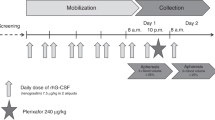
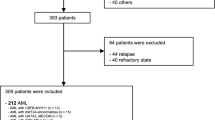
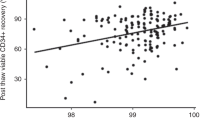
Summary:
Large volume leukapheresis (LVL) has been proposed as a simplified single-apheresis approach to collect the target number of CD34+ cells. We retrospectively analyzed results of LVL in cytokine-mobilized patients weighing less than 20 kg to evaluate adverse events and variables affecting the yield. The only major adverse event recorded was transient and reversible systolic hypotension (three episodes). All the other adverse events were mild and did not require treatment. In multivariate analysis leukocyte count (P=0.001) and younger age (P=0.009) affected the CD34+ cell number in the peripheral blood before apheresis. The number of CD34+ cells before the apheresis was the only variable affecting CD34+ cell yield in multivariate analysis (P=0.0001). In all, 77% of patients achieved the target CD34+ cell dose of 2×106/kg in their first apheresis. Recruitment was seen in 72% of the procedures, and this was related to the total blood volume processed (P=0.0005).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gorlin JB, Humphreys D, Kent P et al. Pediatric large volume PBPC collections from patients under 25 kg: a primer. J Clin Apheresis 1996; 11: 195–203.
Diaz MA, Alegre A, Benito A et al. PBPC collection by large-volume leukapheresis in low-weight children. J Hematother 1998; 7: 63–68.
Kanold J, Halle P, Berger M et al. Large-volume leukapheresis procedure for PBPC collection in children weighing 15 kg or less: efficacy and safety evaluation. Med Pediatr Oncol 1999; 32: 7–10.
Alegre A, Díaz MA, Madero L . Large-volume leukapheresis for peripheral blood stem cell collection in children: a simplified single-apheresis approach. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996; 17: 923–927.
Torrabadella M, Olivé T, Ortega JJ et al. Enhanced HPC recruitment in children using LVL and a new automated apheresis system. Transfusion 2000; 40: 404–410.
Jeter EK, Rogers RL . Pediatric apheresis. In: Apheresis: Principles and Practice, McLeod BC, Price TH, Drew MJ (eds). AABB Editorial Board: Maryland, 1997, pp 409–421.
Madero L, Ruano D, Villa M et al. Non-tunneled catheters in children undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 87–89.
Diaz MA, Garcia-Sánchez F, Lillo R et al. Large-volume leukapheresis in pediatric patients: pre-apheresis peripheral blood CD34+ cell count predicts progenitor cell yield. Haematologica 1999; 84: 30–33.
Diaz MA, Villa M, Madero L . Analysis of engraftment kinetics in pediatric patients undergoing autologous PBPC transplantation. J Hematother 1998; 7: 367–373.
Ford CD, Pace N, Lehman C . Factors affecting the efficiency of collection of CD34-positive peripheral blood cells by a blood cell separator. Transfusion 1998; 38: 1046–1050.
Cull G, Ivey J, Chase P et al. Collection and recruitment of CD34+ cells during large-volume leukapheresis. J Hematother 1997; 6: 309–314.
Mc Leod BC, Price TH, Owen H et al. Frequency of immediate adverse effects associated with apheresis donation. Transfusion 1998; 38: 938–943.
Takaue Y, Kawano Y, Abe T et al. Collection and transplantation of peripheral blood stem cells in very small children weighing 20 kg or less. Blood 1995; 86: 372–380.
Cassens U, Momkvist PH, Zuehlsdorf M et al. Kinetics of standardized large volume leukpheresis (LVL) in patients do not show a recruitment phenomenon of peripheral blood progenitor cells (PBPC). Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 13–20.
Gorlin JB, Vamvakas EC, Cooke E et al. LVL in pediatric patients: processing more blood diminishes the apparent magnitude of intra-apheresis recruitment. Transfusion 1996; 36: 879–885.
Abe T, Makimoto A, Kawano Y et al. Intra-apheresis recruitment of blood progenitor cells in children. Transfusion 1998; 38: 944–950.
Gutierrez-Delgado F, Bensinger W . Safety of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in normal donors. Curr Opin Hematol 2001; 8: 155–160.
Kletzel M, Longino R, Rademaker AW et al. Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in young children: experience with harvesting, mobilization and engraftment. Pediatr Transplant 1998; 2: 191–196.
Watanabe T, Kawano Y, Watanabe A et al. Autologous and allogeneic transplantation with peripheral blood CD34+ cells: a pediatric experience. Haematologica 1999; 84: 167–176.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sevilla, J., González-Vicent, M., Madero, L. et al. Large volume leukapheresis in small children: safety profile and variables affecting peripheral blood progenitor cell collection. Bone Marrow Transplant 31, 263–267 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1703850
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1703850
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Peripheral blood progenitor cell collection in pediatric patients optimized by high pre-apheresis count of circulating CD34+ cells and high blood flow
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)
-
Safety and efficacy of allogeneic PBSC collection in normal pediatric donors: The Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Consortium Experience (PBMTC) 1996–2003
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2005)