Abstract
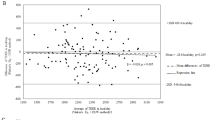
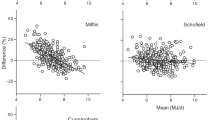
Estimation of energy requirements relies on adequate values of basal metabolic rate (BMR). Prediction equations recommended for international use have been shown to overestimate BMR in populations living in the tropics. We have previously shown the inadequacy of these equations in samples of Brazilians living in tropical and temperate regions of the country. We sought to investigate whether BMR could adequately be estimated by prediction equations in a sample of Brazilians living in a different setting: the Sonoran desert of the Southwestern USA. BMR was measured under standard conditions in 33 subjects (14 men). Mean bias (estimated–measured) varied from 404.4 to 708.6 kJ day−1 in women and 566.8 to 1122.8 kJ day−1 in men, representing 8.5–15 and 8.9–17.6% overestimation, respectively, using the Schofield equations. Bland and Altman analyses showed large, relevant limits of agreement. The results using the recommended equations for the American population (IOM, 2005) were only 2% different from the Schofield equations. The Harris and Benedict equations yielded higher overestimations (15.0 and 16.8% for women and men, respectively) and the Henry and Rees equations also overestimated BMR (8.5 and 8.9%) even though they were developed for populations from the tropics, although to a lesser degree. It is concluded that the equations currently recommended for international use are not appropriate for Brazilians living in the Southwestern USA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfonso-González G, Doucet E, Alméras N, Bouchard C, Tremblay A (2004). Estimation of daily energy needs with the FAO/WHO/UNU 1985 procedures in adults: comparison to whole-body indirect calorimetry measurements. Eur J Clin Nutr 58, 1125–1131.
Almeida AO (1919). Le métabolisme minimum et le métabolism basal de l'homme tropical de race blanche. J Physiol Pathol Gén 18, 713–729.
Almeida AO (1920). Le métabolism basal de l'homme tropical. J Physiol Pathol Gén 18, 958–964.
Almeida AO (1924). L'émission de chaleur le métabolisme basal et le métabolism minimum de l'homme noir tropical. J Physiol Pathol Gén 22, 12–18.
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986). Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet I, 307–312.
Buchholz AC, Rafii M, Pencharz PB (2001). Is resting metabolic rate different between men and women? Br J Nutr 86, 641–646.
Clark HD, Hoffer LJ (1991). Reappraisal of the resting metabolic rate of normal young men. Am J Clin Nutr 53, 21–26.
Cruz CM, Silva AF, Anjos LA (1999). A taxa metabólica basal é superestimada pelas equações preditivas em universitárias do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Arch Latinoamer Nutr 49, 232–237.
FAO/WHO/UNU (1985). Energy and Protein Requirements. WHO – Technical Report Series, World Health Organization: Geneva. p 724.
FAO/WHO/UNU (2004). Human Energy Requirements, Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Food and Nutrition Technical Report Series 1, FAO: Rome.
Galvão PE (1948). Human heat production in relation to body weight and body surface. I. Inapplicability of the Surface Law on lean men of tropical zone. J Appl Physiol 1, 385–394.
Harris JA, Benedict FG (1919). A Biometric Study of Basal Metabolism in Man. Carnegie Institution of Washington: Boston, MA.
Hayter JE, Henry CJ (1993). Basal metabolic rate in human subjects migrating between tropical and temperate regions: a longitudinal study and a review of previous work. Eur J Clin Nutr 47, 724–734.
Hayter JE, Henry CJ (1994). A re-examination of basal metabolic rate predictive equations: the importance of geographic origin of subjects in sample selection. Eur J Clin Nutr 48, 702–707.
Henry CJ, Rees DG (1991). New predictive equations for the estimation of basal metabolic rate in tropical peoples. Eur J Clin Nutr 45, 177–185.
IOM (2005). Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids (Macronutrients). Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. The National Academies Press: Washington, DC.
Lawrence M, Thongprasert K, Durnin JVGA (1988). Between group differences in basal metabolic rate: an analysis of data collected in Scotland, the Gambia and Thailand. Eur J Clin Nutr 42, 877–891.
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R (1988). Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual. Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA.
Lorenzo AD, Tagliabue A, Andreoli A, Testolin G, Comelli M, Deurenberg P (2001). Measured and predicted resting metabolic rate in Italian males and females, aged 18–59 years. Eur J Clin Nutr 55, 208–214.
Müller MJ, Bosy-Westphal A, Klaus S, Kreymann G, Lührmann PM, Neuhäuser-Berthold M et al. (2004). World Health Organization equations have shortcomings for predicting resting energy expenditure in persons from a modern, affluent population: generation of a new reference standard from a retrospective analysis of a German database of resting energy expenditure. Am J Clin Nutr 80, 1379–1390.
Nielsen S, Hensrud DD, Romanski S, Levine JA, Burguera B, Jensen MD (2000). Body composition and resting energy expenditure in humans: role of fat, fat-free mass and extracellular fluid. Int J Obes 24, 1153–1157.
Piers LS, Diffey B, Soares MJ, Frandsen SL, McCormack LM, Lutschini MJ et al. (1997). The validity of predicting the basal metabolic rate of young Australian men and women. Eur J Clin Nutr 51, 333–337.
Piers LS, Shetty PS (1993). Basal metabolic rates of Indian women. Eur J Clin Nutr 47, 586–591.
Schofield WN (1985). Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum Nutr Clin Nutr 39C (Suppl 1), 5–41.
Soares MJ, Francis DG, Shetty PS (1993). Predictive equations for basal metabolic rates of Indian males. Eur J Clin Nutr 47, 389–394.
St-Onge MP, Rubiano F, Jones A, Heymsfield SB (2004). A new hand-held indirect calorimeter to measure postprandial energy expenditure. Obes Res 12, 704–709.
Wahrlich V, Anjos LA (2001a). Historical and methodological aspects of the measurement and prediction of basal metabolic rate: a review. Cad Saúde Públ 17, 801–817.
Wahrlich V, Anjos LA (2001b). Basal metabolic rate of men and women living in tropical and temperate regions of Brazil. Ann Nutr Metabol 45 (Suppl 1), 169.
Wahrlich V, Anjos LA (2001c). Validation of predictive equations of basal metabolic rate of women living in Southern Brazil. Rev Saúde Públ 35, 39–45.
Weir J (1949). New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol 109, 1–9.
Acknowledgements
VW and LAA received fellowships from the Brazilian National Research Council (CNPq, Proc. 200837/03-6 and 200309/04-8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wahrlich, V., Anjos, L., Going, S. et al. Basal metabolic rate of Brazilians living in the Southwestern United States. Eur J Clin Nutr 61, 290–294 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602498
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602498