Abstract
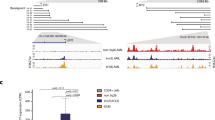
In t(14;18) lymphomas, bcl-2 is juxtaposed to the immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene (IgH), resulting in increased bcl-2 transcription and resistance to apoptosis. Regulatory elements of both the bcl-2 promoter and the IgH enhancers are believed to play a role in the increased expression of bcl-2 in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. In addition, transcription of the translocated bcl-2 allele is deregulated with activation of the normally minor bcl-2 P2 promoter. The mechanisms involved in the promoter shift from P1 to P2 are not known. We found that the murine IgH 3′ enhancers increased bcl-2 P2 promoter activity in an episomal model of the translocation, and IgH enhancer region HS12 had the greatest effect. Quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays revealed that localized histone H3 hyperacetylation of the P2 promoter was observed on the translocated allele in t(14;18) DHL-4 cells and also on the stably transfected bcl-2 promoter-IgH enhancer episomal construct. Analysis of the HS12 enhancer region revealed that a previously identified nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) site and a previously uncharacterized downstream Cdx site, both of which are conserved in the human and murine IgH enhancers, were important for its enhancer activity and promoter activation. ChIP assays showed that C/EBPβ bound to the HS12 Cdx site in vivo, and mutation of this site abrogated the binding of C/EBPβ. Reduced expression of C/EBPβ by transfection of small interfering RNA or interference with NF-κB activity decreased transcription from the bcl-2 promoters. These results demonstrate that the IgH 3′ enhancers, particularly HS12, are important for the deregulation of bcl-2 promoter usage in t(14;18) lymphomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cleary ML, Smith SD, Sklar J . (1986). Cloning and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18) translocation. Cell 47: 19–28.
Decary S, Decesse JT, Ogryzko V, Reed JC, Naguibneva I, Harel-Bellan A et al. (2002). The retinoblastoma protein binds the promoter of the survival gene bcl-2 and regulates its transcription in epithelial cells through transcription factor AP-2. Mol Cell Biol 22: 7877–7888.
Desoize B . (1994). Anticancer drug resistance and inhibition of apoptosis. Anticancer Res 14: 2291–2294.
Duan H, Heckman CA, Boxer LM . (2005). HDAC inhibitors down-regulate Bcl-2 expression and induce apoptosis in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 25: 1608–1619.
Heckman CA, Cao T, Somsouk L, Duan H, Mehew JW, Zhang C et al. (2003a). Critical elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancers for deregulated expression of bcl-2. Cancer Res 63: 6666–6673.
Heckman CA, Mehew JW, Boxer LM . (2002). NF-κB activates bcl-2 expression in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. Oncogene 21: 3898–3908.
Heckman CA, Wheeler MA, Boxer LM . (2003b). Regulation of bcl-2 by C/EBP in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. Oncogene 22: 7891–7899.
Hockenberry D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ . (1990). Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature 348: 334–336.
Ji L, Mochon E, Arcinas M, Boxer LM . (1996). CREB proteins function as positive regulators of the translocated bcl-2 allele in t(14;18) lymphomas. J Biol Chem 271: 22687–22691.
Khamlichi AA, Pinaud E, Decourt C, Chauveau C, Cogne M . (2000). The 3′ regulatory region: a complex structure in a search for a function. Adv Immunol 75: 317–345.
Krumm A, Hickey LB, Groudine M . (1995). Promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II defines a general rate-limiting step after transcription initiation. Genes Dev 9: 559–572.
Krumm A, Madisen L, Yang XJ, Goodman R, Nakatani Y, Groudine M . (1998). Long-distance transcriptional enhancement by the histone acetyltransferase PCAF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 13501–13506.
Madisen L, Groudine M . (1994). Identification of a locus control region in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus that deregulates c-myc expression in plasmacytoma and Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Genes Dev 8: 2212–2226.
Madisen L, Krumm A, Hebber TR, Groudine M . (1998). The immunoglobulin heavy chain locus control region increases histone acetylation along linked c-myc genes. Mol Cell Biol 18: 6281–6292.
Reed JC, Kitada S, Takayama S, Miyashita T . (1994). Regulation of chemoresistance by the bcl-2 oncoprotein in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and lymphocytic leukemia cell lines. Ann Oncol 5 (Suppl 1): S61–S65.
Schmitt CA, Lowe SW . (2001). Bcl-2 mediates chemoresistance in matched pairs of primary Eμ-myc lymphomas in vivo. Blood Cells Mol Dis 27: 206–216.
Seto M, Jaeger U, Hockett RD, Graninger W, Bennett S, Goldman P et al. (1988). Alternative promoters and exons, somatic mutation and deregulation of the bcl-2-Ig fusion gene in lymphoma. EMBO J 7: 123–131.
Tsujimoto Y, Gorham J, Cossman J, Jaffe E, Croce CM . (1985). The t(14;18) chromosome translocations involved in B-cell neoplasms result from mistakes in VDJ joining. Science 229: 1390–1393.
Wu Y, Mehew JW, Heckman CA, Arcinas M, Boxer LM . (2001). Negative regulation of bcl-2 expression by p53 in hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 20: 240–251.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health Grant CA56764.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, H., Heckman, C. & Boxer, L. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene 3′ enhancers deregulate bcl-2 promoter usage in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. Oncogene 26, 2635–2641 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210061
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210061
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inter- and intratumoral heterogeneity of BCL2 correlates with IgH expression and prognosis in follicular lymphoma
Blood Cancer Journal (2014)
-
The immunoglobulin heavy chain gene 3′ enhancers induce Bcl2 deregulation and lymphomagenesis in murine B cells
Leukemia (2011)
-
Functional long-range interactions of the IgH 3′ enhancers with the bcl-2 promoter region in t(14;18) lymphoma cells
Oncogene (2008)