantravahi R, Patil SR, Davey FR, Berg DT, Schiffer CA, Arthur DC, Mayer RJ . Frequency of prolonged remission duration after high-dose cytarabine intensification in acute myeloid leukemia varies by cytogenetic subtype Cancer Res 1998 58: 4173–4179
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley K, Harrison C, Harrison G, Rees J, Hann I, Stevens R, Burnett A, Goldstone A . The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children's Leukaemia Working Parties Blood 1998 92: 2322–2333
Mrozek K, Heinonen K, Lawrence D, Carroll AJ, Koduru PR, Rao KW, Strout MP, Hutchison RE, Moore JO, Mayer RJ, Schiffer CA, Bloomfield CD . Adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia and t(9; 11)(p22;q23) have a superior outcome to patients with other translocations involving band 11q23: a cancer and leukemia group B study Blood 1997 90: 4532–4538
Dreyling MH, Schrader K, Fonatsch C, Schlegelberger B, Haase D, Schoch C, Ludwig W, Loffler H, Buchner T, Wormann B, Hiddemann W, Bohlander SK . MLL and CALM are fused to AF10 in morphologically distinct subsets of acute leukemia with translocation t(10;11): both rearrangements are associated with a poor prognosis Blood 1998 91: 4662–4667
Fenaux P, Le Deley MC, Castaigne S, Archimbaud E, Chomienne C, Link H, Guerci A, Duarte M, Daniel MT, Bowen D et al. Effect of all transretinoic acid in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Results of a multicenter randomized trial. European APL 91 Group Blood 1993 82: 3241–3249
Tallman MS, Andersen JW, Schiffer CA, Appelbaum FR, Feusner JH, Ogden A, Shepherd L, Willman C, Bloomfield CD, Rowe JM, Wiernik PH . All-trans-retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia (see comments) (published erratum appears in New Engl J Med 1997 Nov 27; 337(22):1639) New Engl J Med 1997 337: 1021–1028
Lo Coco F, Nervi C, Avvisati G, Mandelli F . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: a curable disease Leukemia 1998 12: 1866–1880
Schoch C, Haferlach T, Haase D, Fonatsch C, Schlegelberger B, Sauerland MC, Loffler H, Staib P, Wormann B, Buchner T, Hiddemann W, the German AML Cooperative Group . Complex chromosome aberrations in patients with de novo AML are associated with a very poor prognosis despite intensive treatment: a study of 90 patients Blood 1997 90: 62a
Hiddemann W, Martin WR, Sauerland CM, Heinecke A, Buchner T . Definition of refractoriness against conventional chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia: a proposal based on the results of retreatment by thioguanine, cytosine arabinoside, and daunorubicin (TAD 9) in 150 patients with relapse after standardized first line therapy Leukemia 1990 4: 184–188
Estey E . Treatment of refractory AML Leukemia 1996 10: 932–936
Keating MJ, Kantarjian H, Smith TL, Estey E, Walters R, Andersson B, Beran M, McCredie KB, Freireich EJ . Response to salvage therapy and survival after relapse in acute myelogenous leukemia J Clin Oncol 1989 7: 1071–1080
Kern W, Schleyer E, Unterhalt M, Wormann B, Buchner T, Hiddemann W . High antileukemic activity of sequential high dose cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone in patients with refractory acute leukemias. Results of a clinical phase II study Cancer 1997 79: 59–68
Kern W, Schoch C, Haferlach T, Braess J, Unterhalt M, Wormann B, Buchner T, Hiddemann W . Significance of cytogenetic abnormalities in a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in patients with refractory and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia Blood 1998 92: 78a
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C . Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report of the French–American–British Cooperative Group Ann Intern Med 1985 103: 620–625
Buchner T, Urbanitz D, Hiddemann W, Ruhl H, Ludwig WD, Fischer J, Aul HC, Vaupel HA, Kuse R, Zeile G, Nowrousian MR, Konig HJ, Walter M, Wendt FC, Sodomann H, Hossfeld DK, von Paleske A, Loffler H, Gassmann W, Hellriegel KP, Fulle HH, Lunscken C, Emmerich B, Pralle H, Pees HW, Pfreundschuh M, Bartels H, Koeppen KM, Schwerdtfeger R, Donhuijsen-Ant R, Mainzer K, Bonfert B, Koppler H, Zurborn KH, Ranft K, Thiel E, Heinecke A . Intensified induction and consolidation with or without maintenance chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML): two multicenter studies of the German AML Cooperative Group J Clin Oncol 1985 3: 1583–1589
Buchner T, Hiddemann W, Wormann B, Loffler H, Maschmeyer G, Hossfeld D, Ludwig WD, Nowrousian M, Aul C, Schaefer UW, Sauerland C, Heinecke A . Long-term effects of prolonged maintenance and of very early intensification chemotherapy in AML: data from AMLCG Leukemia 1992 6: (Suppl. 2) 68–71
Kern W, Aul C, Maschmeyer G, Schönrock-Nabulsi R, Ludwig WD, Bartholomaus A, Bettelheim P, Wormann B, Buchner T, Hiddemann W, for the German AML Cooperative Group . Superiority of high-dose over intermediate-dose cytosine arabinoside in the treatment of patients with high-risk acute myeloid leukemia: results of a age-adjusted prospective randomized comparison Leukemia 1998 12: 1049–1055
Kern W, Behre G, Rudolf T, Kerkhoff A, Grote-Metke A, Eimermacher H, Kubica U, Wormann B, Buchner T, Hiddemann W, for the German AML Cooperative Group . Failure of fluconazole prophylaxis to reduce mortality and the requirement of systemic amphotericin B therapy during treatment for refractory acute myeloid leukemia: results of a prospective randomized phase III study Cancer 1998 83: 291–301
Patt YZ, Peters RE, Chuang VP, Wallace S, Mavligit G . Effective retreatment of patients with colorectal cancer and liver metastases Am J Med 1983 75: 237–240
Yates J, Glidewell O, Wiernik P, Cooper MR, Steinberg D, Dosik H, Levy R, Hoagland C, Henry P, Gottlieb A, Cornell C, Berenberg J, Hutchison JL, Raich P, Nissen N, Ellison RR, Frelick R, James GW, Falkson G, Silver RT, Haurani F, Green M, Henderson E, Leone L, Holland JF . Cytosine arabinoside with daunorubicin or adriamycin for therapy of acute myelocytic leukemia: a CALGB study Blood 1982 60: 454–462
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete estimations Am Stat Assoc J 1958 53: 457–481
Schoch C, Haase D, Fonatsch C, Haferlach T, Loffler H, Schlegelberger B, Hossfeld DK, Becher R, Sauerland MC, Heinecke A, Wormann B, Buchner T, Hiddemann W . The significance of trisomy 8 in de novo acute myeloid leukaemia: the accompanying chromosome aberrations determine the prognosis. German AML Cooperative Study Group Br J Haematol 1997 99: 605–611
Schoch C, Haase D, Haferlach T, Gudat H, Buchner T, Freund M, Link H, Lengfelder E, Wandt H, Sauerland MC, Loffler H, Fonatsch C . Fifty-one patients with acute myeloid leukemia and translocation t(8;21)(q22;q22): an additional deletion in 9q is an adverse prognostic factor Leukemia 1996 10: 1288–1295
Schoch C, Haase D, Haferlach T, Freund M, Link H, Lengfelder E, Loffler H, Buchner T, Fonatsch C . Incidence and implication of additional chromosome aberrations in acute promyelocytic leukaemia with translocation t(15;17)(q22;q21): a report on 50 patients Br J Haematol 1996 94: 493–500
Buchner T, Hiddemann W, Wormann B et al. Threapeutic outcome in AML is mainly determined by cytogenetics, LDH in serum, early response and, in a poor risk subgroup, by intensified induction treatment Blood 1997 90: 504a
Byrd JC, Lawrence D, Arthur DC, Pettenati MJ, Tantravahi R, Qumsiyeh M, Stamberg J, Davey FR, Schiffer CA, Bloomfield CD . Patients with isolated trisomy 8 in acute myeloid leukemia are not cured with cytarabine-based chemotherapy: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B 8461 Clin Cancer Res 1998 4: 1235–1241
Bloomfield CD, Shuma C, Regal L, Philip PP, Hossfeld DK, Hagemeijer AM, Garson OM, Peterson BA, Sakurai M, Alimena G, Berger R, Rowley JD, Ruutu T, Mitelman F, Dewald GW, Swansbury J . Long-term survival of patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a third follow-up of the Fourth International Workshop on Chromosomes in Leukemia Cancer 1997 80: 2191–2198
Lowenberg B, Suciu S, Archimbaud E, Ossenkoppele G, Verhoef GE, Vellenga E, Wijermans P, Berneman Z, Dekker AW, Stryckmans P, Schouten H, Jehn U, Muus P, Sonneveld P, Dardenne M, Zittoun R . Use of recombinant GM-CSF during and after remission induction chemotherapy in patients aged 61 years and older with acute myeloid leukemia: final report of AML-11, a phase III randomized study of the Leukemia Cooperative Group of European Organisation for the Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Dutch Belgian Hemato-Oncology Cooperative Group Blood 1997 90: 2952–2961
Archimbaud E, Thomas X, Leblond V, Michallet M, Fenaux P, Cordonnier C, Dreyfus F, Troussard X, Jaubert J, Travade P et al. Timed sequential chemotherapy for previously treated patients with acute myeloid leukemia: long-term follow-up of the etoposide, mitoxantrone, and cytarabine-86 trial (see comments) J Clin Oncol 1995 13: 11–18
Archimbaud E, Leblond V, Fenaux P, Dombret H, Cordonnier C, Dreyfus F, Cony Makhoul P, Tilly H, Troussard X, Auzanneau G, Thomas X, Ffrench M, Marie JP . Timed sequential chemotherapy for advanced acute myeloid leukemia Hematol Cell Ther 1996 38: 161–167
Montillo M, Mirto S, Petti MC, Latagliata R, Magrin S, Pinto A, Zagonel V, Mele G, Tedeschi A, Ferrara F . Fludarabine, cytarabine, and G-CSF (FLAG) for the treatment of poor risk acute myeloid leukemia Am J Hematol 1998 58: 105–109
Sierra J, Granena A, Bosch F, Carreras E, Marti JM, Urbano Ispizua A, Rovira M, Rozman C . Mitoxantrone and intermediate-dose cytosine arabinoside for poor-risk acute leukemias: response to treatment and factors influencing outcome Hematol Oncol 1992 10: 301–309
Harousseau JL, Milpied N, Briere J, Desablens B, Ghandour C . Mitoxantrone and intermediate-dose cytarabine in relapsed or refractory acute myeloblastic leukemia Nouv Rev Fr Hematol 1990 32: 227–230
Smits P, Schoots L, de Pauw BE, de Witte T, Holdrinet RS, Janssen JT, Haanen C . Prognostic factors in adult patients with acute leukemia at first relapse Cancer 1987 59: 1631–1634
Herzig RH, Lazarus HM, Wolff SN, Phillips GL, Herzig GP . High-dose cytosine arabinoside therapy with and without anthracycline antibiotics for remission reinduction of acute nonlymphoblastic leukemia J Clin Oncol 1985 3: 992–997
Hiddemann W, Kreutzmann H, Straif K, Ludwig WD, Mertelsmann R, Donhuijsen Ant R, Lengfelder E, Arlin Z, Buchner T . High-dose cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone: a highly effective regimen in refractory acute myeloid leukemia Blood 1987 69: 744–749
Walters RS, Kantarjian HM, Keating MJ, Plunkett WK, Estey EH, Andersson B, Beran M, McCredie KB, Freireich EJ . Mitoxantrone and high-dose cytosine arabinoside in refractory acute myelogenous leukemia Cancer 1988 62: 677–682
Martiat P, Ghilain JM, Ferrant A, Doyen C, Delannoy A, Chatelain C, Bosly A, Michaux JL, Sokal G . High-dose cytosine arabinoside and amsacrine or mitoxantrone in relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: a prospective randomized study Eur J Haematol 1990 45: 164–167
Carella AM, Carlier P, Pungolino E, Resegotti L, Liso V, Stasi R, Montillo M, lacopino P, Mirto S, Pagano L et al. Idarubicin in combination with intermediate-dose cytarabine and VP-16 in the treatment of refractory or rapidly relapsed patients with acute myeloid leukemia. The GIMEMA Cooperative Group Leukemia 1993 7: 196–199
Spadea A, Petti MC, Fazi P, Vegna ML, Arcese W, Avvisati G, Aloe Spiriti MA, Latagliata R, Meloni G, Testi AM et al. Mitoxantrone, etoposide and intermediate-dose Ara-C (MEC): an effective regimen for poor risk acute myeloid leukemia Leukemia 1993 7: 549–552
Vogler WR, McCarley DL, Stagg M, Bartolucci AA, Moore J, Martelo O, Omura GA . A phase III trial of high-dose cytosine arabinoside with or without etoposide in relapsed and refractory acute myelogenous leukemia. A Southeastern Cancer Study Group trial Leukemia 1994 8: 1847–1853
Garson OM, Hagemeijer A, Sakurai M, Reeves BR, Swansbury GJ, Williams GJ, Alimena G, Arthur DC, Berger R, de la Chapelle A et al. Cytogenetic studies of 103 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia in relapse Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1989 40: 187–202
Kern W, Schoch C, Fonatsch C, Heinecke A, Wormann B, Buchner T, Hiddemann W . Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia in the elderly Home Health Care Consultant 1999 6: 2–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kern, W., Schoch, C., Haferlach, T. et al. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in patients with refractory and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia undergoing sequential high-dose cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone (S-HAM) salvage therapy: relevance of cytogenetic abnormalities. Leukemia 14, 226–231 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401668
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401668
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sequential high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone (S-HAM) versus standard double induction in acute myeloid leukemia—a phase 3 study
Leukemia (2018)
-
Long-term follow-up of the AML97 study for patients aged 60 years and above with acute myeloid leukaemia: a study of the East German Haematology and Oncology Study Group (OSHO)
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2016)
-
Homoharringtonine in combination with cytarabine and aclarubicin in the treatment of refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: a single-center experience
Annals of Hematology (2013)
-
Low dose of homoharringtonine and cytarabine combined with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor priming on the outcome of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2011)
-
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation in second rather than first complete remission in selected patients with good-risk acute myeloid leukemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2005)