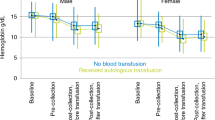
Summary:
This prospective study compared the donor experience of blood cell (BC) mobilization and leukapheresis (n=116) with that of bone marrow (BM) harvest (n=55). Internal jugular catheters were inserted electively in 89% of BC donors. Most (80%) BM donors had a harvest with general anesthesia; 20% had epidural or spinal anesthesia. Pain and fatigue were frequent with both procedures and were compared in responses to questionnaires. A total of 85% of BM donors reported moderate or severe pain compared with 68% of BC donors (P=0.02). The median duration of pain was 14 days for BM donors compared with 3 days after BC mobilization (P<0.0001). More BM donors had pain for more than 7 days (75% vs 0%, P<0.0001). Severe fatigue was experienced by more BM donors (49 vs 16%, P<0.0001). Fatigue lasted significantly longer in BM donors (median 11 vs 4 days, P<0.0001) and more BM donors were fatigued for more than 1 week (69 vs 0%, P<0.0001). A total of 11 donors had both BM and BC collection; seven preferred the latter. Simply considered with respect to pain and fatigue, BC donation appears better tolerated by donors. However, there are other sequelae of both influencing the acceptability for individual donors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
IBMTR/ABMTR Newsletter 2002; 9: 4–11.
Russell JA, Luider J, Weaver M et al. Collection of progenitor cells for allogeneic transplantation from peripheral blood of normal donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 111–115.
Anderlini P, Donato M, Chan KW et al. Allogeneic blood progenitor cell collection in normal donors after mobilization with filgrastim: the M.D. Anderson Cancer Centre experience. Transfusion 1999; 39: 555–560.
Luider J, Brown C, Selinger S et al. Factors influencing yields of progenitor cells for allogeneic transplantation: optimization of G-CSF dose, day of collection and duration of leukapheresis. J Hematother 1997; 6: 575–580.
Dreger P, Haferlach T, Eckstein V et al. G-CSF-mobilized peripheral blood progenitor cells for allogeneic transplantation: safety, kinetics of mobilization, and composition of the graft. Br J Haematol 1994; 87: 609–613.
Blaise D, Kuentz M, Fortanier C et al. Randomized trial of bone marrow versus lenograstim-primed blood cell allogeneic transplantation in patients with early-stage leukemia: a report from the Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 537–546.
Wiesneth M, Schreiner T, Friedrich W et al. Mobilization and collection of allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cells for transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21 (Suppl. 3): S21–S24.
Cavallaro AM, Lilleby K, Majolino I et al. Three to six year follow-up of normal donors who received recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 85–89.
Stroncek DF, Confer DL, Leitman SF . Peripheral progenitor cells for HPC transplants involving unrelated donors. Transfusion 2000; 40: 731–741.
Bensinger WI, Price TH, Dale DC et al. The effects of daily recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration on normal granulocyte donors undergoing leukapheresis. Blood 1993; 7: 1883–1888.
Miflin G, Charley C, Stainer C et al. Stem cell mobilization in normal donors for allogeneic transplantation: analysis of safety and factors affecting efficacy. Br J Haematol 1996; 95: 345–348.
Anderlini P, Przepiorka D, Seong D et al. Clinical toxicity and laboratory effects of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor (filgrastim) mobilization and blood stem cell apheresis from normal donors. An analysis of charges for the procedures. Transfusion 1996; 36: 590–595.
Majolino I, Cavallaro AM, Bacigalupo A et al. Mobilization and collection of PBSC in healthy donors: a retrospective analysis of the Italian Bone Marrow Transplantation Group (GITMO). Haematologica 1997; 82: 47–52.
Anderlini P, Korbling M, Date D et al. Allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation: considerations for donors. Blood 1997; 3: 903–908.
Stroncek DF, Clay ME, Herr G et al. Blood counts in healthy donors 1 year after the collection of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor-mobilized progenitor cells and the results of a second mobilization and collection. Transfusion 1997; 37: 304–308.
Novotny J, Kadar J, Hertenstein B et al. Sustained decrease of peripheral lymphocytes after allogeneic blood stem cell aphereses. Br J Haematol 1998; 100: 695–697.
Anderlini P, Przepiorka D, Korbling M, Champlin R . Blood stem cell procurement: donor safety issues. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21 (Suppl. 3): 35–39.
Korbling M . Collection of allogeneic peripheral blood stem cells. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 1999; 1: 41–45.
De la Rubia J, Martinez C, Solano C et al. Administration of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor to normal donors: results of the Spanish Group of Allo-PBT. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 723–728.
Murata M, Harada M, Kato S et al. Peripheral blood stem cell mobilization and apheresis: analysis of adverse events in 94 normal donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 1065–1071.
Stroncek DF, Clay ME, Jaszcz W et al. Collection of two peripheral blood stem cell concentrates from healthy donors. Transfus Med 1999; 9: 37–50.
Ordemann R, Holig K, Wagner K et al. Acceptance and feasibility of peripheral stem cell mobilisation compared to bone marrow collection from healthy unrelated donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21 (Suppl. 3): S25–S28.
Heldal D, Tjonnfjord G, Brinch L et al. A randomised study of allogeneic transplantation with stem cells from blood or bone marrow. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 1129–1136.
Bensinger Wi, Martin PJ, Storer B et al. Transplantation of bone marrow as compared with peripheral-blood cells from HLA identical relatives in patients with hematologic cancers. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 175–181.
Couban S, Simpson DR, Bredeson C et al. First 100 donors in the Canadian Bone Marrow Transplant Group trial comparing peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) in allogeneic transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21 (Suppl. 1): S36 (abstract 128).
Schmitz N, Bacigalupo A, Hansenclever D al . Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation vs filgrastim-mobilised peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation in patients with early leukemia: first results of a randomized multicentre trial of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21: 995–1003.
Cleaver SA, Goldman JM . Use of G-CSF to mobilize PBSC in normal healthy donors – an international survey. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21 (Suppl. 3): S29–S31.
Ringden O, Remberger M, Runde V et al. Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors: a comparison with marrow transplantation. Blood 1999; 94: 455–464.
Switzer GE, Goycoolyea JM, Dew EC et al. Donating stimulated peripheral blood stem cells vs bone marrow: do donors experience the procedures differently? Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 917–923.
Becker PS, Wagle M, Matous S et al. Spontaneous splenic rupture following administration of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): occurrence in an allogeneic donor of peripheral blood stem cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 1997; 3: 45–49.
Kawachi Y, Watanabe A, Uchida T et al. Acute arterial thrombosis due to platelet aggregation in a patient receiving granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Br J Haematol 1996; 94: 413–416.
Parkkali T, Volin L, Sirdn MK, Ruutu T . Acute iritis induced by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor used for mobilization in a volunteer unrelated peripheral blood progenitor cell donor. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 433–434.
Powles R, Mehta J, Kulkami S et al. Allogeneic blood and bone-marrow stem-cell transplantation in haematological malignant diseases: a randomised trial. Lancet 2000; 355: 1231–1237.
Anderlini P, Rizzo JD, Nugent ML et al. Peripheral blood stem cell donation: an analysis from the International Bone marrow Transplant Registry (IBMTR) and European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplant (EBMT) databases. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 689–692.
Fortanier C, Kuentz M, Sutton L et al. Healthy sibling donor anxiety and pain during bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cell harvesting for allogeneic transplantation: results of a randomized study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 145–149.
Heldal D, Brinch L, Tjonnfjord G et al. Donation of stem cells from blood or bone marrow: results of a randomized study of safety and complaints. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 479–486.
Rowley SD, Donaldson G, Lilleby K et al. Experiences of donors enrolled in a randomized study of allogeneic bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood 2001; 97: 2541–2548.
Stroncek DF, Holland PV, Bartch G et al. Experiences of the first 493 unrelated marrow donors in the National marrow Donor program. Blood 1993; 81: 1940–1946.
Bortin MM, Buckner CD . Major complications of marrow harvesting for transplantation. Exp Hematol 1983; 11: 916–921.
Buckner CD, Clift RA, Sanders JE et al. Marrow harvesting from normal donors. Blood 1984; 64: 630–634.
Sadler DJ, McCarthy M, Saliken JC et al. Image guided central venous catheter placement for apheresis in allogeneic stem cell donors. J Clin Apheresis 2000; 15: 173–175.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the data collection done by Sue Kimber, RN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlsson, L., Quinlan, D., Guo, D. et al. Mobilized blood cells vs bone marrow harvest: experience compared in 171 donors with particular reference to pain and fatigue. Bone Marrow Transplant 33, 709–713 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704418
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704418
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A review of the haematopoietic stem cell donation experience: is there room for improvement?
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Hematopoietic stem cell donation
International Journal of Hematology (2013)
-
The role of donor characteristics and post-granulocyte colony-stimulating factor white blood cell counts in predicting the adverse events and yields of stem cell mobilization
International Journal of Hematology (2011)
-
Regeneration, health status and quality of life after rhG-CSF-stimulated stem cell collection in healthy donors: a cross-sectional study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2009)
-
Pain syndromes in the setting of haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for haematological malignancies
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)