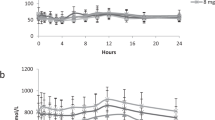
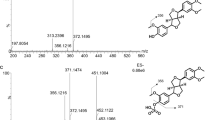
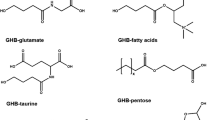
Abstract
THE main end products of the metabolism of sulphur amino-acids in mammals are inorganic sulphate and taurine1,2. In mammalian liver, taurine participates in the formation of conjugated bile acids3. Substantial amounts of taurine are, however, present in many extra-hepatic tissues, notably heart, muscle, brain, skin, leucocytes and platelets4–7. The biological function, if any, of taurine in these tissues is unknown.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young, L., and Maw, G. A., The Metabolism of Sulphur Compounds, 33 (Methuen and Co., Ltd., London, 1958).
Kun, E., in Metabolic Pathways (edit. by Greenberg, D. M.), 2, 237 (Academic Press, New York and London, 1961).
Bremer, J., and Gloor, U., Acta Chem. Scand., 9, 689 (1955).
Awapara, J., J. Biol. Chem., 218, 571 (1956).
Garvin, J. E., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 91, 219 (1960).
Vinh An, Huynh, and Fromageot, P., Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol., 42, 221 (1960).
Soupart, P., in Amino Acid Pools (edit. by Holden, J. T.), 220 (Elsevier Publishing Co., Amsterdam, London and New York, 1962).
Koechlin, B. A., Proc. U. S. Nat. Acad. Sci., 40, 60 (1954).
Koechlin, B. A., J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol., 1, 511 (1955).
Deffner, G. G. J., and Hafter, R. E., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 42, 200 (1960).
Braun, R., and Fromageot, P., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 62, 548 (1962).
Cotty, V. F., Henry, S. M., and Hilchey, J. D., Contr. Boyce Thompson Inst., 19, 379 (1958).
Schram, E., Arch. Intern. Physiol. Biochem., 68, 698 (1960).
Welty, J. D., Read, W. O., and Shaw, jun., E. H., J. Biol. Chem., 237, 1160 (1962).
Read, W. 0., and Welty, J. D., J. Biol. Chem., 237, 1521 (1962).
Welty, jun., J. D., thesis, Univ. South Dakota (1963).
Peck, jun., E. J., and Awapara, J., Fed. Proc., 25, 642 (1966).
Jacobsen, J. G., and Smith, jun., L. H., Nature, 200, 575 (1963).
Jacobsen, J. G., Thomas, L. L., and Smith, jun., L. H., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 85, 103 (1964).
Kliman, B., and Peterson, R. E., J. Biol. Chem., 235, 1639 (1960).
Gibbs, W., Amer. J. Sci., second ser., 25, 18 (1858).
Peterson, D. W., Lilyblade, A. L., and Lyon, J., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 113, 798 (1963).
Tyler, F. H., in The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease (edit. by Stanbury, J. B., Wyngaarden, J. B., and Frederickson, D. S.), 939 (McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York and London, 1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
JACOBSEN, J., COLLINS, L. & SMITH, L. Urinary Excretion of Isethionic Acid in Man. Nature 214, 1247–1248 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/2141247a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2141247a0
This article is cited by
-
Isethionate as a product from taurine during nitrogen-limited growth of Klebsiella oxytoca TauN1
Archives of Microbiology (2005)
-
Isethionate in certain red algae
Journal of Applied Phycology (1994)
-
Rate of disappearance of isethionic acid in the rat central nervous system
Neurochemical Research (1979)
-
Possible Involvement of Taurine in the Genesis of Muscular Dystrophy
Nature (1973)
-
Mediated transport of chloride from blood into cerebrospinal fluid
Experimental Brain Research (1970)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.