Abstract
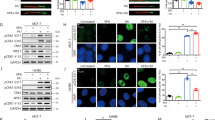
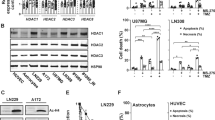
Therapy resistance represents a major problem for disease management in oncology. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) have been shown to modulate the cell cycle, to induce apoptosis and to sensitize cancer cells for other chemotherapeutics. Our study shows that the HDACi valproic acid (VPA) and the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor hydroxyurea (HU) potentiate the pro-apoptotic effects of each other towards several cancer cell lines. This correlates with the HU-induced degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKI) p21 and p27, mediated by the proteasome or caspase-3. Moreover, we found that caspase-3 activation is required for VPA-induced apoptosis. Remarkably, p21 and p27 can confer resistance against VPA and HU. Both CDKI interact with caspase-3 and compete with other caspase-3 substrates. Hence, p21 and p27 may contribute to chemotherapy resistance as apoptosis inhibitors. Since the biological effects of VPA and HU could be achieved at concentrations used in current treatment protocols, the combined application of these compounds might be considered as a potential strategy for cancer treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blagosklonny MV . (2002). Are p27 and p21 cytoplasmic oncoproteins? Cell Cycle 1: 391–393.
Boyle GM, Martyn AC, Parsons PG . (2005). Histone deacetylase inhibitors and malignant melanoma. Pigment Cell Res 18: 160–166.
Bug G, Ritter M, Wassmann B, Schoch C, Heinzel T, Schwarz K et al. (2005). Clinical trial of valproic acid and all-trans retinoic acid in patients with poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 104: 2717–2725.
Drexler HC, Pebler S . (2003). Inducible p27(Kip1) expression inhibits proliferation of K562 cells and protects against apoptosis induction by proteasome inhibitors. Cell Death Differ 10: 290–301.
Eymin B, Haugg M, Droin N, Sordet O, Dimanche-Boitrel MT, Solary E . (1999). p27Kip1 induces drug resistance by preventing apoptosis upstream of cytochrome c release and procaspase-3 activation in leukemic cells. Oncogene 18: 1411–1418.
Finzer P, Kuntzen C, Soto U, zur Hausen H, Rosl F . (2001). Inhibitors of histone deacetylase arrest cell cycle and induce apoptosis in cervical carcinoma cells circumventing human papillomavirus oncogene expression. Oncogene 20: 4768–4776.
Göttlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, Krämer OH, Schimpf A, Giavara S et al. (2001). Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J 20: 6969–6978.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57–70.
Harris AL . (1985). DNA repair: relationship to drug and radiation resistance, metastasis and growth factors. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med 48: 675–690.
Jänicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR, Porter AG . (1998). Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem 273: 9357–9360.
Klisovic DD, Katz SE, Effron D, Klisovic MI, Wickham J, Parthun MR et al. (2003). Depsipeptide (FR901228) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in primary and metastatic human uveal melanoma cell lines. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44: 2390–2398.
Knauer SK, Bier C, Habtemichael N, Stauber RH . (2006). The Survivin-Crm1 interaction is essential for chromosomal passenger complex localization and function. EMBO R 7: 1259–1265.
Koon HB, Atkins MB . (2007). Update on therapy for melanoma: opportunities for patient selection and overcoming tumor resistance. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 7: 79–88.
Kouzarides T . (2000). Acetylation: a regulatory modification to rival phosphorylation? EMBO J 19: 1176–1179.
Krämer OH, Baus D, Knauer SK, Stein S, Jager E, Stauber RH et al. (2006). Acetylation of Stat1 modulates NF-kappaB activity. Genes Dev 20: 473–485.
Krämer OH, Göttlicher M, Heinzel T . (2001). Histone deacetylase as a therapeutic target. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12: 294–300.
Krämer OH, Zhu P, Ostendorff HP, Golebiewski M, Tiefenbach J, Peters MA et al. (2003). The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid selectively induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2. EMBO J 22: 3411–3420.
Kuendgen A, Schmid M, Schlenk R, Knipp S, Hildebrandt B, Steidl C et al. (2006). The histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor valproic acid as monotherapy or in combination with all-trans retinoic acid in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 106: 112–119.
La Porta CA . (2007). Drug resistance in melanoma: new perspectives. Curr Med Chem 14: 387–391.
Levkau B, Koyama H, Raines EW, Clurman BE, Herren B, Orth K et al. (1998). Cleavage of p21Cip1/Waf1 and p27Kip1 mediates apoptosis in endothelial cells through activation of Cdk2: role of a caspase cascade. Mol Cell 1: 553–563.
Maggio SC, Rosato RR, Kramer LB, Dai Y, Rahmani M, Paik DS et al. (2004). The histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 interacts synergistically with fludarabine to induce apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Cancer Res 64: 2590–2600.
Montefusco E, Fazi F, Cordone I, Ariola C, Nanni M, Spadea A et al. (2001). Molecular remission following high-dose hydroxyurea and fludarabine plus cytarabine in a patient with simultaneous acute myeloid leukemia and low-grade lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 40: 671–674.
Mouriaux F, Maurage CA, Labalette P, Sablonniere B, Malecaze F, Darbon JM . (2000). Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory protein expression in human choroidal melanoma tumors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41: 2837–2843.
Nguyen DM, Schrump WD, Chen GA, Tsai W, Nguyen P, Trepel JB et al. (2004). Abrogation of p21 expression by flavopiridol enhances depsipeptide-mediated apoptosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells. Clin Cancer Res 10: 1813–1825.
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, Beer-Romero P, Del Sal G, Chau V et al. (1995). Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science 269: 682–685.
Pantazis P, Chatterjee D, Han Z, Wyche J . (1999). Differentiation of human malignant melanoma cells that escape apoptosis after treatment with 9-nitrocamptothecin in vitro. Neoplasia 1: 231–240.
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Grant S . (2003). The histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 promotes differentiation or apoptosis in human leukemia cells through a process regulated by generation of reactive oxygen species and induction of p21CIP1/WAF1 1. Cancer Res 63: 3637–3645.
Schmidt M, Lu Y, Liu B, Fang M, Mendelsohn J, Fan Z . (2000). Differential modulation of paclitaxel-mediated apoptosis by p21Waf1 and p27Kip1. Oncogene 19: 2423–2429.
Schrell UM, Rittig MG, Anders M, Kiesewetter F, Marschalek R, Koch UH et al. (1997a). Hydroxyurea for treatment of unresectable and recurrent meningiomas. I. Inhibition of primary human meningioma cells in culture and in meningioma transplants by induction of the apoptotic pathway. J Neurosurg 86: 845–852.
Schrell UM, Rittig MG, Anders M, Koch UH, Marschalek R, Kiesewetter F et al. (1997b). Hydroxyurea for treatment of unresectable and recurrent meningiomas. II. Decrease in the size of meningiomas in patients treated with hydroxyurea. J Neurosurg 86: 840–844.
Shin HJ, Baek KH, Jeon AH, Kim SJ, Jang KL, Sung YC et al. (2003). Inhibition of histone deacetylase activity increases chromosomal instability by the aberrant regulation of mitotic checkpoint activation. Oncogene 22: 3853–3858.
St Croix B, Florenes VA, Rak JW, Flanagan M, Bhattacharya N, Slingerland JM et al. (1996). Impact of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 on resistance of tumor cells to anticancer agents. Nat Med 2: 1204–1210.
Suzuki A, Kawano H, Hayashida M, Hayasaki Y, Tsutomi Y, Akahane K . (2000). Procaspase 3/p21 complex formation to resist fas-mediated cell death is initiated as a result of the phosphorylation of p21 by protein kinase A. Cell Death Differ 7: 721–728.
Suzuki A, Tsutomi Y, Miura M, Akahane K . (1999). Caspase 3 inactivation to suppress Fas-mediated apoptosis: identification of binding domain with p21 and ILP and inactivation machinery by p21. Oncogene 18: 1239–1244.
Szekeres T, Fritzer-Szekeres M, Elford HL . (1997). The enzyme ribonucleotide reductase: target for antitumor and anti-HIV therapy. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 34: 503–528.
Van den Berg C, Von Hoff DD . (1995). Use of hydroxyurea to alter drug resistance of human tumor cells. Cancer Treat Res 78: 95–114.
Zhu P, Martin E, Mengwasser J, Schlag P, Janssen KP, Göttlicher M . (2004). Induction of HDAC2 expression upon loss of APC in colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 5: 455–463.
Acknowledgements
We thank S Reichardt, G Greiner and A Schimpf for excellent technical assistance. Expression constructs, antibodies and cells were generously provided by M Zörnig, W Wels, B Dälken, E Jäger and E Jänicke. Grant support: NGFN to TH (N1KR-S31T30) and Deutsche Krebshilfe to RHS (FKZ:102362).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krämer, O., Knauer, S., Zimmermann, D. et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and hydroxyurea modulate the cell cycle and cooperatively induce apoptosis. Oncogene 27, 732–740 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210677
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210677
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The epigenetic modifier HDAC2 and the checkpoint kinase ATM determine the responses of microsatellite instable colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2023)
-
Inhibitors of class I HDACs and of FLT3 combine synergistically against leukemia cells with mutant FLT3
Archives of Toxicology (2022)
-
HDAC1 and HDAC2 integrate checkpoint kinase phosphorylation and cell fate through the phosphatase-2A subunit PR130
Nature Communications (2018)
-
UHRF2 promotes DNA damage response by decreasing p21 via RING finger domain
Biotechnology Letters (2018)
-
t-BuOOH induces ferroptosis in human and murine cell lines
Archives of Toxicology (2018)