Abstract
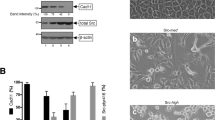
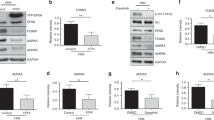
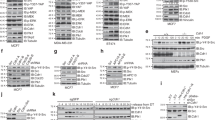
The cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase Src has been implicated in signal transduction induced by growth factors and integrins. Src also shows oncogenic activity when deregulated. Accumulating evidence indicates that the tyrosine kinase Abl is an important substrate for Src signalling in normal cells. Here we show that Abl is also required for Src-induced transformation of mouse fibroblasts. Abl does not mediate tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat3 and Shc, two important regulators of Src oncogenic activity. In contrast, Abl controls the activation of the small GTPase Rac for oncogenic signalling and active Rac partly rescued Src transformation in cells with inactive Abl. Moreover, Abl mediates Src-induced extracellular regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) activation to drive cell transformation. Finally, we find that Abl/Rac and Abl/ERK5 pathways also operate in human MCF7 and BT549 breast cancer cells, where neoplastic transformation depends on Src-like activities. Therefore, Abl is an important regulator of Src oncogenic activity both in mouse fibroblasts and in human cancer cells. Targeting these Abl-dependent signalling cascades may be of therapeutic value in breast cancers where Src-like function is important.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros JC, Marshall CJ . (2005). Activation of either ERK1/2 or ERK5 MAP kinase pathways can lead to disruption of the actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci 118: 1663–1671.
Boureux A, Furstoss O, Simon V, Roche S . (2005). c-Abl tyrosine kinase regulates a Rac/JNK and a Rac/Nox pathway for DNA synthesis and c-myc expression induced by growth factors. J Cell Sci 118: 3717–3726.
Bromann PA, Korkaya H, Courtneidge SA . (2004). The interplay between Src family kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases. Oncogene 23: 7957–7968.
Bromberg JF, Horvath CM, Besser D, Lathem WW, Darnell Jr JE . (1998). Stat3 activation is required for cellular transformation by v-src. Mol Cell Biol 18: 2553–2558.
Buschbeck M, Hofbauer S, Di Croce L, Keri G, Ullrich A . (2005). Abl-kinase-sensitive levels of ERK5 and its intrinsic basal activity contribute to leukaemia cell survival. EMBO Rep 6: 63–69.
Chan AY, Coniglio SJ, Chuang YY, Michaelson D, Knaus UG, Philips MR et al. (2005). Roles of the Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases in human tumor cell invasion. Oncogene 24: 7821–7829.
Chen T, George JA, Taylor CC . (2006). Src tyrosine kinase as a chemotherapeutic target: is there a clinical case? Anticancer Drugs 17: 123–131.
Daniels CE, Wilkes MC, Edens M, Kottom TJ, Murphy SJ, Limper AH et al. (2004). Imatinib mesylate inhibits the profibrogenic activity of TGF-beta and prevents bleomycin-mediated lung fibrosis. J Clin Invest 114: 1308–1316.
Deroanne C, Vouret-Craviari V, Wang B, Pouyssegur J . (2003). EphrinA1 inactivates integrin-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell spreading via the Rac/PAK pathway. J Cell Sci 116: 1367–1376.
Dilworth SM . (2002). Polyoma virus middle T antigen and its role in identifying cancer-related molecules. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 951–956.
Finn RS, Dering J, Ginther C, Wilson CA, Glaspy P, Tchekmedyian N et al. (2007). Dasatinib, an orally active small molecule inhibitor of both the src and abl kinases, selectively inhibits growth of basal-type/‘triple-negative’ breast cancer cell lines growing in vitro. Breast Cancer Res Treat: (in press) Doi 10.1007/s.10549-006-5463-x.
Frame MC . (2004). Newest findings on the oldest oncogene; how activated src does it. J Cell Sci 117: 989–998.
Franco M, Furstoss O, Simon V, Benistant C, Hong WJ, Roche S . (2006). The adaptor protein Tom1L1 is a negative regulator of Src mitogenic signaling induced by growth factors. Mol Biol Cell 26: 1932–1947.
Furstoss O, Dorey K, Simon V, Barilla D, Superti-Furga G, Roche S . (2002). c-Abl is an effector of Src for growth factor-induced c-myc expression and DNA synthesis. EMBO J 27: 514–524.
Garaude J, Cherni S, Kaminski S, Delepine E, Chable-Bessia C, Benkirane M et al. (2006). ERK5 activates NF-kappaB in leukemic T cells and is essential for their growth in vivo. J Immunol 177: 7607–7617.
Hantschel O, Superti-Furga G . (2004). Regulation of the c-Abl and Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 33–44.
Ishizawar R, Parsons SJ . (2004). c-Src and cooperating partners in human cancer. Cancer Cell 6: 209–214.
Kato Y, Kravchenko VV, Tapping RI, Han J, Ulevitch RJ, Lee JD . (1997). BMK1/ERK5 regulates serum-induced early gene expression through transcription factor MEF2C. EMBO J 16: 7054–7066.
Kayahara M, Wang X, Tournier C . (2005). Selective regulation of c-jun gene expression by mitogen-activated protein kinases via the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate- responsive element and myocyte enhancer factor 2 binding sites. Mol Cell Biol 25: 3784–3792.
Kovalenko M, Ronnstrand L, Heldin CH, Loubtchenkov M, Gazit A, Levitzki A et al. (1997). Phosphorylation site-specific inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor autophosphorylation by the receptor blocking tyrphostin AG1296. Biochemistry 36: 6260–6269.
Krause DS, Van Etten RA . (2005). Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med 353: 172–187.
Lewis JM, Baskaran R, Taagepera S, Schwartz MA, Wang JY . (1996). Integrin regulation of c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity and cytoplasmic-nuclear transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 15174–15179.
Martin GS . (2001). The hunting of the Src. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 467–475.
Minden A, Lin A, Claret FX, Abo A, Karin M . (1995). Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell 81: 1147–1157.
Mulloy R, Salinas S, Philips A, Hipskind RA . (2003). Activation of cyclin D1 expression by the ERK5 cascade. Oncogene 22: 5387–5398.
Nicholson PR, Empereur S, Glover HR, Dilworth SM . (2001). ShcA tyrosine phosphorylation sites can replace ShcA binding in signalling by middle T-antigen. EMBO J 20: 6337–6346.
Pendergast AM . (2002). The Abl family kinases: mechanisms of regulation and signaling. Adv Cancer Res 85: 51–100.
Plattner R, Irvin BJ, Guo S, Blackburn K, Kazlauskas A, Abraham RT et al. (2003). A new link between the c-Abl tyrosine kinase and phosphoinositide signalling through PLC-gamma1. Nat Cell Biol 5: 309–319.
Plattner R, Kadlec L, DeMali KA, Kazlauskas A, Pendergast AM . (1999). c-Abl is activated by growth factors and Src family kinases and has a role in the cellular response to PDGF. Genes Dev 13: 2400–2411.
Roussidis AE, Mitropoulou TN, Theocharis AD, Kiamouris C, Papadopoulos S, Kletsas D et al. (2004). STI571 as a potent inhibitor of growth and invasiveness of human epithelial breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res 24: 1445–1447.
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D, Blair J, Hann B, Shokat KM et al. (2007). Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature 445: 437–441.
Servitja JM, Marinissen MJ, Sodhi A, Bustelo XR, Gutkind JS . (2003). Rac1 function is required for Src-induced transformation. Evidence of a role for Tiam1 and Vav2 in Rac activation by Src. J Biol Chem 278: 34339–34346.
Sini P, Cannas A, Koleske AJ, Di Fiore PP, Scita G . (2004). Abl-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Sos-1 mediates growth-factor-induced Rac activation. Nat Cell Biol 6: 268–274.
Srinivasan D, Plattner R . (2006). Activation of Abl tyrosine kinases promotes invasion of aggressive breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66: 5648–5655.
Suzuki J, Sukezane T, Akagi T, Georgescu MM, Ohtani M, Inoue H et al. (2004). Loss of c-abl facilitates anchorage-independent growth of p53- and RB-deficient primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Oncogene 23: 8527–8534.
Tanis KQ, Veach D, Duewel HS, Bornmann WG, Koleske AJ . (2003). Two distinct phosphorylation pathways have additive effects on Abl family kinase activation. Mol Cell Biol 23: 3884–3896.
Turkson J, Bowman T, Adnane J, Zhang Y, Djeu JY, Sekharam M et al. (1999). Requirement for Ras/Rac1-mediated p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling in Stat3 transcriptional activity induced by the Src oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol 19: 7519–7528.
Urich M, Senften M, Shaw PE, Ballmer-Hofer K . (1997). A role for the small GTPase Rac in polyomavirus middle-T antigen-mediated activation of the serum response element and in cell transformation. Oncogene 14: 1235–1241.
Ushio-Fukai M, Zuo L, Ikeda S, Tojo T, Patrushev NA, Alexander RW . (2005). cAbl tyrosine kinase mediates reactive oxygen species- and caveolin-dependent AT1 receptor signaling in vascular smooth muscle: role in vascular hypertrophy. Circ Res 97: 829–836.
Veracini L, Franco M, Boureux A, Simon V, Roche S, Benistant C . (2006). Two distinct pools of Src family tyrosine kinases regulate PDGF-induced DNA synthesis and actin dorsal ruffles. J Cell Sci 20: 2921–2934.
Yang L, Lin C, Liu ZR . (2006). P68 RNA helicase mediates PDGF-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition by displacing Axin from beta-catenin. Cell 127: 139–155.
Yeatman TJ . (2004). A renaissance for SRC. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 470–480.
Zipfel PA, Zhang W, Quiroz M, Pendergast AM . (2004). Requirement for Abl kinases in T-cell receptor signaling. Curr Biol 14: 1222–1231.
Zou X, Calame K . (1999). Signaling pathways activated by oncogenic forms of Abl tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 274: 18141–18144.
Acknowledgements
We thank K Ballmer-Hofer (Paul Scherrer Institute), XB Bustelo (University of Salamenca), SA Courtneidge (the Burnham Institute for Medical research), A Pandiella (University of Salamenca), J Raingeaud (INSERM U641) and B Willi (Novartis Pharma) for various reagents. We thank C Tournier (University of Manchester) and R Hipskind (CNRS UMR 5535) for constructs and helpful discussion, and our colleagues for critically reading the manuscript. This work was supported by the CNRS, ARC, AICR and INCa. AB was supported by AICR, CL by INCa, AS by Laboratoires Servier and SR by INSERM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirvent, A., Boureux, A., Simon, V. et al. The tyrosine kinase Abl is required for Src-transforming activity in mouse fibroblasts and human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 26, 7313–7323 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210543
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210543
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Advances in studies of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their acquired resistance
Molecular Cancer (2018)
-
Enabling Tumor Growth and Progression: Recent Progress in Unraveling the Functions of ABL Kinases in Solid Tumor Cells
Current Pharmacology Reports (2018)
-
Atomic view of the energy landscape in the allosteric regulation of Abl kinase
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2017)
-
Mutant p53 dictates the oncogenic activity of c-Abl in triple-negative breast cancers
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
The Ron receptor tyrosine kinase activates c-Abl to promote cell proliferation through tyrosine phosphorylation of PCNA in breast cancer
Oncogene (2014)