Abstract
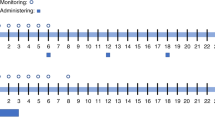
High doses of busulphan are used in conditioning regimens before stem cell transplantation. Great inter-patient variations in pharmacokinetics and a correlation between toxicity and high systemic exposure of busulphan have been shown in several studies. Some authors have suggested therapeutic drug monitoring and intravenous busulphan aiming to reduce the conditioning-related toxicity. Liposomal busulphan (LBu) might be an alternative to intravenous administration of high-dose busulphan in conditioning. In the present study, we investigated the pharmacokinetics of LBu in man. Seventeen consecutive patients were enrolled in the study. LBu as a single low dose (2 to 8 mg) was given to 12 patients (six adults and six children). Five patients received two high doses of LBu which replaced the first and the last doses of the conditioning regimen. The high dose of LBu was raised from 0.4 to 0.9 mg/kg. A significant linear correlation (r2 = 0.928) was found between the dose of LBu and the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) (P < 0.001). AUC corrected for 1 mg/kg was 5491 ± 912 ng·h/ml and 5955 ± 627 ng·h/ml (low dose of LBu in children and adults, respectively) and 6167 ± 1385 ng·h/ml and 6933 ± 656 ng·h/ml (ie the first and the last high doses of LBu, respectively). No significant correlation was found between clearance and age or apparent volume of distribution and age (r2 = 0.146 and r2 = 0.046, respectively). No toxicity related to the liposomal formulation of busulphan was observed. We conclude that LBu is suitable for conditioning before stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplantation (2001) 27, 479–485.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaise D, Maraninchi D, Archimbaud E et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first remission: a randomized trial of a busulfan-cytoxan versus cytoxan-total body irradiation as preparative regimen: a report from the Group d'Etudes de la Greffe de Moelle Osseuse (see comments) Blood 1992 79: 2578–2582
Santos GW, Tutschka PJ, Brookmeyer R et al. Marrow transplantation for acute nonlymphocytic leukemia after treatment with busulfan and cyclophosphamide New Engl J Med 1983 309: 1347–1353
Blume KG, Kopecky KJ, Henslee-Downey JP et al. A prospective randomized comparison of total body irradiation-etoposide versus busulfan-cyclophosphamide as preparatory regimens for bone marrow transplantation in patients with leukemia who were not in first remission: a Southwest Oncology Group study Blood 1993 81: 2187–2193
Ringden O, Ruutu T, Remberger M et al. A randomized trial comparing busulfan with total body irradiation as conditioning in allogeneic marrow transplant recipients with leukemia: a report from the Nordic Bone Marrow Transplantation Group Blood 1994 83: 2723–2730
Ringden O, Labopin M, Tura S et al. A comparison of busulphan versus total body irradiation combined with cyclophosphamide as conditioning for autograft or allograft bone marrow transplantation in patients with acute leukaemia. Acute Leukaemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) Br J Haematol 1996 93: 637–645
Grochow LB, Krivit W, Whitley CB, Blazar B . Busulfan disposition in children Blood 1990 75: 1723–1727
Hassan M, Oberg G, Bekassy AN et al. Pharmacokinetics of high-dose busulphan in relation to age and chronopharmacology Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1991 28: 130–134
Vassal G, Fischer A, Challine D et al. Busulfan disposition below the age of three: alteration in children with lysosomal storage disease Blood 1993 82: 1030–1034
Hassan M, Ljungman P, Bolme P et al. Busulfan bioavailability Blood 1994 84: 2144–2150
Grochow LB, Jones RJ, Brundrett RB et al. Pharmacokinetics of busulfan: correlation with veno-occlusive disease in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1989 25: 55–61
Vassal G, Deroussent A, Hartmann O et al. Dose-dependent neurotoxicity of high-dose busulfan in children: a clinical and pharmacological study Cancer Res 1990 50: 6203–6207
Hassan M, Fasth A, Gerritsen B et al. Busulphan kinetics and limited sampling model in children with leukemia and inherited disorders Bone Marrow Transplant 1996 18: 843–850
Chattergoon DS, Saunders EF, Klein J et al. An improved limited sampling method for individualised busulphan dosing in bone marrow transplantation in children Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 20: 347–354
Ehninger G, Schuler U, Renner U et al. Use of a water-soluble busulfan formulation – pharmacokinetic studies in a canine model Blood 1995 85: 3247–3249
Bhagwatwar HP, Phadungpojna S, Chow DS, Andersson BS . Formulation and stability of busulfan for intravenous administration in high-dose chemotherapy Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1996 37: 401–408
Schuler US, Ehrsam M, Schneider A et al. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous busulfan and evaluation of the bioavailability of the oral formulation in conditioning for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 22: 241–244
Kennedy GL Jr, Sherman H . Acute and subchronic toxicity of dimethylformamide and dimethylacetamide following various routes of administration Drug Chem Toxicol 1986 9: 147–170
Kinney LA, Burgess BA, Stula EF, Kennedy GL Jr . Inhalation studies in rats exposed to dimethylacetamide (DMAc) from 3 to 12 hours per day Drug Chem Toxicol 1993 16: 175–194
Yellowlees P, Greenfield C, McIntyre N . Dimethylsulphoxide-induced toxicity Lancet 1980 2: 1004–1006
Olavarria E, Hassan M, Eades A et al. A phase I/II study of multiple-dose intravenous busulfan as myeloablation prior to stem cell transplantation Leukemia 2000 14: 1954–1959
Hassan M, Hassan Z, Nilsson C et al. Pharmacokinetics and distribution of liposomal busulfan in the rat: a new formulation for intravenous administration Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1998 42: 471–478
Hassan Z, Nilsson C, Hassan M . Liposomal busulphan: bioavailability and effect on bone marrow in mice Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 22: 913–918
Ostro MJ, Cullis PR . Use of liposomes as injectable-drug delivery systems Am J Hosp Pharm 1989 46: 1576–1587
Lopez-Berestein G, Fainstein V, Hopfer R et al. Liposomal amphotericin B for the treatment of systemic fungal infections in patients with cancer: a preliminary study J Infect Dis 1985 151: 704–710
Tollemar J, Ringdén O, Tydén G . Liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome) treatment in solid organ and bone marrow transplant recipients. Efficacy and safety evaluation Clin Transplant 1990 4: 167–175
Hassan M, Ehrsson H . Gas chromatographic determination of busulfan in plasma with electron-capture detection J Chromatogr 1983 277: 374–380
Vassal G, Challine D, Koscielny S et al. Chronopharmacology of high-dose busulfan in children Cancer Res 1993 53: 1534–1537
Ljungman P, Hassan M, Bekassy AN et al. High busulfan concentrations are associated with increased transplant-related mortality in allogeneic bone marrow transplant patients Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 20: 909–913
Gibbs JP, Murray G, Risler L et al. Age-dependent tetrahydrothiophenium ion formation in young children and adults receiving high-dose busulfan Cancer Res 1997 57: 5509–5516
Vassal G, Gouyette A, Hartmann O et al. Pharmacokinetics of high-dose busulfan in children Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1989 24: 386–390
Shaw PJ, Scharping CE, Brian RJ, Earl JW . Busulfan pharmacokinetics using a single daily high-dose regimen in children with acute leukemia Blood 1994 84: 2357–2362
Regazzi MB, Locatelli F, Buggia I et al. Disposition of high-dose busulfan in pediatric patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation Clin Pharmacol Ther 1993 54: 45–52
Janoff A (ed) . Liposomes: Rational Design Marcel Dekker: New York 1999 p 324
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Children's Cancer Society (grant 1997/035, 1999/033), King's Gustaf V Jubilee Fund (grant 00:510) and the Mary Bèves Stiftelse. The authors thank the nursing staff on wards B87, B78 and M72, Huddinge University Hospital for all their help during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, Z., Ljungman, P., Ringdén, O. et al. Pharmacokinetics of liposomal busulphan in man. Bone Marrow Transplant 27, 479–485 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702823
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702823
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of Algorithms for Oral Busulphan Area Under the Concentration–Time Curve Limited Sampling Estimate
Clinical Drug Investigation (2014)
-
A prospective randomized study using N-acetyl-L-cysteine for early liver toxicity after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
Correction of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease by gene therapy, augmented by insertional activation of MDS1-EVI1, PRDM16 or SETBP1
Nature Medicine (2006)
-
Intravenous busulfan in children prior to stem cell transplantation: study of pharmacokinetics in association with early clinical outcome and toxicity
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2005)
-
N-acetyl-L-cysteine does not affect the pharmacokinetics or myelosuppressive effect of busulfan during conditioning prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2003)