Abstract
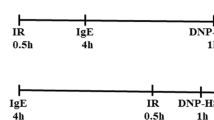
THE pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) is not definitely known and yet it is frequently used as an experimental model for the study of autoimmune disease of the central nervous system. Waksman contends that the principal event giving rise to EAE after injection of the antigen is the passage of immunologically competent cells or histiocytes through small venules into the nervous system1. These cells originate in the blood stream and are held responsible for the destruction of elements containing antigen in the central nervous system by an undefined mechanism. It has been found that EAE can be suppressed, either by generalized physical or chemical cytotoxic agents, or by destruction of the regional lymph nodes draining the inoculation site2–9. This communication reports the suppressive effect of localized irradiation of the brain in mice during the induction of EAE, and compares the effect with that of total body irradiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waksman, B. H., Amer. J. Path., 37, 673 (1960).
Condie, R. M., Kelly, J. T., Thomas, L., and Good, R. A., Anat. Rec., 127, 405 (1957).
Condie, R. M., and Good, R. A., in Progress in Neurobiology (The Biology of Myelin) (edit. by Korey, S. R.), 3, 321 (1959).
Hoyer, L. W., Good, R. A., and Condie, R. M., J. Exp. Med., 116, 311 (1962).
Field, E. J., Proc. Roy. Soc. Med., 54, 14 (1961).
Patterson, P. Y., and Beisaw, N. E., J. Immunol., 90, 532 (1963).
Field, E. J., Brit. Med. J., i, 843 (1963).
Brandriss, M. W., Smith, J. W., and Friedman, R. M., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 122, 356 (1965).
Kibler, R. F., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 122, 469 (1965).
Lee, J. M., and Olitsky, P. K., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 89, 263 (1955).
Edelman, F. L., Aleu, F., Scheinberg, L. C., Evans, J. C., and Davidoff, L. M., J. Neuropathol. and Exp. Neurol., 23, 1 (1964).
Olitsky, P. K., and Yager, R. H., J. Exp. Med., 90, 213 (1949).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SCHEINBEBG, L., LEE, J. & TAYLOR, J. Suppression of Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis in Mice by Irradiation of the Target Organ. Nature 216, 924–925 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/216924a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/216924a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.