Abstract
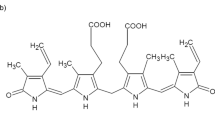
CONJUGATED bilirubins (esters) are formed within the liver cells from bilirubin and glucuronic or sulphuric acid. These compounds are very unstable because of the highly reactive central methylene bridge. They are oxidized rapidly by the air and react immediately with diazotized sulphanilic acid. Contrary to the esters, pure bilirubin is relatively stable and reacts with the diazoreagent only when an accelerator is added.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
FOG, J., JELLUM, E. Structure of Bilirubin. Nature 198, 88–89 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/198088b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/198088b0
This article is cited by
-
Bilirubin metabolism: delving into the cellular and molecular mechanisms to predict complications
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine (2024)
-
Structure of bilirubin
Nature (1976)
-
Effect on Bilirubin Excretion of Blocking the Carboxyl Sites of Glucuronide Conjugation by Methylation
Nature (1968)
-
Stability of Bilirubin
Nature (1964)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.