Abstract
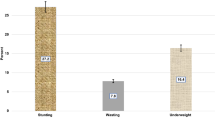
A cross-sectional study of children in West Kalimantan, Indonesia, was conducted to examine the relationship between malnutrition history, child IQ, school attendance, socioeconomic status, parental education and parental IQ. In unadjusted analyses, severely stunted children had significantly lower IQ scores than mild–moderately stunted children. This effect was significant when stunting, school attendance and parental education were included in multivariable models but was attenuated when parental IQ was included. Our research underscores the importance of accounting for parental IQ as a critical covariate when modeling the association between childhood stunting and IQ.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkman DS, Lescano AG, Gilman RH, Lopez SL & Black MM (2002): Effects of stunting, diarrhoeal disease, and parasitic infection during infancy on cognition in late childhood: a follow-up study. Lancet 359, 564–571.
Brown L, Sherbenou RJ & Johnsen SK (1982): Test of Nonverbal Intelligence-3, 3rd Edition, revised 1997. Austin, TX: ProEd.
Cnaan A, Laird NM & Slasor P (1997): Using the general linear mixed model to analyze unbalanced repeated measures and longitudinal data. Stat. Med. 16, 2349–2380.
de Onis M, Monteiro C, Akré J & Clugston G (1993): The worldwide magnitude of protein-energy malnutrition: an overview from the World Health Organization Global Database on Child Growth. Bull. WHO 71, 703–712.
Freeman HE, Klein RE, Townsend JW & Lechtig A (1980): Nutrition and cognitive development among rural Guatemalan children. Am. J. Public Health 70, 1277–1285.
Galler JR, Ramsey FC, Solimano G, Lowell WE & Mason E (1983): The influence of early malnutrition on subsequent behavioral development. I. Degree of impairment in intellectual performance. J. Am. Acad. Child Psychol. 22, 8–15.
Galler JR, Ramsey FC, Morely DS, Archer E & Salt P (1990): The long-term effects of early kwashiorkor compared with marasmus. IV. Performance on the national high school entrance examination. Ped. Res. 28, 235–239.
Grantham-McGregor SM (1995): A review of studies of the effect of severe malnutrition on mental development. J. Nutr. 25, 2233S–2238S.
Grantham-McGregor SM, Powell CA, Walker SP & Himes JH (1991): Nutritional supplementation, psychosocial stimulation, and mental development of stunted children: the Jamaican Study. Lancet 338, 1–5.
Harrington RG (1985): Test of non-verbal intelligence. In Test Critiques, eds DJ Keyser & RC Sweetland, pp 787–798. Kansas City, MO: Test Corp. of America/ West Port Publishers.
Ivanovic DM, Levia BP, Perez HT, Inzunza NB, Almagia AF, Toro TD, Urrutia MS, Cervilla JO & Bosch EO (2000): Long-term effects of severe undernutrition during the first year of life on brain development and learning in Chilean high-school graduates. Nutrition 16, 1056–1063.
Ivanovic DM, Leiva BP, Perez HT, Olivares MG, Diaz NS, Urrutia MS, Almagia AF, Toro TD, Miller PT, Bosch EO & Larrain CG (2004): Head size and intelligence, learning, nutritional status and brain development: head, IQ, learning, nutrition and brain. Neuropsychologia 42, 1118–1131.
Jianghong L, Raine A, Venables PH, Dalais C & Mednick SA (2003): Malnutrition at age 3 years and lower cognitive ability at age 11 years: independence from psychosocial adversity. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 157, 593–600.
Mendez MA & Adair LS (1999): Severity and timing of stunting in the first two years of life affect performance on cognitive tests in late childhood. J. Nutr. 129, 1555–1562.
Rose SA (1994): Relation between physical growth and information processing in infants born in India. Child Dev. 65, 889–902.
SAS Institute Inc (2001): SAS/STAT Software: Changes and Enhancements, Release 8.2. Cary, NC.
Super CM, Herrera MG & Mora JO (1990): Long-term effects of food supplementation and psychosocial intervention on the physical growth of Columbian Infants at risk for malnutrition. Child Dev. 61, 29–49.
Walka H & Pollitt E (2000): A preliminary test of developmental model for the study of undernourished children in Indonesia. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 54 (Suppl 2), S21–S22.
Whorton JE & Morgan RL (1990): Comparison of the test of nonverbal intelligence and Wechsler intelligence scale for children-revised in rural native American and white children. Percep. Motor Skills 70, 12–14.
Acknowledgements
Marjorie Geary, Pak Alexius Hernadi, and multiple nurses made the study possible through their work on the village-health program and support of the study. Ibu Marsiana adeptly provided all translating and research assistance. Dr Sara Sparrow helped design the study and Dr Paul Geary assisted with implementation. Dr Cam Webb assisted at all stages. Funding was provided by the Yale Council for South East Asian Studies and the Yale School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guarantor: KE Webb.
Contributors: KW designed study, conducted all field research and primarily wrote paper. NH designed statistical analyses and assisted with planning and write-up. DK advised throughout process of research design and assisted with analysis and write-up.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Webb, K., Horton, N. & Katz, D. Parental IQ and cognitive development of malnourished Indonesian children. Eur J Clin Nutr 59, 618–620 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602103