Summary:
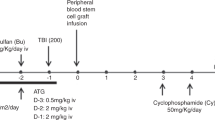
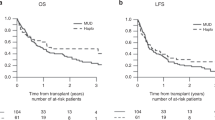
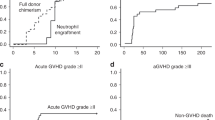
Allogeneic hemopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the only curative option for many patients with hematological malignancies. Since many of these patients lack HLA-identical sibling donors and are older or have comorbidity, a fully ablative HSCT is not feasible and an alternative approach is required. We studied 22 consecutive patients who could not have myeloablative conditioning because of comorbidity or age – 21/22 being over the age of 50 years (median 58 years range 20–70 years). A conditioning regimen consisting of fludarabine, total body radiation 450 cGy and alemtuzumab (CD52 mAb) was used for 15 patients. A second group of seven patients received CD45 monoclonal antibodies in addition. Unrelated donor stem cells were HLA matched (15 patients – 68%) or one locus mismatched (seven patients – 32%). In all, 16 patients had high-risk disease, including 12 with active malignancy at the time of transplant. With a median follow-up of 715 (216–1470) days, nonrelapse mortality, actuarial event-free and overall survival is 27, 45 and 45%, respectively. Hence the outcome of reduced intensity HSCT with lymphodepleting antibodies in older patients with intermediate/high-risk hematological malignancies appears comparable to that obtained with fully ablative transplantation in younger patients, even when these older recipients lack HLA-identical sibling donors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giralt S, Estey E, Albitar M et al. Engraftment of allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cells with purine analog-containing chemotherapy: harnessing graft-versus-leukemia without myeloablative therapy. Blood 1997; 89: 4531–4536.
Giralt S, Thall PF, Khouri I et al. Melphalan and purine analog-containing preparative regimens: reduced-intensity conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies undergoing allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation. Blood 2001; 97: 631–637.
Khouri IF, Keating M, Korbling M et al. Transplant-lite: induction of graft-versus-malignancy using fludarabine-based nonablative chemotherapy and allogeneic blood progenitor-cell transplantation as treatment for lymphoid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 2817–2824.
Kottaridis PD, Milligan DW, Chopra R et al. In vivo CAMPATH-1H prevents graft-versus-host disease following nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation. Blood 2000; 96: 2419–2425.
McSweeney PA, Niederwieser D, Shizuru JA et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in older patients with hematologic malignancies: replacing high-dose cytotoxic therapy with graft-versus-tumor effects. Blood 2001; 97: 3390–3400.
Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases. Blood 1998; 91: 756–763.
Storb RF, Champlin R, Riddell SR et al. Non-myeloablative transplants for malignant disease. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) 2001, 375–391.
Beatty PG, Clift RA, Mickelson EM et al. Marrow transplantation from related donors other than HLA-identical siblings. N Engl J Med 1985; 313: 765–771.
Hale G, Zhang MJ, Bunjes D et al. Improving the outcome of bone marrow transplantation by using CD52 monoclonal antibodies to prevent graft-versus-host disease and graft rejection. Blood 1998; 92: 4581–4590.
Hale G, Jacobs P, Wood L et al. CD52 antibodies for prevention of graft-versus-host disease and graft rejection following transplantation of allogeneic peripheral blood stem cells. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 69–76.
Klangsinsirikul P, Carter GI, Byrne JL et al. Campath-1G causes rapid depletion of circulating host dendritic cells (DCs) before allogeneic transplantation but does not delay donor DC reconstitution. Blood 2002; 99: 2586–2591.
Bindon CI, Hale G, Clark M et al. Therapeutic potential of monoclonal antibodies to the leukocyte-common antigen. Synergy and interference in complement-mediated lysis. Transplantation 1985; 40: 538–544.
Wulf GG, Luo KL, Goodell MA et al. Anti-CD45-mediated cytoreduction to facilitate allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2003; 101: 2434–2439.
Krance RA, Kuehnle I, Rill DR et al. Hematopoietic and immunomodulatory effects of lytic CD45 monoclonal antibodies in patients with hematologic malignancy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2003; 9: 273–281.
Anasetti C, Amos D, Beatty PG et al. Effect of HLA compatibility on engraftment of bone marrow transplants in patients with leukemia or lymphoma. N Engl J Med 1989; 320: 197–204.
Anasetti C, Beatty PG, Storb R et al. Effect of HLA incompatibility on graft-versus-host disease, relapse, and survival after marrow transplantation for patients with leukemia or lymphoma. Hum Immunol 1990; 29: 79–91.
Bornhauser M, Thiede C, Platzbecker U et al. Dose-reduced conditioning and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors in 42 patients. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 2254–2262.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storer B et al. Comparing morbidity and mortality of HLA-matched unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation after nonmyeloablative and myeloablative conditioning: influence of pretransplantation comorbidities. Blood 2004; 104: 961–968.
Maris MB, Niederwieser D, Sandmaier BM et al. HLA-matched unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation after nonmyeloablative conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood 2003; 102: 2021–2030.
Nagler A, Aker M, Or R et al. Low-intensity conditioning is sufficient to ensure engraftment in matched unrelated bone marrow transplantation. Exp Hematol 2001; 29: 362–370.
Wong R, Giralt SA, Martin T et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning for unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation as treatment for myeloid malignancies in patients older than 55 years. Blood 2003; 102: 3052–3059.
Cornelissen JJ, Carston M, Kollman C et al. Unrelated marrow transplantation for adult patients with poor-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: strong graft-versus-leukemia effect and risk factors determining outcome. Blood 2001; 97: 1572–1577.
McGlave PB, Shu XO, Wen W et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia: 9 years' experience of the national marrow donor program. Blood 2000; 95: 2219–2225.
Sierra J, Storer B, Hansen JA et al. Transplantation of marrow cells from unrelated donors for treatment of high-risk acute leukemia: the effect of leukemic burden, donor HLA-matching, and marrow cell dose. Blood 1997; 89: 4226–4235.
Morris EC, Rebello P, Thomson KJ et al. Pharmacokinetics of alemtuzumab used for in vivo and in vitro T-cell depletion in allogeneic transplantations: relevance for early adoptive immunotherapy and infectious complications. Blood 2003; 102: 404–406.
Chakraverty R, Peggs K, Chopra R et al. Limiting transplantation-related mortality following unrelated donor stem cell transplantation by using a nonmyeloablative conditioning regimen. Blood 2002; 99: 1071–1078.
Castro-Malaspina H, Harris RE, Gajewski J et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation for myelodysplastic syndromes: outcome analysis in 510 transplants facilitated by the National Marrow Donor Program. Blood 2002; 99: 1943–1951.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popat, U., Carrum, G., May, R. et al. CD52 and CD45 monoclonal antibodies for reduced intensity hemopoietic stem cell transplantation from HLA matched and one antigen mismatched unrelated donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 35, 1127–1132 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704975
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704975
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Central nervous system graft-versus-host disease: report of two cases and literature review
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2007)
-
Outcome of reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (RISCT) using antilymphocyte antibodies in patients with high-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2006)