Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate the effect of antioxidant Vitamins E and C as adjunct therapy of severe acute lower respiratory infection (ALRI) in children.
Design:
Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Setting:
A large childrens' hospital serving the urban poor in Kolkata, India.
Subjects:
Children aged 2–35 months admitted with severe ALRI.
Intervention:
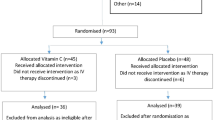
In total, 174 children were randomly assigned to receive α-tocopherol 200 mg and ascorbic acid 100 mg twice daily or placebo for 5 days. All children received standard treatment for severe ALRI. Outcome measures were: time taken to recover from a very ill status, fever, tachypnoea, and feeding difficulty; and improvement in oxidative stress and immune response indicated by thiobarbituric acid reacting substances (TBARS) and response to skin antigens, respectively.
Results:
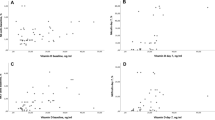
Recovery rate ratios (95% CI) using proportional hazards model were 0.89 (0.64–1.25), 1.01 (0.72–1.41), 0.86 (0.57–1.29), and 1.12 (0.77–1.64) for very ill status, feeding difficulty, fever, and tachypnoea, respectively. TBARS values were high and similar in the two groups at admission, discharge, and at 2 weeks follow-up. Serum α-tocopherol significantly increased in treated group at discharge. Immune response to skin antigens were very poor at admission and after 2 weeks, in both groups.
Conclusion:
Infants with severe ALRI failed to benefit from two antioxidant nutrients as adjunct therapy. Severe ALRI in infants may cause cell-mediated immune dysfunction. We need a better understanding of oxidative processes in growing infants to help us better design interventions with antioxidant therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckman JS, Beckman TW, Chen J, Marshall PA, Freeman BA (1990). Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87, 1620–1624.
Chow CK (1991). Vitamin E and oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 11, 215–232.
Demling R, Lalonde C, Ikegami K, Picard L, Nayak U (1995). Alpha-tocopherol attenuates lung edema and lipid peroxidation caused by acute zymosan-induced peritonitis. Surgery 117, 226–231.
De Lamirande E, Gagnon C (1995). Impact of reactive oxygen species on spermatozoa: a balancing act between beneficial and detrimental effects. Hum Reprod 10 (Suppl 1), 15–21.
Draper HH, Squires EJ, Mahmood H, Wu J, Agarwal S, Hadley M (1993). A comparative evaluation of thiobarbituric acid methods for the determination of malondialdehyde in biological materials. Free Rad Biol Med 15, 353–363.
Fan J, Shek PN, Suntres ZE, Li YH, Oreopoulos GD, Rotstein OD (2000). Liposomal antioxidants provide prolonged protection against acute respiratory syndrome. Surgery 128, 332–338.
Granot E, Golan D, Rivkin L, Kohen R (1999). Oxidative stress in healthy breast-fed versus formula-fed infants. Nutr Res 19, 869–880.
Granot E, Kohen R (2004). Oxidative stress in childhood – in health and disease states. Clin Nutr 23, 3–11.
Haklar G, Vegenaga I, Yalcin AS (1995). Evaluation of oxidant stress in chronic hemodialysis patients: use of different parameters. Clin Chim Acta 234, 109–114.
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2000). Free Radical in Biology and Medicine. Clarendon Press, University Press: Oxford, 160–165.
Harats D, Ben-Naim M, Debach Y, Hollander G, Havivi E, Stein O et al. (1990). Effect of vitamin D and E supplementation on susceptibility of plasma lipoproteins to peroxidation induced by acute smoking. Atheroscierosis 85, 47–54.
Harris ML, Schiller JH, Reilly PM, Donovitz M, Grisham MB, Bulkley GB (1992). Free radicals and other reactive oxygen metabolites in inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmacol Ther 53, 375–408.
Hemila H, Douglas RM (1999). Vitamin C and acute respiratory infections. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 3, 756–761.
Hunt C, Chakravorty NK, Annan G, Habibzadeh N, Schorah CJ (1994). The clinical effects of vitamin C supplementtion in elderly hospitalised patients with acute respiratory infections. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 64, 212–219.
Jacques PF, Cylack LT, McGandy RB, Hartz SC (1988). Antioxidant status in persons with and without senile cateract. Arch Ophthalmal 106, 337–340.
Khaled MA (1994). Oxidative stress in childhood malnutrition and diarrheal disease. J Diar Dis Res 12, 165–172.
Kirschvink N, Fievez L, Bougnet V, Art T, Degand G, Smith N et al. (2002). Effect of nutritional antioxidant supplementation on systemic and pulmonary antioxidant status, airway inflammation and lung infection in heaves-affected horses. Equine Vet J 34, 705–712.
Klein JP, Maeschberger ML (1997). Survival Analysis Techniques for Censored and Truncated Data. Springer: New York, 110–111.
Kohen R, Fauberstein D, Tirosh O (1997). Reducing equivalents in the aging process. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 24, 103–123.
Mahalanabis D, Lahiri M, Paul D, Gupta S, Gupta A, Wahed MA et al. (2004). Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the efficacy of treatment with zinc or vitamin A in infants and young children with severe acute lower respiratory infection. Am J Clin Nutr 79, 430–436.
Menzal DB (1994). The toxicity of air pollution in experimental animals and humans; the role of oxidative stress. Toxicol Lett 72, 269–277.
Podda M, Traber MG, Weber C, Yan Li, Pakcer L (1998). UV-irradiation depletes antioxidants and causes damage in a model of human skin. Feee Rad Biol Med 92, 5258–5265.
Portal B, Richard MJ, Coudray C, Arnaud J, Favier A (1995). Effect of double-blind cross-over selenium supplementation on lipid peroxidation markers in cystic fibrosis patients. Clin Chim Acta 234, 137–146.
Powell CVE, Nash AA, Powers HJ, Primhak RA (1994). Antioxidant status in asthma. Pediatr Pulmonol 18, 34–38.
Remacle J, Raes M, Toussaint O, Renard P, Rao G (1995). Low levels of reactive oxygen species as modulators of cell function. Mutat Res 316, 103–122.
Rocksen D, Ekstrand-Hammarstrom B, Johansson L, Bucht A (2003). Vitamin E reduces transendothelian migration of neutrophils and prevents lung injury in endotoxin-induced airway in flammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 28, 199–207.
Rylander R, Snella MC (1983). Endotoxin and the lung: cellular reactions and risk for disease. Prog Allergy 33, 332–344.
Schwartz KB (1996). Oxidative stress during viral infection: a review. Free Rad Biol Med 21, 641–649.
Spitzer JA (1995). Active oxygen intermediates-beneficial or deleterious? Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 209, 102–103.
Stansfield SK, Shepard DS (1993). Acute respiratory infection. In: Jamison DT, Mosley WH, Measham AR, Bourdilla JL (eds). Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries. Oxford University Press (for World Bank): New York. pp 67–90.
Stone WL, Papas AM (1997). Tocopherois and the etiology of colon cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 89, 1006–1014.
Suntres ZE, Shek PN (1996). Treatment of LPS-induced tissue injury: role of liposomal antioxidants. Shock 6, 57–64.
Traber MG, Packer L (1995). Vitamin E: beyond antioxidant function. Am J Clin Nutr 62, 1501S–1509S.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by a research Grant from Nestle Foundation, Switzerland. We thank Dr Mrinal Kanti Chatterjee (Superintendent), the doctors and healthcare workers of BC Roy Memorial Hospital for Children and ML Chakrabarti of Kothari Medical Research Centre, Kolkata, for their assistance in conduct of the study. We thank Mr Jakir Hossain for computer data management and analysis, and Mr Subodh Karmakar for typing and editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guarantor: D Mahalanabis.
Contributors: DM was responsible for study design, data analysis and writing the manuscript. MB, DP and SG took part in case management and evaluation, skin antigen tests and data collection, and assisted in writing the manuscript. SS and MAW took part in laboratory tests and interpretation and assisted in the writing of the manuscript. MAK took part in the study design, in establishing and standardizing TBARS procedures and interpreting the results, and in writing the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahalanabis, D., Basak, M., Paul, D. et al. Antioxidant vitamins E and C as adjunct therapy of severe acute lower-respiratory infection in infants and young children: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 60, 673–680 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602368
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602368