Abstract
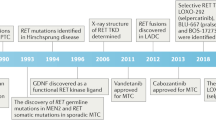
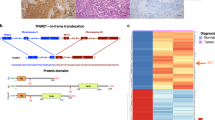
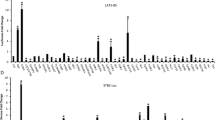
The RET gene encodes two main isoforms of a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) implicated in various human diseases. Activating germ-line point mutations are responsible for multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2-associated medullary thyroid carcinomas, inactivating germ-line mutations for Hirschsprung's disease, while somatic rearrangements (RET/PTCs) are specific to papillary thyroid carcinomas. SH2B1β, a member of the SH2B adaptors family, and binding partner for several RTKs, has been recently described to interact with proto-RET. Here, we show that both RET isoforms and its oncogenic derivatives bind to SH2B1β through the SRC homology 2 (SH2) domain and a kinase activity-dependent mechanism. As a result, RET phosphorylates SH2B1β, which in turn enhances its autophosphorylation, kinase activity, and downstream signaling. RET tyrosine residues 905 and 981 are important determinants for functional binding of the adaptor, as removal of both autophosphorylation sites displaces its recruitment. Binding of SH2B1β appears to protect RET from dephosphorylation by protein tyrosine phosphatases, and might represent a likely mechanism contributing to its upregulation. Thus, overexpression of SH2B1β, by enhancing phosphorylation/activation of RET transducers, potentiates the cellular differentiation and the neoplastic transformation thereby induced, and counteracts the action of RET inhibitors. Overall, our results identify SH2B1β as a key enhancer of RET physiologic and pathologic activities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed Z, Pillay TS . (2001). Functional effects of APS and SH2-B on insulin receptor signalling. Biochem Soc Trans 29: 529–534.
Ahmed Z, Pillay TS . (2003). Adapter protein with a pleckstrin homology (PH) and an Src homology 2 (SH2) domain (APS) and SH2-B enhance insulin-receptor autophosphorylation, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signalling. Biochem J 371: 405–412.
Airaksinen MS, Saarma M . (2002). The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 383–394.
Alberti L, Carniti C, Miranda C, Roccato E, Pierotti MA . (2003). RET and NTRK1 Proto-Oncogenes in Human Diseases. J Cell Physiol 195: 168–186.
Arighi E, Alberti L, Torriti F, Ghizzoni S, Rizzetti MG, Pelicci G et al. (1997). Identification of SHC docking site on Ret tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 14: 773–782.
Arighi E, Borrello MG, Sariola H . (2005). RET tyrosine kinase signaling in development and cancer. Cytokine Growth F R 16: 441–467.
Besser D, Bromberg JF, Darnell Jr JE, Hanafusa H . (1999). A single amino acid substitution in the v-Eyk intracellular domain results in activation of Stat3 and enhances cellular transformation. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1401–1409.
Bongarzone I, Monzini N, Borrello MG, Carcano C, Ferraresi G, Arighi E et al. (1993). Molecular characterization of a thyroid tumor-specific transforming sequence formed by the fusion of ret tyrosine kinase and the regulatory subunit RIa of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A. Mol Cell Biol 13: 358–366.
Borrello MG, Alberti L, Arighi E, Bongarzone I, Battistini C, Bardelli A et al. (1996). The full oncogenic activity of Ret/ptc2 depends on tyrosine 539, a docking site for phospholipase Cgamma. Mol Cell Biol 16: 2151–2163.
Borrello MG, Smith DP, Pasini B, Bongarzone I, Greco A, Lorenzo MJ et al. (1995). RET activation by germline MEN2A and MEN2B mutations. Oncogene 11: 2419–2427.
Bromberg JF, Horvath CM, Besser D, Lathem WW, Darnell Jr JE . (1998). Stat3 activation is required for cellular transformation by v-src. Mol Cell Biol 18: 2553–2558.
Canu N, Possenti R, Rinaldi AM, Trani E, Levi A . (1997). Molecular cloning and characterization of the human VGF promoter region. J Neurochem 68: 1390–1399.
Carlomagno F, Vitagliano D, Guida T, Napolitano M, Vecchio G, Fusco A et al. (2002). The kinase inhibitor PP1 blocks tumorigenesis induced by RET oncogenes. Cancer Res 62: 1077–1082.
Cuccuru G, Lanzi C, Cassinelli G, Pratesi G, Tortoreto M, Petrangolini G et al. (2004). Cellular effects and antitumor activity of RET inhibitor RPI-1 on MEN2A-associated medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 96: 1006–1014.
de Graaff E, Srinivas S, KilKenny C, D'Agati V, Mankoo BS, Costantini F et al. (2001). Differential activities of the RET tyrosine kinase receptor isoforms during mammalian embryogenesis. Genes Dev 15: 2433–2444.
Dhe-Paganon S, Werner ED, Nishi M, Hansen L, Chi YI, Shoelson SE . (2004). A phenylalanine zipper mediates APS dimerization. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 968–974.
Donatello S, Alberti L, Fiorino A, Degl'Innocenti D, Rizzetti MG, Gorla L et al. (2004). Identification of SH2-Bβ as a RET adaptor protein. Tumori 4: 122.
Duan C, Yang H, White MF, Rui L . (2004). Disruption of the SH2-B gene causes age-dependent insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Mol Cell Biol 24: 7435–7443.
Gorla L, Cantu M, Micciche' F, Patelli C, Mondellini P, Pierotti MA et al. (2006). Ret oncoproteins induce tyrosine phosphorylation changes of proteins involved in RNA metabolism. Cell Signal 18: 2272–2282.
Gryz EA, Meakin SO . (2000). Acidic substitution of the activation loop tyrosines in TrkA supports nerve growth factor-independent cell survival and neuronal differentiation. Oncogene 19: 417–430.
Hennige AM, Lammers R, Hoppner W, Arlt D, Strack V, Teichmann R et al. (2001). Inhibition of Ret oncogene activity by the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP1. Endocrinology 142: 4441–4447.
Hu J, Liu J, Ghirlando R, Saltiel AR, Hubbard SR . (2003). Structural basis for recruitment of the adaptor protein APS to the activated insulin receptor. Mol Cell 12: 1379–1389.
Ichihara M, Murakumo Y, Takahashi M . (2004). RET and neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Lett 204: 197–211.
Kawamoto Y, Takeda K, Okuno Y, Yamakawa Y, Ito Y, Taguchi R et al. (2004). Identification of RET autophosphorylation sites by mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem 279: 14213–14224.
Kong M, Wang CS, Donoghue DJ . (2002). Interaction of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 and the adapter protein SH2-B. A role in STAT5 activation. J Biol Chem 277: 15962–15970.
Kotani K, Wilden P, Pillay TS . (1998). SH2-Balpha is an insulin-receptor adapter protein and substrate that interacts with the activation loop of the insulin-receptor kinase. Biochem J 335: 103–109.
Kurzer JH, Argetsinger LS, Zhou YJ, Kouadio JL, O'Shea JJ, Carter-Su C . (2004). Tyrosine 813 is a site of JAK2 autophosphorylation critical for activation of JAK2 by SH2-B beta. Mol Cell Biol 24: 4557–4570.
Lee RJ, Albanese C, Stenger RJ, Watanabe G, Inghirami G, Haines GK et al. (1999). pp60(v-src) induction of cyclin D1 requires collaborative interactions between the extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38, and Jun kinase pathways. A role for cAMP response element-binding protein and activating transcription factor-2 in pp60(v-src) signaling in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 274: 7341–7350.
Lorenzo MJ, Gish GD, Houghton C, Stonehouse TJ, Pawson T, Ponder BAJ et al. (1997). RET alternate splicing influences the interaction of activated RET with the SH2 and PTB domains of Shc, and the SH2 domain of Grb2. Oncogene 14: 763–771.
Nelms K, O'Neill TJ, Li S, Hubbard SR, Gustafson TA, Paul WE . (1999). Alternative splicing, gene localization, and binding of SH2-B to the insulin receptor kinase domain. Mamm Genome 10: 1160–1167.
O'Brien KB, Argetsinger LS, Diakonova M, Carter-Su C . (2003). YXXL motifs in SH2-Bbeta are phosphorylated by JAK2, JAK1, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor and are required for membrane ruffling. J Biol Chem 278: 11970–11978.
Ohtsuka S, Takaki S, Iseki M, Miyoshi K, Nakagata N, Kataoka Y et al. (2002). SH2-B is required for both male and female reproduction. Mol Cell Biol 22: 3066–3077.
Osborne MA, Dalton S, Kochan JP . (1995). The yeast tribrid system-genetic detection of trans-phosphorylated ITAM-SH2-interactions. Biotechnology 13: 1474–1478.
Qian X, Ginty DD . (2001). SH2-B and APS are multimeric adapters that augment trkA signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21: 1613–1620.
Qian X, Riccio A, Zhang Y, Ginty DD . (1998). Identification and characterization of novel substrates of Trk receptors in developing neurons. Neuron 21: 1017–1029.
Ravichandran KS . (2001). Signaling via Shc family adapter proteins. Oncogene 20: 6322–6330.
Ren D, Li M, Duan C, Rui L . (2005). Identification of SH2-B as a key regulator of leptin sensitivity, energy balance, and body weight in mice. Cell Metab 2: 95–104.
Riedel H, Wang J, Hansen H, Yousaf N . (1997). PSM, an insulin-dependent, pro-rich, PH, SH2 domain containing partner of the insulin receptor. J Biochem (Tokyo) 122: 1105–1113.
Roccato E, Miranda C, Raho G, Pagliardini S, Pierotti MA, Greco A . (2005). Analysis of SHP-1 mediated down-regulation of the TRK-T3 oncoprotein identifies TFG as a novel SHP-1 interacting protein. J Biol Chem 280: 3382–3389.
Rui L, Carter-Su C . (1998). Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates the association of SH2-Bbeta with PDGF receptor and phosphorylation of SH2-Bbeta. J Biol Chem 273: 21239–21245.
Rui L, Carter-Su C . (1999). Identification of SH2-bbeta as a potent cytoplasmic activator of the tyrosine kinase Janus kinase 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 7172–7177.
Rui L, Gunter DR, Herrington J, Carter-Su C . (2000). Differential binding to and regulation of JAK2 by the SH2 domain and N-terminal region of SH2-Bbeta. Mol Cell Biol 20: 3168–3177.
Rui L, Mathews LS, Hotta K, Gustafson TA, Carter-Su C . (1997). Identification of SH2-Bbeta as a substrate of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 involved in growth hormone signaling. Mol Cell Biol 17: 6633–6644.
Takahashi M . (2001). The GDNF/RET signaling pathway and human diseases. Cytokine Growth F 12: 361–373.
Wang J, Riedel H . (1998). Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and insulin receptor association with a Src homology-2 domain-containing putative adapter. J Biol Chem 273: 3136–3139.
Yousaf N, Deng Y, Kang Y, Riedel H . (2001). Four PSM/SH2-B alternative splice variants and their differential roles in mitogenesis. J Biol Chem 276: 40940–40948.
Zhang Y, Zhu W, Wang YG, Liu XJ, Jiao L, Liu X et al. (2006). Interaction of SH2-B{beta} with RET is involved in signaling of GDNF-induced neurite outgrowth. J Cell Sci 119: 1666–1676.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to C Carter-Su (University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) for generously providing SH2B1β cDNA, to J Darnell (The Rockfeller University, New York, NY, USA) for STAT3 and pm674TATAluc constructs, to A Ullrich (Max-Planck-Institut, Martinsried, Germany) for SHP-1 plasmid, to R Possenti (Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy) for pvgf8luc, and R Pestell (Georgetown University, Washington, DC, USA) for pCD1luc reporter. We thank Piera Mondellini for SH2B1β expression studies on thyroid tissues, Marco Cantù for MS analysis, Maria Teresa Radice for technical assistance, Vijay Kumar and Elena Arighi for critical reading of the article. This research was supported by the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) and by the European Community's Sixth Framework Programme under the SIMAP Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donatello, S., Fiorino, A., Degl'Innocenti, D. et al. SH2B1β adaptor is a key enhancer of RET tyrosine kinase signaling. Oncogene 26, 6546–6559 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210480
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210480
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RET signaling in breast cancer therapeutic resistance and metastasis
Breast Cancer Research (2023)
-
Intracellular RET signaling pathways activated by GDNF
Cell and Tissue Research (2020)
-
SH2B1 promotes NSCLC cell proliferation through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade
Cancer Cell International (2018)
-
What model organisms and interactomics can reveal about the genetics of human obesity
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2012)