Abstract
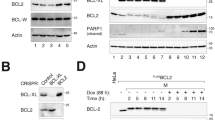
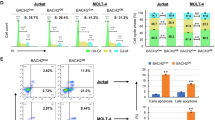
BCL2 expression is finely tuned by a variety of environmental and endogenous stimuli and regulated at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Our previous investigations demonstrated that the BCL2 major breakpoint region (mbr) in the 3′-UTR upregulates reporter gene expression, which implies that this region possessed intrinsic regulatory function. However, the effect of the mbr on BCL2 expression, and the underlying regulatory mechanisms, remain to be elucidated. To assess the direct effect of the mbr on the transcriptional activity of the BCL2 gene, we employed targeted homologous recombination to establish a mbr+/mbr− heterozygous Nalm-6 cell line and then compared the transcriptional activity and apoptotic effect on transcription between the wild type and targeted alleles. We found that deletion of the mbr significantly decreased the transcriptional activity of the corresponding allele in the mbr+/mbr− cell. The BCL2 allele deleted of the mbr had a slower response to apoptotic stimuli than did the wild type allele. The regulatory function of the mbr was mediated through SATB1. Overexpression of SATB1 increased BCL2 expression, while knockdown of SATB1 with RNAi decreased BCL2 expression. Our results clearly indicated that the mbr could positively regulate BCL2 gene expression and this regulatory function was closely related to SATB1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- mbr:
-
major breakpoint region
- SATB1:
-
special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 1
- MAR:
-
matrix attachment region
- CRE:
-
cAMP responsive element
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-kappa B
- UTR:
-
untranslated region
- EMSA:
-
electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- DT:
-
diphtheria-toxin
References
Adams JM, Huang DC, Puthalakath H, Bouillet P, Vairo G, Moriishi K et al. (1999). Control of apoptosis in hematopoietic cells by the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 64: 351–358.
Alvarez JD, Yasui DH, Niida H, Joh T, Loh DY, Kohwi-Shigematsu T . (2000). The MAR-binding protein SATB1 orchestrates temporal and spatial expression of multiple genes during T-cell development. Genes Dev 14: 521–535.
Chen DF, Schneider GE, Martinou JC, Tonegawa S . (1997). Bcl-2 promotes regeneration of severed axons in mammalian CNS. Nature 385: 434–439.
Chen HM, Boxer LM . (1995). Pi 1 binding sites are negative regulators of bcl-2 expression in pre-B cells. Mol Cell Biol 15: 3840–3847.
Chen M, Quintans J, Fuks Z, Thompson C, Kufe DW, Weichselbaum RR . (1995). Suppression of Bcl-2 messenger RNA production may mediate apoptosis after ionizing radiation, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and ceramide. Cancer Res 55: 991–994.
Delic J, Onclercq R, Moisan-Coppey M . (1991). Inhibition and enhancement of eukaryotic gene expression by potential non-B DNA sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181: 818–826.
Dickinson LA, Joh T, Kohwi Y, Kohwi-Shigematsu T . (1992). A tissue-specific MAR/SAR DNA-binding protein with unusual binding site recognition. Cell 70: 631–645.
DiCroce PA, Krontiris TG . (1995). The BCL2 major breakpoint region is a sequence- and cell-cycle-specific binding site of the Ku antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 10137–10141.
Donnini M, Lapucci A, Papucci L, Witort E, Jacquier A, Brewer G et al. (2004). Identification of TINO: a new evolutionarily conserved BCL-2 AU-rich element RNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem 279: 20154–20166.
Grawunder U, Zimmer D, Fugmann S, Schwarz K, Lieber MR . (1998). DNA ligase IV is essential for V(D)J recombination and DNA double-strand break repair in human precursor lymphocytes. Mol Cell 2: 477–484.
Grigoriev M, Praseuth D, Robin P, Hemar A, Saison-Behmoaras T, Dautry-Varsat A et al. (1992). A triple helix-forming oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugate acts as a transcriptional repressor via inhibition of NF kappa B binding to interleukin-2 receptor alpha-regulatory sequence. J Biol Chem 267: 3389–3395.
Heckman CA, Mehew JW, Boxer LM . (2002). NF-kappaB activates Bcl-2 expression in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. Oncogene 21: 3898–3908.
Heckman CA, Mehew JW, Ying GG, Introna M, Golay J, Boxer LM . (2000). A-Myb up-regulates Bcl-2 through a Cdx binding site in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem 275: 6499–6508.
Hockenbery D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ . (1990). Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature 348: 334–336.
Kato M, Shimizu N . (1992). Effect of the potential triplex DNA region on the in vitro expression of bacterial beta-lactamase gene in superhelical recombinant plasmids. J Biochem (Tokyo) 112: 492–494.
Kohwi Y, Kohwi-Shigematsu T . (1991). Altered gene expression correlates with DNA structure. Genes Dev 5: 2547–2554.
Lang G, Gombert WM, Gould HJ . (2005). A transcriptional regulatory element in the coding sequence of the human Bcl-2 gene. Immunology 114: 25–36.
Miyashita T, Harigai M, Hanada M, Reed JC . (1994). Identification of a p53-dependent negative response element in the bcl-2 gene. Cancer Res 54: 3131–3135.
Narla RK, Dong Y, Uckun FM . (2001). Apoptosis inducing novel anti-leukemic agent, bis(4,7-dimethyl-1,10 phenanthroline) sulfatooxovanadium(IV) [VO(SO4)(Me2-Phen)2] depolarizes mitochondrial membranes. Leuk Lymphoma 41: 625–634.
Patrone G, Puppo F, Cusano R, Scaranari M, Ceccherini I, Puliti A et al. (2000). Nuclear run-on assay using biotin labeling, magnetic bead capture and analysis by fluorescence-based RT-PCR. Biotechniques 29: 1012–1014, 1016–1017.
Perillo B, Sasso A, Abbondanza C, Palumbo G . (2000). 17beta-estradiol inhibits apoptosis in MCF-7 cells, inducing bcl-2 expression via two estrogen-responsive elements present in the coding sequence. Mol Cell Biol 20: 2890–2901.
Raghavan SC, Chastain P, Lee JS, Hegde BG, Houston S, Langen R et al. (2005). Evidence for a triplex DNA conformation at the bcl-2 major breakpoint region of the t(14;18) translocation. J Biol Chem 280: 22749–22760.
Ramakrishnan M, Liu WM, DiCroce PA, Posner A, Zheng J, Kohwi-Shigematsu T et al. (2000). Modulated binding of SATB1, a matrix attachment region protein, to the AT-rich sequence flanking the major breakpoint region of BCL2. Mol Cell Biol 20: 868–877.
Sato N, Hotta K, Waguri S, Nitatori T, Tohyama K, Tsujimoto Y et al. (1994). Neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells as a result of prevention of cell death by bcl-2. J Neurobiol 25: 1227–1234.
Schiavone N, Rosini P, Quattrone A, Donnini M, Lapucci A, Citti L et al. (2000). A conserved AU-rich element in the 3′-untranslated region of bcl-2 mRNA is endowed with a destabilizing function that is involved in bcl-2 down-regulation during apoptosis. FASEB J 14: 174–184.
Sun Y, Wang T, Su Y, Yin Y, Xu S, Ma C, Han X . (2006). The behavior of SATB1, a MAR-binding protein, in response to apoptosis stimulation. Cell Biol Int 30: 244–247.
Suzuki A, Matsuzawa A, Iguchi T . (1996). Down regulation of Bcl-2 is the first step on Fas-mediated apoptosis of male reproductive tract. Oncogene 13: 31–37.
Tong X, Yin L, Joshi S, Rosenberg DW, Giardina C . (2005). Cyclooxygenase-2 regulation in colon cancer cells: modulation of RNA polymerase II elongation by histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 280: 15503–15509.
Tsurusawa M, Saeki K, Fujimoto T . (1997). Differential induction of apoptosis on human lymphoblastic leukemia Nalm-6 and Molt-4 cells by various antitumor drugs. Int J Hematol 66: 79–88.
van Holde K, Zlatanova J . (1994). Unusual DNA structures, chromatin and transcription. Bioessays 16: 59–68.
Wilson BE, Mochon E, Boxer LM . (1996). Induction of bcl-2 expression by phosphorylated CREB proteins during B-cell activation and rescue from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 16: 5546–5556.
Wu Y, Mehew JW, Heckman CA, Arcinas M, Boxer LM . (2001). Negative regulation of bcl-2 expression by p53 in hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 20: 240–251.
Yasui D, Miyano M, Cai S, Varga-Weisz P, Kohwi-Shigematsu T . (2002). SATB1 targets chromatin remodelling to regulate genes over long distances. Nature 419: 641–645.
Young RL, Korsmeyer SJ . (1993). A negative regulatory element in the bcl-2 5′-untranslated region inhibits expression from an upstream promoter. Mol Cell Biol 13: 3686–3697.
Zhang J, Ma C, Han X, Durrin LK, Sun Y . (2006). The bcl-2 major breakpoint region (mbr) possesses transcriptional regulatory function. Gene 379: 127–131.
Zhang MX, Ou H, Shen YH, Wang J, Wang J, Coselli J et al. (2005). Regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by small RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 16967–16972.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Krontiris for his kind help in this work. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30371592), the Nature Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2003003), the Special Funds for Major State Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2006CB503908) and Opening Foundation from Jiangsu key laboratory for molecular and medical biotechnology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, C., Zhang, J., Durrin, L. et al. The BCL2 major breakpoint region (mbr) regulates gene expression. Oncogene 26, 2649–2657 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210069
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210069
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Specific-detection of clinical samples, systematic functional investigations, and transcriptome analysis reveals that splice variant MUC4/Y contributes to the malignant progression of pancreatic cancer by triggering malignancy-related positive feedback loops signaling
Journal of Translational Medicine (2014)
-
Inhibition of human glioma U251 cells growth in vitro and in vivo by hydroxyapatite nanoparticle-assisted delivery of short hairpin RNAs against SATB1
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
Upregulation of SATB1 is associated with the development and progression of glioma
Journal of Translational Medicine (2012)
-
Coexpression of Bcl-2 with epithelial–mesenchymal transition regulators is a prognostic indicator in hepatocellular carcinoma
Medical Oncology (2012)
-
Hypoxia-induced vasculogenic mimicry formation via VE-cadherin regulation by Bcl-2
Medical Oncology (2012)