Abstract
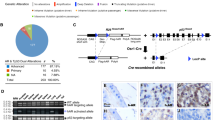
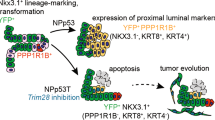
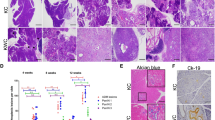
Upregulated gene 19 (U19)/ELL-associated factor 2 (Eaf2) is a potential human tumor suppressor that exhibits frequent allelic loss and downregulation in high-grade prostate cancer. U19/Eaf2, along with its homolog Eaf1, has been reported to regulate transcriptional elongation via interaction with the eleven-nineteen lysine-rich leukemia (ELL) family of proteins. To further explore the tumor-suppressive effects of U19/Eaf2, we constructed and characterized a murine U19/Eaf2-knockout model. Homozygous or heterozygous deletion of U19/Eaf2 resulted in high rates of lung adenocarcinoma, B-cell lymphoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and prostate intraepithelial neoplasia. Within the mouse prostate, U19/Eaf2 deficiency enhanced cell proliferation and increased epithelial cell size. The knockout mice also exhibited cardiac cell hypertrophy. These data indicate a role for U19/Eaf2 in growth suppression and cell size control as well as argue for U19/Eaf2 as a novel tumor suppressor in multiple mouse tissues. The U19/Eaf2 knockout mouse also provides a unique animal model for three important cancers: lung adenocarcinoma, B-cell lymphoma and hepatocellular carcinoma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cioce M, Lamond AI . (2005). Cajal bodies: a long history of discovery. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21: 105–131.
Clarke AR, Maandag ER, van Roon M, van der Lugt NM, van der Valk M, Hooper ML et al. (1992). Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature 359: 328–330.
Gall JG . (2003). The centennial of the Cajal body. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 975–980.
Haase VH, Glickman JN, Socolovsky M, Jaenisch R . (2001). Vascular tumors in livers with targeted inactivation of the von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 1583–1588.
Haber D, Harlow E . (1997). Tumour-suppressor genes: evolving definitions in the genomic age. Nat Genet 16: 320–322.
Jacks T, Fazeli A, Schmitt EM, Bronson RT, Goodell MA, Weinberg RA . (1992). Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature 359: 295–300.
Kaighn ME, Narayan KS, Ohnuki Y, Lechner JF, Jones LW . (1979). Establishment and characterization of a human prostatic carcinoma cell line (PC-3). Invest Urol 17: 16–23.
Kong SE, Banks CA, Shilatifard A, Conaway JW, Conaway RC . (2005). ELL-associated factors 1 and 2 are positive regulators of RNA polymerase II elongation factor ELL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 10094–10098.
Li M, Wu X, Zhuang F, Jiang S, Jiang M, Liu Y-H . (2003). Expression of murine ELL-associated factor 2 (Eaf2) is developmentally regulated. Dev Dynam 228: 273–280.
Luo RT, Lavau C, Du C, Simone F, Polak PE, Kawamata S et al. (2001). The elongation domain of ELL is dispensable but its ELL-associated factor 1 interaction domain is essential for MLL-ELL-induced leukemogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5678–5687.
Ma W, Tessarollo L, Hong SB, Baba M, Southon E, Back TC et al. (2003). Hepatic vascular tumors, angiectasis in multiple organs, and impaired spermatogenesis in mice with conditional inactivation of the VHL gene. Cancer Res 63: 5320–5328.
Maurus D, Héligon C, Bürger-Schwärzler A, Brändli AW, Kühl M . (2005). Noncanonical Wnt-4 signaling and EAF2 are required for eye development in Xenopus laevis. EMBO J 24: 1181–1191.
Mitani K, Yamagata T, Iida C, Oda H, Maki K, Ichikawa M et al. (2000). Nonredundant roles of the elongation factor MEN in postimplantation development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 279: 563–567.
Polak PE, Simone F, Kaberlein JJ, Luo RT, Thirman MJ . (2003). ELL and EAF1 are Cajal body components that are disrupted in MLL–ELL leukemia. Mol Biol Cell 14: 1517–1528.
Selfridge J, Pow AM, McWhir J, Magin TM, Melton DW . (1992). Gene targeting using a mouse HPRT minigene/HPRT-deficient embryonic stem cell system: inactivation of the mouse ERCC-1 gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet 18: 325–336.
Shappell SB, Thomas GV, Roberts RL, Herbert R, Ittmann MM, Rubin MA et al. (2004). Prostate pathology of genetically engineered mice: definitions and classification. The consensus report from the Bar Harbor meeting of the Mouse Models of Human Cancer Consortium Prostate Pathology Committee. Cancer Res 64: 2270–2305.
Shilatifard A, Duan DR, Haque D, Florence C, Schubach WH, Conaway JW et al. (1997a). ELL2, a new member of an ELL family of RNA polymerase II elongation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 3639–3643.
Shilatifard A, Haque D, Conaway RC, Conaway JW . (1997b). Structure and function of RNA polymerase II elongation factor ELL. J Biol Chem 272: 22355–22363.
Shilatifard A, Lane WS, Jackson KW, Conaway RC, Conaway JW . (1996). An RNA polymerase II elongation factor encoded by the human ELL gene. Science 271: 1873–1876.
Simone F, Luo RT, Polak PE, Kaberlein JJ, Thirman MJ . (2003). ELL-associated factor 2 (EAF2), a functional homolog of EAF1 with alternative ELL binding properties. Blood 101: 2355–2362.
Simone F, Polak PE, Kaberlein JJ, Luo RT, Levitan DA, Thirman MJ . (2001). EAF1, a novel ELL-associated factor that is delocalized by expression of the MLL–ELL fusion protein. Blood 98: 201–209.
Thirman MJ, Levitan DA, Kobayashi H, Simon MC, Rowley JD . (1994). Cloning of ELL, a gene that fuses to MLL in a t(11;19)(q23;p13.1) in acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 12110–12114.
Tybulewicz VL, Crawford CE, Jackson PK, Bronson RT, Mulligan RC . (1991). Neonatal lethality and lymphopenia in mice with a homozygous disruption of the c-abl proto-oncogene. Cell 65: 1153–1163.
Wang Z, Tufts R, Haleem R, Cai X . (1997). Genes regulated by androgen in the rat ventral prostate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 12999–13004.
Xiao W, Zhang Q, Jiang F, Pins M, Kozlowski JM, Wang Z . (2003). Suppression of prostate tumor growth by U19, a novel testosterone-regulated apoptosis inducer. Cancer Res 63: 4698–4704.
Zhu N, Wang Z . (1999). Calreticulin expression is associated with androgen regulation of the sensitivity to calcium ionophore-induced apoptosis in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 59: 1896–1902.
Acknowledgements
We thank Moira Hitchens for editing, Katherine Rundell for providing reagents, Minh Nguyen for critical reading, Katherine O’Malley and Fei Su for technical support and members of the Wang lab for extensive discussion. This work was supported in part by NIH R01 DK51193, NIH R01 CA120386, and NIH P50 CA90386 Prostate Cancer SPORE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, W., Zhang, Q., Habermacher, G. et al. U19/Eaf2 knockout causes lung adenocarcinoma, B-cell lymphoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Oncogene 27, 1536–1544 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210786
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210786
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
FOXC1-mediated LINC00301 facilitates tumor progression and triggers an immune-suppressing microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the HIF1α pathway
Genome Medicine (2020)
-
EAF2 regulates DNA repair through Ku70/Ku80 in the prostate
Oncogene (2017)
-
EAF2 mediates germinal centre B-cell apoptosis to suppress excessive immune responses and prevent autoimmunity
Nature Communications (2016)
-
Expression and prognostic significance of ELL-associated factor 2 in human prostate cancer
International Urology and Nephrology (2016)
-
Transcriptional profiling of mouse B cell terminal differentiation defines a signature for antibody-secreting plasma cells
Nature Immunology (2015)