Abstract
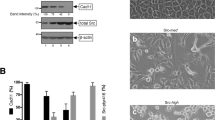
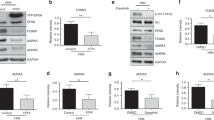
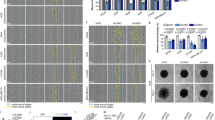
The majority of anaplastic large cell lymphomas (ALCLs) express the nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (NPM-ALK) fusion protein, which is oncogenic due to its constitutive tyrosine kinase activity. Transformation by NPM-ALK not only increases proliferation, but also modifies cell shape and motility in both lymphoid and fibroblastic cells. We report that the Rac1 GTPase, a known cytoskeletal regulator, is activated by NPM-ALK in ALCL cell lines (Karpas 299 and Cost) and transfected cells (lymphoid Ba/F3 cells, NIH-3T3 fibroblasts). We have identified Vav3 as one of the exchange factors involved in Rac1 activation. Stimulation of Vav3 and Rac1 by NPM-ALK is under the control of Src kinases. It involves formation of a signaling complex between NPM-ALK, pp60c-src, Lyn and Vav3, in which Vav3 associates with tyrosine 343 of NPM-ALK via its SH2 domain. Moreover, Vav3 is phosphorylated in NPM-ALK positive biopsies from patients suffering from ALCL, demonstrating the pathological relevance of this observation. The use of Vav3-specific shRNA and a dominant negative Rac1 mutant demonstrates the central role of GTPases in NPM-ALK elicited motility and invasion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrogio C, Voena C, Manazza AD, Piva R, Riera L, Barberis L et al. (2005). p130Cas mediates the transforming properties of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Blood 106: 3907–3916.
Amin HM, Medeiros LJ, Ma Y, Feretzaki M, Das P, Leventaki V et al. (2003). Inhibition of JAK3 induces apoptosis and decreases anaplastic lymphoma kinase activity in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Oncogene 22: 5399–5407.
Armstrong F, Duplantier MM, Trempat P, Hieblot C, Lamant L, Espinos E et al. (2004). Differential effects of X-ALK fusion proteins on proliferation, transformation, and invasion properties of NIH3T3 cells. Oncogene 23: 6071–6082.
Aznar S, Fernandez-Valeron P, Espina C, Lacal JC . (2004). Rho GTPases: potential candidates for anticancer therapy. Cancer Lett 206: 181–191.
Bai RY, Dieter P, Peschel C, Morris SW, Duyster J . (1998). Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase of large-cell anaplastic lymphoma is a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that utilizes phospholipase C-gamma to mediate its mitogenicity. Mol Cell Biol 18: 6951–6961.
Bai RY, Ouyang T, Miething C, Morris SW, Peschel C, Duyster J . (2000). Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt antiapoptotic signaling pathway. Blood 96: 4319–4327.
Bassermann F, Jahn T, Miething C, Seipel P, Bai RY, Coutinho S et al. (2002). Association of Bcr-Abl with the proto-oncogene Vav is implicated in activation of the Rac-1 pathway. J Biol Chem 277: 12437–12445.
Benard V, Bokoch GM . (2002). Assay of Cdc42, Rac, and Rho GTPase activation by affinity methods. Methods Enzymol 345: 349–359.
Bustelo XR . (2000). Regulatory and signaling properties of the Vav family. Mol Cell Biol 20: 1461–1477.
Bustelo XR . (2001). Vav proteins, adaptors and cell signaling. Oncogene 20: 6372–6381.
Charvet C, Canonigo AJ, Billadeau DD, Altman A . (2005). Membrane localization and function of Vav3 in T cells depend on its association with the adapter SLP-76. J Biol Chem 280: 15289–15299.
Chiarle R, Gong JZ, Guasparri I, Pesci A, Cai J, Liu J et al. (2003). NPM-ALK transgenic mice spontaneously develop T-cell lymphomas and plasma cell tumors. Blood 101: 1919–1927.
Chiarle R, Simmons WJ, Cai H, Dhall G, Zamo A, Raz R et al. (2005). Stat3 is required for ALK-mediated lymphomagenesis and provides a possible therapeutic target. Nat Med 11: 623–629.
Cho YJ, Zhang B, Kaartinen V, Haataja L, de Curtis I, Groffen J et al. (2005). Generation of rac3 null mutant mice: role of Rac3 in Bcr/Abl-caused lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Cell Biol 25: 5777–5785.
Contri A, Brunati AM, Trentin L, Cabrelle A, Miorin M, Cesaro L et al. (2005). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells contain anomalous Lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J Clin Invest 115: 369–378.
Crockett DK, Lin Z, Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Lim MS . (2004). Identification of NPM-ALK interacting proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Oncogene 23: 2617–2629.
Cussac D, Greenland C, Roche S, Bai RY, Duyster J, Morris SW et al. (2004). Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma recruits, activates, and uses pp60c-src to mediate its mitogenicity. Blood 103: 1464–1471.
Cussac D, Pichereaux C, Colomba A, Capilla F, Pont F, Gaits-Iacovoni F et al. (2006). Proteomic analysis of anaplastic lymphoma cell lines: identification of potential tumour markers. Proteomics 6: 3210–3222.
Duyster J, Bai RY, Morris SW . (2001). Translocations involving anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). Oncogene 20: 5623–5637.
Falini B . (2001). Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: pathological, molecular and clinical features. Br J Haematol 114: 741–760.
Falini B, Bigerna B, Fizzotti M, Pulford K, Pileri SA, Delsol G et al. (1998). ALK expression defines a distinct group of T/null lymphomas (‘ALK lymphomas’) with a wide morphological spectrum. Am J Pathol 153: 875–886.
Fawal M, Armstrong F, Ollier S, Dupont H, Touriol C, Monsarrat B et al. (2006). A ‘liaison dangereuse’ between AUF1/hnRNPD and the oncogenic tyrosine kinase NPM-ALK. Blood 108: 2780–2788.
Fritz G, Kaina B . (2006). Rho GTPases: promising cellular targets for novel anticancer drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6: 1–14.
Fujimoto J, Shiota M, Iwahara T, Seki N, Satoh H, Mori S et al. (1996). Characterization of the transforming activity of p80, a hyperphosphorylated protein in a Ki-1 lymphoma cell line with chromosomal translocation t(2;5). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 4181–4186.
Gao Y, Dickerson JB, Guo F, Zheng J, Zheng Y . (2004). Rational design and characterization of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 7618–7623.
Genth H, Huelsenbeck J, Hartmann B, Hofmann F, Just I, Gerhard R . (2006). Cellular stability of Rho-GTPases glucosylated by Clostridium difficile toxin B. FEBS Lett 580: 3565–3569.
Hall A . (1998). Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279: 509–514.
Hall A . (2005). Rho GTPases and the control of cell behaviour. Biochem Soc Trans 33: 891–895.
Honorat JF, Ragab A, Lamant L, Delsol G, Ragab-Thomas J . (2006). SHP1 tyrosine phosphatase negatively regulates NPM-ALK tyrosine kinase signaling. Blood 107: 4130–4138.
Hornstein I, Alcover A, Katzav S . (2004). Vav proteins, masters of the world of cytoskeleton organization. Cell Signal 16: 1–11.
Lamant L, De Reynies A, Duplantier MM, Rickman DS, Sabourdy F, Giuriato S et al. (2006). Gene expression profiling of systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma reveals differences depending on ALK status and two distinct morphological ALK+ subtypes. Blood 109: 2156–2164.
Lamant L, Espinos E, Duplantier M, Dastugue N, Robert A, Allouche M et al. (2004). Establishment of a novel anaplastic large-cell lymphoma-cell line (COST) from a ‘small-cell variant’ of ALCL. Leukemia 18: 1693–1698.
Lamant L, Meggetto F, al Saati T, Brugieres L, de Paillerets BB, Dastugue N et al. (1996). High incidence of the t(2;5)(p23;q35) translocation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and its lack of detection in Hodgkin's disease. Comparison of cytogenetic analysis, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, and P-80 immunostaining. Blood 87: 284–291.
Lim MS, Elenitoba-Johnson KS . (2006). Mass spectrometry-based proteomic studies of human anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Mol Cell Proteomics 5: 1787–1798.
Liu BP, Burridge K . (2000). Vav2 activates Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA downstream from growth factor receptors but not beta1 integrins. Mol Cell Biol 20: 7160–7169.
Llorca O, Arias-Palomo E, Zugaza JL, Bustelo XR . (2005). Global conformational rearrangements during the activation of the GDP/GTP exchange factor Vav3. EMBO J 24: 1330–1340.
Marzec M, Kasprzycka M, Liu X, Raghunath PN, Wlodarski P, Wasik MA . (2007). Oncogenic tyrosine kinase NPM/ALK induces activation of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway independently of c-Raf. Oncogene 26: 813–821.
Marzec M, Kasprzycka M, Ptasznik A, Wlodarski P, Zhang Q, Odum N et al. (2005). Inhibition of ALK enzymatic activity in T-cell lymphoma cells induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation and STAT3 phosphorylation independently of Jak3. Lab Invest 85: 1544–1554.
Movilla N, Bustelo XR . (1999). Biological and regulatory properties of Vav-3, a new member of the Vav family of oncoproteins. Mol Cell Biol 19: 7870–7885.
Petit P, Breard J, Montalescot V, El Hadj NB, Levade T, Popoff M et al. (2003). Lethal toxin from Clostridium sordellii induces apoptotic cell death by disruption of mitochondrial homeostasis in HL-60 cells. Cell Microbiol 5: 761–771.
Rottner K, Hall A, Small JV . (1999). Interplay between Rac and Rho in the control of substrate contact dynamics. Curr Biol 9: 640–648.
Sahai E, Marshall CJ . (2002). RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 133–142.
Theodorescu D, Sapinoso LM, Conaway MR, Oxford G, Hampton GM, Frierson Jr HF . (2004). Reduced expression of metastasis suppressor RhoGDI2 is associated with decreased survival for patients with bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: 3800–3806.
Thompson MA, Stumph J, Henrickson SE, Rosenwald A, Wang Q, Olson S et al. (2005). Differential gene expression in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive and anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Hum Pathol 36: 494–504.
Titus B, Schwartz MA, Theodorescu D . (2005). Rho proteins in cell migration and metastasis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 15: 103–114.
Zakaria S, Gomez TS, Savoy DN, McAdam S, Turner M, Abraham RT et al. (2004). Differential regulation of TCR-mediated gene transcription by Vav family members. J Exp Med 199: 429–434.
Zeng L, Sachdev P, Yan L, Chan JL, Trenkle T, McClelland M et al. (2000). Vav3 mediates receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling, regulates GTPase activity, modulates cell morphology, and induces cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol 20: 9212–9224.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Popoff for Clostridium lethal toxins. We are grateful to Dr H Tronchère, Dr S Manenti, Dr MP Gratacap, Dr C Racaud-Sultan and Dr M Plantavid for helpful discussions. AC and DR were financed by the ‘Ministère de la Recherche et de la Technologie’ and the ‘Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer’. This work was supported by grants from the INSERM, ARC, ARECA, La Ligue contre le Cancer, the ‘Cancéropôle Grand Sud-Ouest’ and the ‘Institut National du Cancer’ (INCa), the Région Midi-Pyrénées and the ‘Pôle de Compétitivité Cancer-Bio Santé’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colomba, A., Courilleau, D., Ramel, D. et al. Activation of Rac1 and the exchange factor Vav3 are involved in NPM-ALK signaling in anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Oncogene 27, 2728–2736 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210921
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210921
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) is a tumor suppressor in T cell lymphoma
Nature Medicine (2019)
-
Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate regulates invasion through binding and activation of Tiam1
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Mechanistic insight into ALK receptor tyrosine kinase in human cancer biology
Nature Reviews Cancer (2013)
-
Inhibition of Rac controls NPM–ALK-dependent lymphoma development and dissemination
Blood Cancer Journal (2011)
-
NF2-deficient cells depend on the Rac1-canonical Wnt signaling pathway to promote the loss of contact inhibition of proliferation
Oncogene (2010)