Summary:
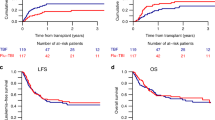
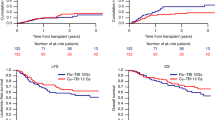
Between September 1986 and June 1997, 24 children with high-risk ALL in CR1 were allografted after TAM (fractionated TBI, high-dose Ara-C, and melphalan; n=10) or BAM protocol (busulfan, high-dose Ara-C, and melphalan; n=14). The EFS for transplants from sibling donors was 33% with TAM and 62% with BAM (P=0.148). The probability of acute GvHD was 70% with TAM and 15% with BAM (P=0.003). Four of 17 evaluable patients relapsed: one after TAM and three after BAM. In all, 46 other children transplanted in CR beyond CR1 were studied for sequelae. Long-term side effects were more frequent in TAM vs BAM. In children with ALL, busulfan may be a good alternative to TBI to improve the quality of life.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kersey JH . Fifty years of studies of the biology and therapy of childhood leukemia. Blood 1997; 90: 4243–4251.
Pinkel D . Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a second remission. New Engl J Med 1995; 332: 823–826.
Dini G, Cornish JM, Gadner H et al. Bone marrow transplant indications for childhood leukemia: achieving a consensus. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 18: 4–7.
Brochstein JA, Kernan NA, Groshen S et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation after hyperfractionated total body irradiation and cyclophosphamide in children with acute leukemiac. New Engl J Med 1987; 317: 1618–1624.
Blume KG, Forman SJ, O'Donnel MR et al. Total body irradiation and high-dose etoposide: a new preparative regimen for bone marrow transplantation in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. Blood 1987; 69: 1015–1020.
Coccia PF, Strandjord SE, Warkentin PI et al. High dose cytosine arabinoside and fractioned total-body irradiation: an improved preparative regimen for bone marrow transplantation of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in remission. Blood 1988; 71: 888–893.
Bordigoni P, Esperou H, Souillet G et al. Total body irradiation, high dose cytosine arabinoside and melphalan followed by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation from HLA-identical siblings in the treatment of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after relapse while receiving chemotherapy: a Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle study. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 656–665.
Sanders JE, Pritchard S, Mahoney P et al. Growth and development following marrow transplantation for leukemia. Blood 1986; 68: 1129–1135.
Sanders JE, Bucker CD, Leonard JM et al. Late effects on gonadal function of cyclophosphamide, total body irradiation, and marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1983; 36: 252–255.
Sklar CA, Kim TH, Ramsay NKC et al. Thyroid dysfunction among long-term survivors of bone marrow transplantation. Am J Med 1982; 73: 688–694.
Von Bueltzingsloewen A, Esperou-Bourdeau H, Souillet G et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation following a busulfan-based conditioning regimen in young children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a cooperative study of the Societé Francaise de Greffe de Moelle. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 16: 521–527.
Matsuyama T Kojima S, Kato K . Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for childhood leukemia following a busulfan and melphalan preparative regimen. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 21–26.
Vilmer E, Suciu S, Ferster A et al. Long term results of three randomized trials (58831,58832,58881) in childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia: a CLCG-EORTC report. Leukemia 2000; 14: 2257–2266.
Bordigoni P, Vernant JP, Souillet G et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission: a cooperative study of the group d'Etude de la Greffe de Moelle Osseuse. J Clin Oncol 1989; 7: 747–753.
Saarinen UM, Mellander L, Nyson K et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in first remission for children with very high risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective case control-study in Nordic countries (NOPHO). Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 357–363.
Uderzo C, Valsecchi MG, Balduzzi A et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation versus chemotherapy in high risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission. Br J Haematol 1997; 96: 387–394.
Wheeler KA, Richards SM, Bailley CC et al. Bone marrow transplantation versus chemotherapy in the treatment of very high risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission: result from Medical Research Council UKALL X an XI. Blood 2000; 96: 2412–2418.
Sadowitz PD, Smith SD, Shuster J et al. Treatment of late bone marrow relapse in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Blood 1993; 81: 602–609.
Boulad F, Steinherz P, Reyes B et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation versus chemotherapy for the treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in second remission: a single-institution Study. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 197–207.
Gordon BG, Warkentin PI, Strandjord SE et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for children with acute leukemia: long-term follow-up of patients prepared with high-dose cytosine arabinoside and fractionated total body irradiation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 5–10.
Ringdén O, Ruutu T, Remberger M et al. A randomized trial comparing busulfan with total body irradiation as conditioning in allogeneic marrow transplant recipients with leukemia: a report from the Nordic Bone Marrow Transplantation Group. Blood 1994; 83: 2723–2730.
Ringdén O, Labopin M, Tura S et al. A comparison of busulfan versus total body irradiation combined with cyclophosphamide as conditioning for autograft or allograft bone marrow transplantation in patients with acute leukemia. Br J Haematol 1996; 93: 637–645.
Davies SM, Ramsay NCK, Klein JP et al. Comparison of preparative regimens, in transplants for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 340–347.
Mineishi S, Longo WL, Atkinson ME et al. Addition of high-dose Ara C to the BMT conditioning regimen reduces leukemia relapse without an increase in toxicity. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 23: 1217–1222.
Sklar C . Growth and endocrine disturbance after bone marrow transplantation in childhood. Acta Paediatr Suppl 1995; 411: 57–61.
Witherspoon RP, Fisher LD, Schoch G et al. Secondary cancers after bone marrow transplantation for leukemia or aplastic anemia. New Engl J Med 1989; 321: 784–789.
Shalet SM, Didi M, Ogilvy-Stuart et al. Growth and endocrine function after bone marrow transplantation. Clin Endocrinol 1995; 42: 333–339.
Wingard JR, Piotnick LP, Freemer CS et al. Growth in children after bone marrow transplantation: busulfan plus cyclophosphamide versus cyclophosphamide plus total body irradiation. Blood 1992; 79: 1068–1073.
Michel G, Solié G, Gebhard F et al. Late effects of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for children with acute myeloblastic leukemia in first remission: the impact of conditioning regimen without total body irradiation. A report from the Société Française de Greffe de Moelle. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 2238–2246.
Dahllöf G, Barr M, Bolme P et al. Disturbance in tental development after total body irradiation in bone marrow transplant recipients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1988; 65: 4144.
Bruno B, Souillet G, Bertrand Y et al. Effects of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation on pulmonary function in 80 children in a single paediatric centre. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 7: 1043–1057.
Bleyzac N, Souillet G, Magron P et al. Improved clinical outcome of pediatric bone marrow recipients by using a test dose and Bayesian pharmacokinetic individualization of busulfan dosage regimens. Bone marrow transplantation. 2001; 28: 743–751.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Q., Souillet, G., Bertrand, Y. et al. Antileukemic and long-term effects of two regimens with or without TBI in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 34, 667–673 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704605
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704605
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Total body irradiation tremendously impair the proliferation, differentiation and chromosomal integrity of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal stem cells
Annals of Hematology (2018)
-
Growth hormone treatment impact on growth rate and final height of patients who received HSCT with TBI or/and cranial irradiation in childhood: a report from the French Leukaemia Long-Term Follow-Up Study (LEA)
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2012)
-
BU- vs TBI-based conditioning for adult patients with ALL
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2011)
-
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation following solid-organ transplantation in children
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2011)
-
The effect of high-dose thiotepa, alone or in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, on a murine B-cell leukemia model simulating autologous stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2007)