Abstract
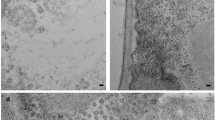
IN view of current opinions on the nature of virus particles1, recent work carried out in this department on the effect of the ‘aspermy’ virus upon nuclear, and especially nucleolar, behaviour in plant cells may have a special significance. Caldwell2 reported prophase collapse in diseased pollen- and embryo-sac mother cells in tomato, accompanied by peculiarities of nucleolar behaviour, and Wilkinson3 has observed similar meiotic abnormalities in Nicotiana glutinosa. Recent examination of somatic divisions in diseased tomato and tobacco plants has revealed the occurrence of widespread nucleolar and other abnormalities, some of which recall the aberrations regarded as typical of the cell-divisions found in malignant animal tissue; for example, arrested metaphase, collapse at metaphase, spindle malformation and breakdown, tendency to form giant nuclei, etc. In particular, abnormal persistence of the nucleolar material, and sometimes an apparent multiplication of nucleolar bodies during the mitotic cycle, have been very striking. Thus, in dividing cells of root tips obtained from tomato shoots heavily infected with the ‘aspermy’ virus, the nucleolar material, instead of dispersing during prophase, persists through anaphase in the form of one or more prominent and somewhat elongated vesicles. The accompanying photograph shows a typical dividing nucleus at early anaphase, with the nucleolar vesicle in a central position upon the somewhat distorted spindle; incidentally, in the cell above can be seen an example of metaphase collapse. Similar results have been obtained in tobacco species infected with the same virus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Findlay, G. M., J. Roy. Micr. Soc., 71, 151 (1951).
Caldwell, J., Ann. App. Biol., 39, 98 (1952).
Wilkinson, J., Ann. Bot. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WILKINSON, J. Virus-induced Nucleolar Abnormalities in Tomato. Nature 171, 658–659 (1953). https://doi.org/10.1038/171658b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/171658b0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.