Abstract
Objectives:
The aim of this study was to determine the: (1) prevalence of undernutrition as determined by the ‘DETERMINE Your Nutritional Health Checklist’ (NHC) and (2) factors independently associated with undernutrition among the older residents of these publicly funded shelter homes in Peninsular Malaysia.
Design:
A total of 1081 elderly people (59%M) over the age of 60 y were surveyed using questionnaires determining baseline demographics, nutritional and cognitive status, physical function and psychological well-being.
Setting:
Shelter homes, Peninsular Malaysia.
Results:
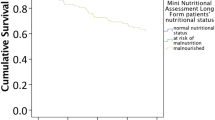
In all, 41.4% (n=447) were nourished (score <3), 32.1% (n=347) at moderate risk (score between 3 and 5) and 26.6% (n=287) were at high risk of undernutrition (score>5) according to the NHC. A large proportion of subjects were underweight with 14.3% of subjects recording a low body mass index (BMI) <18.5 kg/m2 and a further 18.2% recording a BMI between 18.5 and 20 kg/m2. The residential geriatric depression score (GDS-12R) (relative risk (RR)=1.03 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.01–1.05); P=0.002) and the number of illnesses (RR=1.14 (95% CI 1.07–1.21); P< 0.001) were found to be independently associated with nutritional risk (NHC score ≥ 3). Using a BMI<18.5 kg/m2 as an objective marker for nutritional risk, the NHC was shown to have a sensitivity of 66.4% (95% CI 58.0–74.2%), specificity of 42.7% (95% CI 39.3–46.1%), positive predictive value of 16.2% (95% CI 13.3–19.5%) and a negative predictive value of 88.4% (95% CI 84.9–91.4%).
Conclusions:
Many elderly people residing in publicly funded shelter homes in Malaysia may be at-risk of undernutrition, and were underweight. The NHC is better used as an awareness tool rather than as a screening tool.
Sponsorship:
A grant from University Putra Malaysia to Dr Zaiton Ahmad.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azad N, Murphy J, Amos SS & Toppan J (1999): Nutrition survey in an elderly population following admission to a tertiary care hospital. CMAJ 161, 511–515.
Bales CW & Ritchie CS (2002): Sarcopenia, weight loss, and nutritional frailty in the elderly. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 22, 309–323.
De Groot LC, Beck AM, Schroll M & Van Staveren WA (1998): Evaluating the DETERMINE Your Nutritional Health Checklist and the Mini Nutritional Assessment as tools to identify nutritional problems in elderly Europeans. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 52, 877–883.
De Yebenes MJ, Otero A, Zunzunegui MV, Rodriguez-Laso A, Sanchez-Sanchez F & Del Ser T (2003): Validation of a short cognitive tool for the screening of dementia in elderly people with low educational level. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatr. 18, 925–936.
Deurenberg P, Deurenberg-Yap M & Guricci S (2002): Asians are different from Caucasians and from each other in their body mass index/body fat per cent relationship. Obes. Rev. 3, 141–146.
Dwyer J (1994): Strategies to detect and prevent malnutrition in the elderly: the Nutritional Screening Initiative. Nutr. Today 29, 14–24.
Janssen I, Baumgartner RN, Ross R, Rosenberg IH & Roubenoff R (2004): Skeletal muscle cutpoints associated with elevated physical disability risk in older men and women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 159, 413–421.
Katelaris PH, Seow F, Lin BP, Napoli J, Ngu MC & Jones DB (1993): Effect of age, Helicobacter pylori infection, and gastritis with atrophy on serum gastrin and gastric acid secretion in healthy men. Gut 34, 1032–1037.
Kerstetter JE, Holthausen BA & Fitz PA (1992): Malnutrition in the institutionalized older adult. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 92, 1109–1116.
Kua EH & Ko SM (1992): A questionnaire to screen for cognitive impairment among elderly people in developing countries. Acta. Psychiatr. Scand. 85, 119–122.
Luukinen H, Laippala P & Huikuri HV (2003): Depressive symptoms and the risk of sudden cardiac death among the elderly. Eur. Heart J. 24, 2021–2026.
Milne AC, Potter J & Avenell A (2002): Protein and energy supplementation in elderly people at risk from malnutrition. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. CD003288.
Ministry of Health Malaysia (2003): Clinical Practice Guidelines on Managament of Obesity. Malaysia: Ministry of Health.
Morley JE (1997): Anorexia of aging: physiologic and pathologic. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 66, 760–773.
Omran ML & Morley JE (2000): Assessment of protein energy malnutrition in older persons, part I: history, examination, body composition, and screening tools. Nutrition 16, 50–63.
Persson MD, Brismar KE, Katzarski KS, Nordenstrom J & Cederholm TE (2002): Nutritional status using mini nutritional assessment and subjective global assessment predict mortality in geriatric patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 50, 1996–2002.
Posner BM, Jette AM, Smith KW & Miller DR (1993): Nutrition and health risks in the elderly: the nutrition screening initiative. Am. J. Public Health 83, 972–978.
Roubenoff R (1993): Hormones, cytokines and body composition: can lessons from illness be applied to aging? J. Nutr. 123, 469–473.
Sahyoun NR, Jacques PF, Dallal GE & Russell RM (1997): Nutrition Screening Initiative Checklist may be a better awareness/educational tool than a screening one. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 97, 760–764.
Shahar S, Dixon RA & Earland J (1999a): Development of a screening tool for detecting undernutrition and dietary inadequacy among rural elderly in Malaysia: simple indices to identify individuals at high risk. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 50, 435–444.
Shahar S, Earland J, Powers HJ & Rahman SA (1999b): Nutritional status of rural elderly Malays: dietary and biochemical findings. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 69, 277–284.
Shahar S, Earland J & Abd Rahman S (2001): Social and health profiles of rural elderly Malays. Singapore Med. J. 42, 208–213.
Somes GW, Kritchevsky SB, Shorr RI, Pahor M & Applegate WB (2002): Body mass index, weight change, and death in older adults: the systolic hypertension in the elderly program. Am. J. Epidemiol. 156, 132–138.
Suriah Ar ZM, Zainormi Mj, Shafawi S, Suraya M, Zarina M & Wan Zainuddin Wa (1998): Anthropometric measurements in the elderly. Malay. J. Nutr. 4, 55–63.
Sutcliffe C, Cordingley L, Burns A, Mozley CG, Bagley H, Huxley P & Challis D (2000): A new version of the geriatric depression scale for nursing and residential home populations: the geriatric depression scale (residential) (GDS-12R). Int. Psychogeriatr. 12, 173–181.
Suzana S, Earland J, Suriah AR & Warnes AM (2002): Social and health factors influencing poor nutritional status among rural elderly Malays. J. Nutr. Health Aging 6, 363–369.
Taylor Jr DH & Ostbye T (2001): The effect of middle- and old-age body mass index on short-term mortality in older people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 49, 1319–1326.
Thomas P, Hazif-Thomas C & Clement JP (2003): Influence of antidepressant therapies on weight and appetite in the elderly. J. Nutr. Health Aging 7, 166–170.
Visvanathan R (2003): Under-nutrition in older people: a serious and growing global problem!. J. Postgrad. Med. 49, 352–360.
Visvanathan R, Macintosh C, Callary M, Penhall R, Horowitz M & Chapman I (2003): The nutritional status of 250 older Australian recipients of domiciliary care services and its association with outcomes at 12 months. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 51, 1007–1011.
Wade DT & Collin C (1988): The Barthel ADL Index: a standard measure of physical disability? Int. Disabil. Stud. 10, 64–67.
Walker D & Beauchene RE (1991): The relationship of loneliness, social isolation, and physical health to dietary adequacy of independently living elderly. J Am. Diet. Assoc. 91, 300–304.
Wang J, Thornton JC, Russell M, Burastero S, Heymsfield S & Pierson Jr RN (1994): Asians have lower body mass index (BMI) but higher percent body fat than do whites: comparisons of anthropometric measurements. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 60, 23–28.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Vimala Thambypillai for her clinical and editorial advise and Mr Justin Lokhorst from the Department of Public Health, University of Adelaide for his assistance with the statistical analysis. This study was supported by a grant from University Putra Malaysia to Dr Zaiton Ahmad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guarantors: R Visvanathan and Z Ahmad.
Contributors: RV was involved in designing the study, data analysis and writing of the paper. AZ was involved in designing the study, obtaining funding, data analysis and the writing of the paper. MSS and YAM were involved in writing the paper.
Conflict of interest: None.
Presentation at meeting: Oral Presentation at the British Geriatric Society Autumn Meeting in Harrogate, October 2004.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Visvanathan, R., Zaiton, A., Sherina, M. et al. The nutritional status of 1081 elderly people residing in publicly funded shelter homes in Peninsular Malaysia. Eur J Clin Nutr 59, 318–324 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602075
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602075
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nutrition in the Elderly. Frequently Asked Questions
American Journal of Gastroenterology (2013)
-
Nutritional risk of European elderly
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2013)
-
Bridging the gap in ageing: Translating policies into practice in Malaysian Primary Care
Asia Pacific Family Medicine (2011)
-
Efficiency and applicability of comprehensive geriatric assessment in the Emergency Department: a systematic review
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research (2011)