Abstract
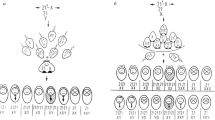
EVIDENCE for the association of the X and Y chromosomes during the first meiotic division in man has been documented1,2. Until the centromere positions of the meiotic chromosomes were located with certainty, no information about the arm relationship between the two sex chromosomes could be obtained. The identification of the positions of the centromere in human male meiotic chromosomes at the late diplotene stage has been reported3. This observation revealed that the short arm of the Y chromosome was in association with the short arm of the X chromosome. Partial support for this finding was presented by Pearson and Bobrow4, who interpreted fluorescent staining of the distal end of the long arm of the Y chromosome of the XY bivalent in man as evidence that the short arm of the Y chromosome was associated with the X chromosome. Because the centromere position of the X chromosome could not be demonstrated in their material, it was not possible to determine which arm of the X chromosome was associated with the short arm of the Y chromosome. The purpose of this communication is to provide additional cytological evidence for the association of the X and Y chromosomes at their short arms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ford, C. E., and Hamerton, J. L., Nature, 178, 1020 (1956).
Hulten, M., Lindsten, J., Ming, P. M. L., and Fraccaro, M., Ann. Human Genet., 30, 119 (1966).
Chen, A. T. L., and Falek, A., Science, 166, 1008 (1969).
Pearson, P. L., and Bobrow, M., Nature, 226, 959 (1970).
Evans, E. P., Breckon, G., and Ford, C. E., Cytogenetics, 3, 289 (1964).
Fredga, K., Exp. Cell Res., 36, 696 (1964).
Fraccaro, M., Hulten, M., and Lindsten, J., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 155, 664 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CHEN, A., FALEK, A. Cytological Evidence for the Association of the Short Arms of the X and Y Chromosomes in the Human Male. Nature 232, 555–556 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/232555a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/232555a0
This article is cited by
-
Immunocytochemical labelling of the kinetochore of human synaptonemal complexes, and the extent of pairing of the X and Y chromosomes
Chromosoma (1987)
-
Distamycin A/DAPI staining of heterochromatin in male meiosis of man
Genetica (1986)
-
The genetics of human reproduction
Experientia (1986)
-
Homologous expressed genes in the human sex chromosome pairing region
Nature (1985)
-
Translocation(X;Y)(p22.33;p11.2) in XX males: Etiology of male phenotype
Human Genetics (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.