Abstract
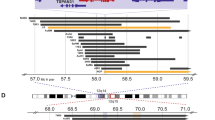
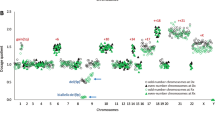
The molecular pathogenesis of pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA), a rare astrocytic brain tumor with a relatively favorable prognosis, is still poorly understood. We characterized 50 PXAs by comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and found the most common imbalance to be loss on chromosome 9 in 50% of tumors. Other recurrent losses affected chromosomes 17 (10%), 8, 18, 22 (4% each). Recurrent gains were identified on chromosomes X (16%), 7, 9q, 20 (8% each), 4, 5, 19 (4% each). Two tumors demonstrated amplifications mapping to 2p23–p25, 4p15, 12q13, 12q21, 21q21 and 21q22. Analysis of 10 PXAs with available high molecular weight DNA by high-resolution array-based CGH indicated homozygous 9p21.3 deletions involving the CDKN2A/p14ARF/CDKN2B loci in six tumors (60%). Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization to tissue sections confirmed the presence of tumor cells with homozygous 9p21.3 deletions. Mutational analysis of candidate genes on 9q, PTCH and TSC1, revealed no mutations in PXAs with 9q loss and no evidence of TSC1 promoter methylation. However, PXAs consistently showed low TSC1 transcript levels. Taken together, our study identifies loss of chromosome 9 as the most common chromosomal imbalance in PXAs and suggests important roles for homozygous CDKN2A/p14ARF/CDKN2B deletion as well as low TSC1 mRNA expression in these tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker AJ, Lobach M, Klein H, Normann S, Nothen MM, von Deimling A et al. (2001). Mutational analysis of TSC1 and TSC2 genes in gangliogliomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 27: 105–114.
du Manoir S, Speicher MR, Joos S, Schrock E, Popp S, Dohner H et al. (1993). Detection of complete and partial chromosome gains and losses by comparative genomic in situ hybridization. Hum Genet 90: 590–610.
Giannini C, Hebrink D, Scheithauer BW, Dei Tos AP, James CD . (2001). Analysis of p53 mutation and expression in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Neurogenetics 3: 159–162.
Giannini C, Scheithauer BW, Burger PC, Brat DJ, Wollan PC, Lach B et al. (1999). Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: what do we really know about it? Cancer 85: 2033–2045.
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A et al. (1996). Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell 85: 841–851.
Harris SL, Levine AJ . (2005). The p53 pathway: positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene 24: 2899–2908.
Jiang WG, Sampson J, Martin TA, Lee-Jones L, Watkins G, Douglas-Jones A et al. (2005). Tuberin and hamartin are aberrantly expressed and linked to clinical outcome in human breast cancer: the role of promoter methylation of TSC genes. Eur J Cancer 41: 1628–1636.
Kallioniemi A, Kallioniemi OP, Sudar D, Rutovitz D, Gray JW, Waldman F et al. (1992). Comparative genomic hybridization for molecular cytogenetic analysis of solid tumors. Science 258: 818–821.
Kaulich K, Blaschke B, Numann A, von Deimling A, Wiestler OD, Weber RG et al. (2002). Genetic alterations commonly found in diffusely infiltrating cerebral gliomas are rare or absent in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61: 1092–1099.
Kepes JJ, Louis DN, Giannini C, Paulus W . (2000). Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK (eds). World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. IARC Press: Lyon, pp. 52–54.
Knowles MA, Habuchi T, Kennedy W, Cuthbert-Heavens D . (2003). Mutation spectrum of the 9q34 tuberous sclerosis gene TSC1 in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Res 63: 7652–7656.
Li YS, Ramsay DA, Fan YS, Armstrong RF, Del Maestro RF . (1995). Cytogenetic evidence that a tumor suppressor gene in the long arm of chromosome 1 contributes to glioma growth. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 84: 46–50.
Lichter P, Bentz M, Joos S . (1995). Detection of chromosomal aberrations by means of molecular cytogenetics: painting of chromosomes and chromosomal subregions and comparative genomic hybridization. Methods Enzymol 254: 334–359.
Long X, Lin Y, Ortiz-Vega S, Yonezawa K, Avruch J . (2005). Rheb binds and regulates the mTOR kinase. Curr Biol 15: 702–713.
Möllemann M, Wolter M, Felsberg J, Collins VP, Reifenberger G . (2005). Frequent promoter hypermethylation and low expression of the MGMT gene in oligodendroglial tumors. Int J Cancer 113: 379–385.
Paulus W, Lisle DK, Tonn JC, Wolf HK, Roggendorf W, Reeves SA et al. (1996). Molecular genetic alterations in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) 91: 293–297.
Pei XH, Xiong Y . (2005). Biochemical and cellular mechanisms of mammalian CDK inhibitors: a few unresolved issues. Oncogene 24: 2787–2795.
Pinkel D, Segraves R, Sudar D, Clark S, Poole I, Kowbel D et al. (1998). High resolution analysis of DNA copy number variation using comparative genomic hybridization to microarrays. Nat Genet 20: 207–211.
Reifenberger G, Collins VP . (2004). Pathology and molecular genetics of astrocytic gliomas. J Mol Med 82: 656–670.
Reifenberger G, Kaulich K, Wiestler OD, Blumcke I . (2003). Expression of the CD34 antigen in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) 105: 358–364.
Reifenberger J, Ring GU, Gies U, Cobbers L, Oberstrass J, An HX et al. (1996). Analysis of p53 mutation and epidermal growth factor receptor amplification in recurrent gliomas with malignant progression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55: 822–831.
Reifenberger J, Wolter M, Knobbe CB, Kohler B, Schonicke A, Scharwachter C et al. (2005). Somatic mutations in the PTCH, SMOH, SUFUH and TP53 genes in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Br J Dermatol 152: 43–51.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (eds) (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Sawyer JR, Roloson GJ, Chadduck WM, Boop FA . (1991). Cytogenetic findings in a pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 55: 225–230.
Sawyer JR, Thomas EL, Roloson GJ, Chadduck WM, Boop FA . (1992). Telomeric associations evolving to ring chromosomes in a recurrent pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 60: 152–157.
Schwaenen C, Nessling M, Wessendorf S, Salvi T, Wrobel G, Radlwimmer B et al. (2004). Automated array-based genomic profiling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: development of a clinical tool and discovery of recurrent genomic alterations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 1039–1044.
Solinas-Toldo S, Lampel S, Stilgenbauer S, Nickolenko J, Benner A, Dohner H et al. (1997). Matrix-based comparative genomic hybridization: biochips to screen for genomic imbalances. Gene Chromosome Canc 20: 399–407.
van den Boom J, Wolter M, Kuick R, Misek DE, Youkilis AS, Wechsler DS et al. (2003). Characterization of gene expression profiles associated with glioma progression using oligonucleotide-based microarray analysis and real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Am J Pathol 163: 1033–1043.
van Slegtenhorst M, de Hoogt R, Hermans C, Nellist M, Janssen B, Verhoef S et al. (1997). Identification of the tuberous sclerosis gene TSC1 on chromosome 9q34. Science 277: 805–808.
Weber RG, Sabel M, Reifenberger J, Sommer C, Oberstrass J, Reifenberger G et al. (1996). Characterization of genomic alterations associated with glioma progression by comparative genomic hybridization. Oncogene 13: 983–994.
Yin XL, Hui AB, Liong EC, Ding M, Chang AR, Ng HK . (2002). Genetic imbalances in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma detected by comparative genomic hybridization and literature review. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 132: 14–19.
Zielinski B, Gratias S, Toedt G, Mendrzyk F, Stange DE, Radlwimmer B et al. (2005). Detection of chromosomal imbalances in retinoblastoma by matrix-based comparative genomic hybridization. Gene Chromosome Canc 43: 294–301.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe (10-1639-Re3; 70-3163-Wi3), the German Ministry for Education and Research (National Network for Genome Research, NGFN-2) and the BONFOR program of the Medical Faculty, Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-University, Bonn (O-149.0058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, R., Hoischen, A., Ehrler, M. et al. Frequent loss of chromosome 9, homozygous CDKN2A/p14ARF/CDKN2B deletion and low TSC1 mRNA expression in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas. Oncogene 26, 1088–1097 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209851
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209851
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Correlation of MTAP immunohistochemical deficiency with CDKN2A homozygous deletion and clinicopathological features in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Brain Tumor Pathology (2023)
-
The evolution of pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: from genesis to molecular alterations and mimics
Laboratory Investigation (2022)
-
Long Non-coding RNA and mRNA Co-expression Network Reveals Novel Players in Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma
Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma is a heterogeneous entity with pTERT mutations prognosticating shorter survival
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2022)
-
Low-grade developmental and epilepsy associated brain tumors: a critical update 2020
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2020)