Abstract
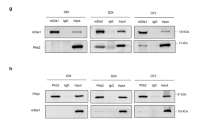
The E2A proteins are basic helix–loop–helix transcription factors that regulate proliferation and differentiation in many cell types. In muscle cells, the E2A proteins form heterodimers with muscle regulatory factors such as MyoD, which then bind to DNA and regulate the transcription of target genes essential for muscle differentiation. We now demonstrate that E2A proteins are primarily localized in the nucleus in both C2C12 myoblasts and myotubes, and are degraded by the ubiquitin proteasome system evidenced by stabilization following treatment with the proteasome inhibitor, MG132. During the differentiation from myoblast to myotube, the cellular abundance of E2A proteins is relatively unaltered, despite significant changes (each ∼5-fold) in the relative rates of protein synthesis and protein degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. The rate of ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated E2A protein degradation depends on the myogenic differentiation state (t½∼2 h in proliferating myoblasts versus t½>10 h in differentiated myotubes), and is also associated with cell cycle in non-muscle cells. Our findings reveal an important role for both translational and post-translational regulatory mechanisms in mediating the complex program of muscle differentiation determined by the E2A proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronheim A, Shiran R, Rosen A, Walker MD . (1993). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 8063–8067.
Bain G, Maandag EC, Izon DJ, Amsen D, Kruisbeek AM, Weintraub BC et al. (1994). Cell 79: 885–892.
Coulombe P, Rodier G, Pelletier S, Pellerin J, Meloche S . (2003). Mol Cell Biol 23: 4542–4558.
Dearth LR, DeWille J . (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 11246–11255.
Deed RW, Armitage S, Norton JD . (1996). J Biol Chem 271: 23603–23606.
Guillemot F, Lo LC, Johnson JE, Auerbach A, Anderson DJ, Joyner AL . (1993). Cell 75: 463–476.
Hsu HL, Cheng JT, Chen Q, Baer R . (1991). Mol Cell Biol 11: 3037–3042.
Huggins GS, Chin MT, Sibinga NE, Lee SL, Haber E, Lee ME . (1999). J Biol Chem 274: 28690–28696.
Kho CJ, Huggins GS, Endege WO, Hsieh CM, Lee ME, Haber E . (1997). J Biol Chem 272: 3845–3851.
Langlands K, Yin X, Anand G, Prochownik EV . (1997). J Biol Chem 272: 19785–19793.
Lassar AB, Davis RL, Wright WE, Kadesch T, Murre C, Voronova A et al. (1991). Cell 66: 305–315.
Lazorchak A, Jones ME, Zhuang Y . (2005). Trends Immunol 26: 334–338.
Lingbeck JM, Trausch-Azar JS, Ciechanover A, Schwartz AL . (2005). Oncogene 24: 6376–6384.
Lluis F, Ballestar E, Suelves M, Esteller M, Munoz-Canoves P . (2005). EMBO J 24: 974–984.
Nie L, Xu M, Vladimirova A, Sun XH . (2003). EMBO J 22: 5780–5792.
Peverali FA, Ramqvist T, Saffrich R, Pepperkok R, Barone MV, Philipson L . (1994). EMBO J 13: 4291–4301.
Quong MW, Romanow WJ, Murre C . (2002). Annu Rev Immunol 20: 301–322.
Riera L, Obach M, Navarro-Sabate A, Duran J, Perales J C, Vinals F et al. (2003). FEBS Lett 550: 23–29.
Riley RL, Van der Put E, King AM, Frasca D, Blomberg BB . (2005). Semin Immunol 17: 330–336.
Roberts VJ, Steenbergen R, Murre C . (1993). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 7583–7587.
Sun L, Trausch-Azar JS, Ciechanover A, Schwartz AL . (2005). J Biol Chem 280: 26448–26456.
Sun XH, Baltimore D . (1991). Cell 64: 459–470.
Van der Put E, Frasca D, King AM, Blomberg BB, Riley RL . (2004). J Immunol 173: 818–827.
Voronova A, Baltimore D . (1990). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 4722–4726.
Weintraub H . (1993). Cell 75: 1241–1244.
Yan W, Young AZ, Soares VC, Kelley R, Benezra R, Zhuang Y . (1997). Mol Cell Biol 17: 7317–7327.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Guojun Bu, Jonathan D Gitlin and Louis J Muglia for critical reading of the manuscript and advice. This study was supported by NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Trausch-Azar, J., Ciechanover, A. et al. E2A protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system is stage-dependent during muscle differentiation. Oncogene 26, 441–448 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209793
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209793
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The beneficial role of proteolysis in skeletal muscle growth and stress adaptation
Skeletal Muscle (2016)
-
Ubiquitination and the Ubiquitin–Proteasome System as regulators of transcription and transcription factorsin epithelial mesenchymal transition of cancer
Tumor Biology (2012)
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase specificity subunit ASB2β is a novel regulator of muscle differentiation that targets filamin B to proteasomal degradation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2009)