Abstract
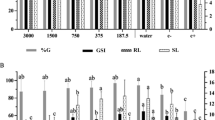
THE effect of a number of organic acids as inhibitors of germination has been tested on the zygotes of the blastikos race of Chlamydomonas eugametos1. It was observed that trans-cinnamic acid inhibits germination to about 50 per cent even at a dilution of 10−7 gm./c.c. The experiment has now been extended to the three different allotropic modifications of cis-cinnamic acid and a few isomeric compounds. The percentage of inhibition of germination with respect to that of control is shown in the accompanying graph. The experimental method and evaluation have been described in greater detail elsewhere2. The percentage germination of the control (in. Volvox solution) is 85.92 ± 0.429 per cent (n = 1,186 zygotes). The activity of cinnamic aldehyde is very small, since at 10−5 gm./c.c. the germination remains unaffected. A similar effect is also found in the case of trans-2-oxy-cinnamic acid (o-coumaric acid). β-d-Glucosido-o-coumaric acid is less active than the aglucone. Coumarin is a hundred times more active; even at a dilution of 10−8 gm./c.c. a statistically significant promotion of germination can be definitely observed. Still more active is trans-cinnamic acid as has been already reported1; though in very dilute solution (10−10 to 10−12 gm./c.c.) no statistically significant promotion of germination was recorded. The range of activity of cis-cinnamic acid is fifty to eighty times more than that of the trans form, since even at a dilution of 10−11 to 10−12 gm./c.c. a significant promotion of germination could be observed. The three allotropic modifications of cis-cinnamic acid (42° C., 58° C., 68° C.) have the same activity2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moewus, F., Z. Naturfg., 5 b, 196 (1950).
Moewus, F., and Baperjee, B., Z. Naturfg., 6 b (in the press).
Moewus, F., Biol. Z., 63, 169 (1943).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MOEWUS, F., BANERJEE, B. Effect of cis-Cinnamic Acid and some Isomeric Compounds on the Germination of Zygotes of Chlamydomonas. Nature 168, 561–562 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1038/168561c0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/168561c0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.