Abstract
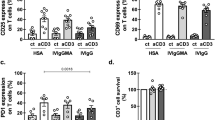
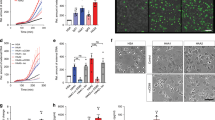
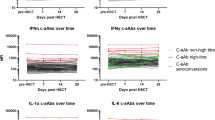
ANTILYMPHOCYTIC serum (ALS) is widely known for its ability to impair immunological responsiveness, especially of cell-mediated immunity1,2. The main immunosuppressive component of ALS in vivo is IgG (7S-γ) immunoglobulin3,4. Administration of ALS to animals also causes a marked reduction in inflammation, as judged by various experimental models5–7, without causing increased adrenal activity5,6.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woodruff, M. F. A., and Anderson, N. F., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 120, 119 (1964).
Levey, R. H., and Medawar, P. B., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 56, 1130 (1966).
James, K., and Medawar, P. B., Nature, 214, 1052 (1967).
Anderson, N. F., James, K., and Woodruff, M. F. A., Lancet, i, 1126 (1967).
Currey, H. L. F., and Ziff, M., Lancet, ii, 889 (1966).
Turk, J. L., Willoughby, D. A., and Stevens, J. E., Immunology, 14, 683 (1968).
Perper, R. J., Glenn, E. M., and Monovich, R. E., Nature, 223, 86 (1969).
Winter, C. A., Risley, E. A., and Nuss, G. W., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 111, 544 (1962).
Billingham, M. E. J., Robinson, B. V., and Robson, J. M., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 35, 543 (1969).
Monaco, A. P., Wood, M., van der Werf, B. A., and Russell, P. S., in Antilymphocytic Serum (edit. by Wolstenholme, G. E. W., and O'Connor, M.), 111 (Churchill, London, 1967).
Billingham, M. E. J., Robinson, B. V., and Robson, J. M., Brit. Med. J., 2, 93 (1969).
Gaugas, J. M., Billingham, M. E. J., and Rees, R. J. W., Amer. Rev. Resp. Dis., 101, 432 (1970).
Di Pasquale, G., and Girerd, R. J., Amer. J. Physiol., 201, 115 (1961).
Di Pasquale, G., Girerd, R. J., Beach, V. L., and Steinetz, G. B., Amer. J. Physiol., 205, 1080 (1963).
Bonta, I. L., Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Neerl., 15, 188 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BILLINGHAM, M., ROBINSON, B. & GAUGAS, J. Two Anti-inflammatory Components in Antilymphocytic Serum. Nature 227, 276–277 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/227276a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/227276a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.