Abstract
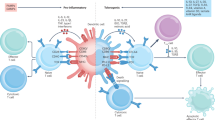
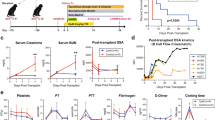
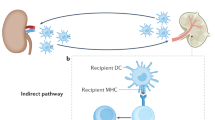
ANTIBODY-MEDIATED immunosuppression is no longer thought to be solely due to the masking of antigen by antibody. The hypothesis that events beyond the binding of antibody to antigen are operative in antibody-mediated immunosuppression is supported by the following facts. (1) Antigen-masking need not be complete to obtain pronounced suppression of immune responses1,2; (2) interactions between antigenic determinants on the same immunogenic particle (molecules to whole cells) take place so that suppression of immune responses to one antigenic determinant may occur with the binding of antibody to another non-cross-reacting and topographically separate antigenic determinant3–5; (3) parts of the antibody molecule, other than that involved in the binding of antigen, are important in the regulation of the immune response by antibody6–9; (4) immunosuppression does not necessarily become more pronounced when the dose of passively administered antibody is increased but proceeds through an optimum beyond which less suppression is observed10,11,13,14; and (5) immunosuppression by antibody can lead to inactivation of the antigen-sensitive cell population12–14. Similarly, immunological tolerance is no longer thought to be the simple elimination of immunologically competent cells by antigen. The following data suggest a more complex mechanism in the induction of immunological tolerance. (1) Animals which demonstrate tolerance seem to possess both sensitized lymphoid cells and soluble factors (antibodies or antigens) which prevent the sensitized cells from functioning15,16; (2) induction of tolerance is often preceded by the production of measurable antibody31 or antibody-forming cells17,18; (3) induction of tolerance requires the presence of a functioning complement system19; and (4) cells capable of binding antigen remain, or may increase, during the attainment of the tolerant state20–23. Consequently, it now seems possible that these two hyporeactive states, antibody mediated immunosuppression and immunological tolerance, share common characteristics and common modes of induction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uhr, J. W., and Baumann, J. B., J. Exp. Med., 113, 935 (1961).
Haughton, G., and Nash, D. R., Transplant. Proc., 1, 616 (1969).
Henney, C. S., and Ishizaka, K., J. Immunol., 101, 896 (1968).
Henney, C. S., and Ishizaka, K., J. Immunol., 104, 1540 (1970).
Brody, N. I., Walker, J. G., and Siskind, G. W., J. Exp. Med., 126, 81 (1967).
Hamaoka, T., and Kitagawa, M., Immunology, 20, 119 (1971).
Sinclair, N. R. StC., J. Exp. Med., 129, 1183 (1969).
Sinclair, N. R. StC., Lees, R. K., Chan, P. L., and Khan, R. H., Immunology, 19, 105 (1970).
McConahey, P. J., Cerottini, J.-C., and Dixon, F. J., J. Exp. Med., 127, 1003 (1968).
Sinclair, N. R. Stc., and Chan, P. L., Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 12, 609 (1971).
Chan, P. L., and Sinclair, N. R. Stc., Immunology (in the press).
Rowley, D. A., and Fitch, F. W., J. Exp. Med., 120, 987 (1964).
Feldmann, M., and Diener, E., J. Exp. Med., 131, 247 (1970).
Diener, E., and Feldmann, M., J. Exp. Med., 132, 31 (1970).
Hellstrom, I., Hellstrom, K. E., and Allison, A. C., Nature, 230, 49 (1971).
Tong, J. L., and Boose, D., J. Immunol., 105, 426 (1970).
Sterzl, J., Nature, 209, 416 (1966).
Medlin, J., Riha, I., and Sterzl, J., Folia. Biol. (Praha), 15, 309 (1969).
Azar, M. M., Yunis, E. J., Pickering, P. J., and Good, R. A., Lancet, i, 1279 (1968).
Howard, J. G., Elson, J., Christie, G. H., and Kinsby, R. G., Clin. Exp. Immunology, 4, 41 (1969).
Ada, G. L., Transplant. Rev., 5, 105 (1970).
Naor, D., and Sulitzeanu, D., Intern. Arch. Allergy. Appl. Immunol., 36, 112 (1969).
Sjoberg, O., J. Exp. Med., 133, 1015 (1971).
Moller, G., in Homeostatic Regulators, Ciba Foundation Symp. (edit. by Wolstenholme, G. E. W., and Knight, J.), 197 (Churchill, London, 1969).
Ada, G. L., Nossal, G. J. V., and Pye, J., Austral. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci., 42, 295 (1964).
McConahey, P. J., Cerottini, J.-C., and Dixon, F. J., J. Exp. Med., 127, 1003 (1968).
Siskind, G. W., Dunn, P., and Walker, J. G., J. Exp. Med., 127, 55 (1968).
Makinodan, T., and Peterson, W. J., J. Immunol., 93, 886 (1964).
Nettesheim, P., Makinodan, T., and Williams, M. L., J. Immunol., 99, 150 (1967).
Nettersheim, P., Williams, M. L., and Hammons, A. S., J. Immunol., 103, 505 (1969).
Mitchison, N. A., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 161, 275 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SINCLAIR, N., CHAN, P. Relationship between Antibody-mediated Immunosuppression and Tolerance Induction. Nature 234, 104–105 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/234104a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/234104a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.