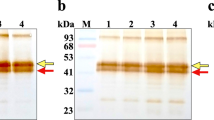
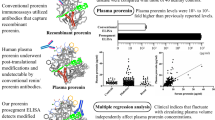
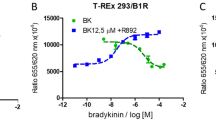
Abstract
ALTHOUGH the action of renin on the blood pressure has been explored by many investigators, some of its basic enzymatic properties are yet to be established1. While studying plasma kinins, we found it to be of advantage to couple enzymes that release or inactivate kinins covalently to water-insoluble complexes2–4. The active insoluble derivatives of enzymes are convenient to use, because, among many other attractive properties, they are stable, re-usable and readily removed from incubation mixture by sedimentation. We have extended these investigations to renin. Our previous results with killikrein, carboxypeptidases, kallikrein and trypsin inhibitors and renin were briefly reported3,4. This report deals with the binding of renin to ‘Sepharose 4B’.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renal Hypertension (edit. by Page, I. H., and McCubbin, J. W.) (Year Book Medical Publishers, Inc., Chicago, 1968).
Erdös, E. G., Seki, T., Yang, H. Y. T., and Tague, L. L., Pharmacol. Res. Commun., 1, 152 (1969).
Seki, T., Yang, H. Y. T., Levin, Y., Jenssen, T. A., and Erdös, E. G., in International Symposium on Cardiovascular and Neuro-actions of Bradykinin and Related Kinins (Fiesole-Florence, July 21–25, 1969).
Seki, T., Yang, H. Y. T., Levin, Y., Jenssen, T. A., and Erdös, E. G., Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology (in the press).
Sen, S., Smeby, R. R., and Bumpus, F. M., Biochemistry, 6, 1572 (1967).
Green, A. A., and Bumpus, F. M., J. Biol. Chem., 210, 281 (1954).
Chiang, T. S., Erdös, E. G., Miwa, I., Tague, L. L., and Coalson, J. J., Circ. Res., 23, 507 (1968).
Axen, R., Porath, J., and Ernback, S., Nature, 214, 1302 (1967).
Cuatrecasas, P., Wilchek, M., and Anfinsen, C. B., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 61, 636 (1968).
Regoli, D., and Vane, J. R., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 23, 351 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SEKI, T., JENSSEN, T., LEVIN, Y. et al. Active Water-insoluble Derivative of Renin. Nature 225, 864–865 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/225864a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/225864a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.