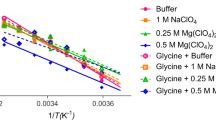
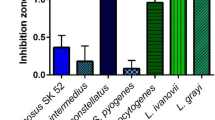
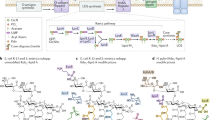
Abstract
FOLLOWING certain pioneer work and suggestions by our former colleague, Dr. H. Henry, it was apparent that much information regarding the structure of Gram-positive bacteria and their behaviour when acted upon by antibiotics could be obtained from a study of bacterial autolysis. The few detailed studies of autolysis which have previously been made have been mainly conftned to the pneumo. coccus group. Goebel and Avery1 showed that the autolytic disintegration of pneumococci was accompanied by proteolysis resulting in an increase in both amino-nitrogen and non-coagulable nitrogen, and by lipolysis liberating ether-soluble fatty acids. A nonspecific cell-free autolytic enzyme system acted upon heat-killed pneumococci to give results comparable with those from spontaneous autolysis and also brought about the partiai lysis of suspensions of heat-killed Streptococcus viridan2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goebel and Avery, J. Exp. Med., 49, 267 (1929).
Avery and Cullen, J. Exp. Med., 38, 199 (1923).
Dubos, J. Exp. Med., 65, 873 (1937).
Kunitz, J. Gen. Physiol., 24, 15 (1940).
Dubos and MacLeod, J. Exp. Med., 67, 791 (1938).
Bartholomew and Umbreit, J. Bact., 48, 567 (1944).
Loring and Carpenter, J. Biol. Chem., 150, 381 (1943).
King and Delory, Biochem. J., 33, 1185 (1939).
Webb, J. Gen. Microbiol. (in the press).
Dubos, J. Exp. Med., 66, 113 (1937).
Henry, Stacey and Teece, Nature, 156, 720 (1945).
Thompson and Dubos, J. Biol. Chem., 125, 65 (1938).
Jones, Swallow and Webb, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (in the press).
McCarty and Avery, J. Exp. Med., 83, 97 (1946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
STACEY, M., WEBB, M. Some Components of the Lytic system of Gram-Positive Micro-Organisms. Nature 162, 11–13 (1948). https://doi.org/10.1038/162011a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/162011a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.