Abstract
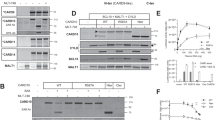
Crk-associated substrate lymphocyte type (Cas-L) is a 105 kDa docking protein with diverse functional properties, including regulation of cell division, proliferation, migration and adhesion. Cas-L is also involved in β1 integrin- or antigen receptor-mediated signaling in B and T cells. In the present study, we demonstrate that Cas-L potentiates transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway by interacting with Smad6 and Smad7. Immunoprecipitation experiments reveal that single domain deletion of full-length Cas-L completely abolishes its docking function with Smad6 and Smad7, suggesting that the natural structure of Cas-L is necessary for its association with Smad6 and Smad7. On the other hand, both N-terminal and C-terminal deletion mutants of Smad6 and Smad7 still retain their docking ability to Cas-L, suggesting that Smad6 and Smad7 possess several binding motifs to Cas-L. Moreover, Cas-L interaction with Mad-homology (MH)2 domain, but not with MH1 domain of Smad6 or Smad7, ameliorates TGF-β-induced signaling pathway. Finally, depletion of Cas-L by small-interfering RNA oligo attenuates TGF-β-induced growth inhibition of Huh-7 cells, with a concomitant reduction in phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3. These results strongly suggest that Cas-L is a potential regulator of TGF-β signaling pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Abbreviations
- Cas-L:
-
Crk-associated substrate lymphocyte type
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor β
References
Astier A, Manié SN, Law SF, Canty T, Haghayghi N, Druker BJ et al. (1997). Association of the Cas-like molecule HEF1 with CrkL following integrin and antigen receptor signaling in human B-cells: potential relevance to neoplastic lymphohematopoietic cells. Leuk Lymphoma 28: 65–72.
Bartel P, Chien CT, Sternglanz R, Fields S . (1993). Elimination of false positives that arise in using the two-hybrid system. Biotechniques 14: 920–924.
Cárcamo J, Weis FM, Ventura F, Wieser R, Wrana JL, Attisano L et al. (1994). Type I receptors specify growth-inhibitory and transcriptional responses to transforming growth factor beta and activin. Mol Cell Biol 14: 3810–3821.
Chacko BM, Qin BY, Tiwari A, Shi G, Lam S, Hayward LJ et al. (2004). Structural basis of heteromeric smad protein assembly in TGF-beta signaling. Mol Cell 15: 813–823.
Datta PK, Moses HL . (2000). STRAP and Smad7 synergize in the inhibition of transforming growth factor beta signaling. Mol Cell Biol 20: 3157–3167.
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A . (2001). TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat Genet 29: 117–129.
Derynck R, Zhang YE . (2003). Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 425: 577–584.
Fashena SJ, Einarson MB, O’Neill GM, Patriotis C, Golemis EA . (2002). Dissection of HEF1-dependent functions in motility and transcriptional regulation. J Cell Sci 115: 99–111.
Grönroos E, Hellman U, Heldin CH, Ericsson J . (2002). Control of Smad7 stability by competition between acetylation and ubiquitination. Mol Cell 10: 483–493.
Hanyu A, Ishidou Y, Ebisawa T, Shimanuki T, Imamura T, Miyazono K . (2001). The N domain of Smad7 is essential for specific inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Cell Biol 155: 1017–1027.
Hayashi H, Abdollah S, Qiu Y, Cai J, Xu YY, Grinnell BW et al. (1997). The MAD-related protein Smad7 associates with the TGFbeta receptor and functions as an antagonist of TGFbeta signaling. Cell 89: 1165–1173.
Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P . (1997). TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 390: 465–471.
Hynes RO . (1992). Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69: 11–25.
Ito Y, Zhao J, Mogharei A, Shuler CF, Weinstein M, Deng C et al. (2001). Antagonistic effects of Smad2 versus Smad7 are sensitive to their expression level during tooth development. J Biol Chem 276: 44163–44172.
Iwata S, Souta-Kuribara A, Yamakawa A, Sasaki T, Shimizu T, Hosono O et al. (2005). HTLV-I Tax induces and associates with Crk-associated substrate lymphocyte type (Cas-L). Oncogene 24: 1262–1271.
Juliano RL, Haskill S . (1993). Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol 120: 577–585.
Kamiguchi K, Tachibana K, Iwata S, Ohashi Y, Morimoto C . (1999). Cas-L is required for beta 1 integrin-mediated costimulation in human Tcells. J Immunol 163: 563–568.
Kato Y, Habas R, Katsuyama Y, Näär AM, He X . (2002). A component of the ARC/Mediator complex required for TGF beta/Nodal signalling. Nature 418: 641–646.
Krishnan P, King MW, Neff AW, Sandusky GE, Bierman KL, Grinnell B et al. (2001). Human truncated Smad 6 (Smad 6s) inhibits the BMP pathway in Xenopus laevis. Dev Growth Differ 43: 115–132.
Law SF, Estojak J, Wang B, Mysliwiec T, Kruh G, Golemis EA . (1996). Human enhancer of filamentation 1, a novel p130cas-like docking protein, associates with focal adhesion kinase and induces pseudohyphal growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 16: 3327–3337.
Law SF, O’Neill GM, Fashena SJ, Einarson MB, Golemis EA . (2000). The docking protein HEF1 is an apoptotic mediator at focal adhesion sites. Mol Cell Biol 20: 5184–5195.
Lee HY, Chun KH, Liu B, Wiehle SA, Cristiano RJ, Hong WK et al. (2002). Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 inhibits the growth of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 62: 3530–3537.
Li L, Elledge SJ, Peterson CA, Bales ES, Legerski RJ . (1994). Specific association between the human DNA repair proteins XPA and ERCC1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 5012–5016.
Liu X, Elia AE, Law SF, Golemis EA, Farley J, Wang T . (2000). A novel ability of Smad3 to regulate proteasomal degradation of a Cas family member HEF1. EMBO J 19: 6759–6769.
Minegishi M, Tachibana K, Sato T, Iwata S, Nojima Y, Morimoto C . (1996). Structure and function of Cas-L, a 105-kD Crk-associated substrate-related protein that is involved in beta 1 integrin-mediated signaling in lymphocytes. J Exp Med 184: 1365–1375.
Miyake-Nishijima R, Iwata S, Saijo S, Kobayashi H, Kobayashi S, Souta-Kuribara A et al. (2003). Role of Crk-associated substrate lymphocyte type in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis in tax transgenic mice and in humans. Arthritis Rheum 48: 1890–1900.
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Morén A, Nakayama T, Christian JL, Heuchel R et al. (1997). Identification of Smad7, a TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of TGF-beta signalling. Nature 389: 631–635.
Ohashi Y, Iwata S, Kamiguchi K, Morimoto C . (1999). Tyrosine phosphorylation of Crk-associated substrate lymphocyte-type is a critical element in TCR- and beta 1 integrin-induced T lymphocyte migration. J Immunol 163: 3727–3734.
Ohashi Y, Tachibana K, Kamiguchi K, Fujita H, Morimoto C . (1998). T cell receptor-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of Cas-L, a 105-kDa Crk-associated substrate-related protein, and its association of Crk and C3G. J Biol Chem 273: 6446–6451.
Ohnuma K, Yamochi T, Uchiyama M, Nishibashi K, Yoshikawa N, Shimizu N et al. (2004). CD26 up-regulates expression of CD86 on antigen-presenting cells by means of caveolin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 14186–14191.
Pugacheva EN, Golemis EA . (2005). The focal adhesion scaffolding protein HEF1 regulates activation of the Aurora-A and Nek2 kinases at the centrosome. Nat Cell Biol 7: 937–946.
Sasaki T, Iwata S, Okano HJ, Urasaki Y, Hamada J, Tanaka H et al. (2005). Nedd9 protein, a Cas-L homologue, is upregulated after transient global ischemia in rats: possible involvement of Nedd9 in the differentiation of neurons after ischemia. Stroke 36: 2457–2462.
Seo S, Asai T, Saito T, Suzuki T, Morishita Y, Nakamoto T et al. (2005). Crk-associated substrate lymphocyte type is required for lymphocyte trafficking and marginal zone B cell maintenance. J Immunol 175: 3492–3501.
Sugano Y, Matsuzaki K, Tahashi Y, Furukawa F, Mori S, Yamagata H et al. (2003). Distortion of autocrine transforming growth factor beta signal accelerates malignant potential by enhancing cell growth as well as PAI-1 and VEGF production in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene 22: 2309–2321.
Tachibana K, Urano T, Fujita H, Ohashi Y, Kamiguchi K, Iwata S et al. (1997). Tyrosine phosphorylation of Crk-associated substrates by focal adhesion kinase. A putative mechanism for the integrin-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of Crk-associated substrates. J Biol Chem 272: 29083–29090.
Tanaka J, Miwa Y, Miyoshi K, Ueno A, Inoue H . (1999). Construction of Epstein–Barr virus-based expression vector containing mini-oriP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 264: 938–943.
van Seventer GA, Salmen HJ, Law SF, O’Neill GM, Mullen MM, Franz AM et al. (2001). Focal adhesion kinase regulates beta1 integrin-dependent T cell migration through an HEF1 effector pathway. Eur J Immunol 31: 1417–1427.
Vojtek AB, Hollenberg SM, Cooper JA . (1993). Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell 74: 205–214.
Xu L, Chen YG, Massagué J . (2000a). The nuclear import function of Smad2 is masked by SARA and unmasked by TGFbeta-dependent phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol 2: 559–562.
Xu W, Angelis K, Danielpour D, Haddad MM, Bischof O, Campisi J et al. (2000b). Ski acts as a co-repressor with Smad2 and Smad3 to regulate the response to type beta transforming growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 5924–5929.
Yagil C, Hubner N, Monti J, Schulz H, Sapojnikov M, Luft FC et al. (2005). Identification of hypertension-related genes through an integrated genomic-transcriptomic approach. Circ Res 96: 617–625.
Zhang Z, Baron R, Horne WC . (2000). Integrin engagement, the actin cytoskeleton, and c-Src are required for the calcitonin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and HEF1, but not for calcitonin-induced Erk1/2 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 275: 37219–37223.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid of Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture (CM), and Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, Japan (CM). T I is the recipients of a grant from Osaka Kidney Foundation (OKF05-0002), and The Yasuda Medical Foundation. We are thankful to Dr Takeshi Imamura (Department of Biochemistry, The JFCR Cancer Institute, Tokyo, Japan), and Dr Kohei Miyazono (Department of Molecular Pathology, Graduate School of Medicine, University of Tokyo, Japan) for providing us with constructs essential for the present work. We also thank Mr Hiroyuki Kayo for his technical assistance and advices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inamoto, S., Iwata, S., Inamoto, T. et al. Crk-associated substrate lymphocyte type regulates transforming growth factor-β signaling by inhibiting Smad6 and Smad7. Oncogene 26, 893–904 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209848
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209848
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The WW-HECT protein Smurf2 interacts with the Docking Protein NEDD9/HEF1 for Aurora A activation
Cell Division (2010)
-
Molecular basis for HEF1/NEDD9/Cas-L action as a multifunctional co-ordinator of invasion, apoptosis and cell cycle
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2007)