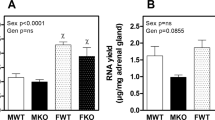
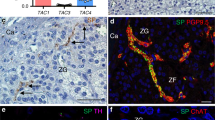
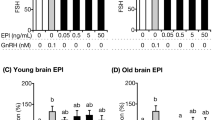
Abstract
Holzbauer and Walter1 have recently reported that the adrenal ascorbic acid–depleting properties of corticotropin are destroyed by treatment with ascorbic acid at room temperature for 18–20 hr. The corticotropin preparation used by these workers had a potency of 3 I.U./mgm. In view of the potential importance of their observation, we have repeated their experiment using highly purified corticotropin. The preparation used was a sample of corticotropin A 1 (for nomenclature, see Dixon and Stack-Dunne2), made in this laboratory by ion-exchange chromatography of an oxycellulose concentrate of pig corticotropin. This preparation had a potency of 110 I.U./mgm. when assayed by the adrenal ascorbic acid–depletion method of Sayers, Sayers and Woodbury3.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Holzbauer, M., and Walter, K., Nature, 177, 379 (1956).
Dixon, H. B. F., and Stack-Dunne, M. P., Biochem. J., 61, 483 (1955).
Sayers, M. A., Sayers, G., and Woodbury, L. A., Endocrin., 42, 379 (1948).
Dedman, M. L., Farmer, T. H., and Morris, C. J. O. R., Biochem. J., 59, xii (1955).
Adams, E., and Smith, E. L., J. Biol. Chem., 191, 651 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DEDMAN, M., FARMER, T. & MORRIS, C. Action of Ascorbic Acid on Corticotropin. Nature 177, 1082 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1038/1771082a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1771082a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.