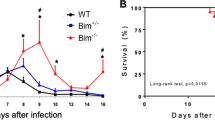
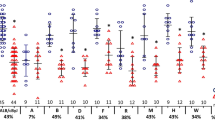
Abstract
VARIOUS immunological changes have been observed in many apparently healthy subjects living in tropical regions that are probably related to multiple parasitic infections from childhood1. Consideration of this in conjunction with the rarity of autoimmune disease in tropical Africa, for example Western Nigeria2, led to the suggestion that the immunological effects of repeated parasitic infection might have some protective action against the development of autoimmune disease2. To investigate this hypothesis we have studied the effects of infection with malaria on the spontaneous autoimmune disease of NZB mice and the (NZB × NZW)F1 hybrid mice (B/W mice). Twenty-one NZB mice and thirteen female B/W mice from the Taplow colony were infected, when one month old, with the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei yoelii3 by the intraperitoneal injection of 1 × 106 parasites derived from a heavily infected mouse of the same strain. The malaria strain was not contaminated with Eperythrozoon coccoides. Parasitaemia was monitored by the examination of Giemsa stained blood films made from the tails of the mice every second day during the acute phase of the infection and at longer intervals thereafter. To determine whether low parasitaemia was persisting, heparinized blood samples were collected from each mouse 4 months after infection and pooled samples injected into young BALB/c mice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenwood, B. M., Herrick, E. M., and Voller, A., Proc. Roy. Soc. Med., 63, 19 (1970).
Greenwood, B. M., Lancet, ii, 380 (1968).
Landau, I., and Killick-Kendrick, R., Trans. Roy. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg., 60, 633 (1966).
Mellors, R. C., and Huang, C. Y., J. Exp. Med., 126, 53 (1967).
Russell, A. S., Lancet, ii, 407 (1968).
Salaman, M. H., Proc. Roy. Soc. Med., 63, 11 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GREENWOOD, B., HERRICK, E. & VOLLER, A. Suppression of Autoimmune Disease in NZB and (NZB×NZW)F1 Hybrid Mice by Infection with Malaria. Nature 226, 266–267 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/226266a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/226266a0
This article is cited by
-
The effects of helminth infections against type 2 diabetes
Parasitology Research (2021)
-
Serologic features of cohorts with variable genetic risk for systemic lupus erythematosus
Molecular Medicine (2018)
-
Unraveling the Hygiene Hypothesis of helminthes and autoimmunity: origins, pathophysiology, and clinical applications
BMC Medicine (2015)
-
Clinical and epidemiological features of rheumatic diseases in patients attending the university hospital in Kinshasa
Clinical Rheumatology (2008)
-
HLA-DR gene frequencies in a Za�rean population with particular reference to rheumatic diseases
Clinical Rheumatology (1998)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.