Abstract
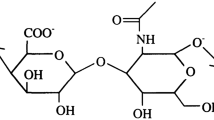
THE mechanism of lubrication in human joints depends on the bearing material (articular cartilage), the joint lubricant (synovial fluid) and the operating conditions (sliding or rolling speeds, load and time of load application). Cartilage is a composite of collagen fibre bundles set at various orientations within a ground substance of chondroitin sulphate, and containing a high proportion of watery fluid1–4. Its surface, which is very important to the lubrication behaviour, has been found to be rough by engineering standards. The centre line average value has been measured at 30 µinch for healthy cartilage, the roughnesses taking the form of undulations with small ones superimposed on others of larger wavelength5,6.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss, C., Rosenburg, L., and Helfet, A. J., J. Bone Joint Surg., 50-A, 663 (1968).
Mankin, H. J., Bull. Rheum. Dis., 17, 447 (1967).
Bullough, P. G., and Goodfellow, J., J. Bone Joint Surg., 50-B, 852 (1968).
McCall, J., Lubrication and Wear in Joints (edit. by Wright, V.), 39 (Sector, London, 1969).
Walker, P. S., Sikorski, J., Dowson, D., Longfield, M. D., Wright, V., and Buckley, T., Ann. Rheum. Dis., 28, 1 (1969).
Gardner, D. L., and Woodward, D., Ann. Rheum. Dis., 28, 379 (1969).
Hamerman, D., Rojkind, M., and Sandson, J., Fed. Proc., 25, 1040 (1966).
Davies, D. V., and Palfrey, A. J., J. Biomech., 1, 79 (1968).
Paul, J. P., Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., 181 (3J), 8 (1967).
Morrison, J. B., Biomed. Eng., 3, 164 (1968).
Linn, F. C., J. Biomech., 1, 193 (1968).
Walker, P. S., Dowson, D., Longfield, M. D., and Wright, V., Ann. Rheum. Dis., 27, 512 (1968).
Maroudas, A., Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., 181 (3J), 122 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WALKER, P., SIKORSKI, J., DOWSON, D. et al. Features of the Synovial Fluid Film in Human Joint Lubrication. Nature 225, 956–957 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/225956a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/225956a0
This article is cited by
-
Current notions of the biomechanics of the synovial medium of joints (a review)
Mechanics of Composite Materials (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.