Abstract
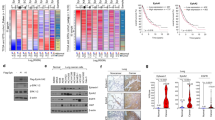
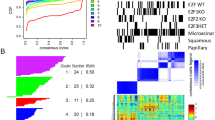
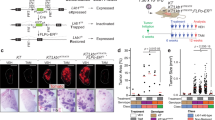
Mitogen-inducible gene 6 (MIG-6) is located in human chromosome 1p36, a locus frequently associated with human lung cancer. MIG-6 is a negative regulator of epidermal growth factor (EGF) signaling, and we show that Mig-6 – like EGF – is induced by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF) in human lung cancer cell lines. Frequently, the receptors for both factors, EGFR and Met, are expressed in same lung cancer cell line, and MIG-6 is induced by both factors in a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent fashion. However, not all tumor lines express MIG-6 in response to either EGF or HGF/SF. In these cases, we find missense and nonsense mutations in the MIG-6 coding region, as well as evidence for MIG-6 transcriptional silencing. Moreover, germline disruption of Mig-6 in mice leads to the development of animals with epithelial hyperplasia, adenoma, and adenocarcinoma in organs like the lung, gallbladder, and bile duct. These data suggests that MIG-6 is a tumor-suppressor gene and is therefore a candidate gene for the frequent 1p36 genetic alterations found in lung cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Amatschek S, Koenig U, Auer H, Steinlein P, Pacher M, Gruenfelder A et al. (2004). Cancer Res 64: 844–856.
Anastasi S, Fiorentino L, Fiorini M, Fraioli R, Sala G, Castellani L et al. (2003). Oncogene 22: 4221–4234.
Anastasi S, Sala G, Huiping C, Caprini E, Russo G, Iacovelli S et al. (2005). Oncogene 24: 4540–4548.
Benhar M, Engelberg D, Levitzki A . (2002). EMBO Rep 3: 420–425.
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, Vande Woude GF . (2003). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 915–925.
Davis RJ . (2000). Cell 103: 239–252.
Ferby I, Reschke M, Kudlacek O, Knyazev P, Pante G, Amann K et al. (2006). Nature Med 12: 568–573.
Fiorentino L, Pertica C, Fiorini M, Talora C, Crescenzi M, Castellani L et al. (2000). Mol Cell Biol 20: 7735–7750.
Fujii T, Dracheva T, Player A, Chacko S, Clifford R, Strausberg RL et al. (2002). Cancer Res 62: 3340–3346.
Girard L, Zochbauer-Muller S, Virmani AK, Gazdar AF, Minna JD . (2000). Cancer Res 60: 4894–4906.
Herzog CR, Devereux TR, Pittman B, You M . (2002). Cancer Res 62: 6424–6429.
Herzog CR, Wang Y, You M . (1995). Oncogene 11: 1811–1815.
Keeton AB, Messina JL . (2005). J Cell Biochem 94: 1190–1198.
Keeton AB, Xu J, Franklin JL, Messina JL . (2004). Biochim Biophys Acta 1679: 248–255.
Kohno T, Yokota J . (1999). Carcinogenesis 20: 1403–1410.
Koo HM, McWilliams MJ, Alvord WG, Vande Woude GF . (1999). Cancer Res 59: 6057–6062.
Ma PC, Jagadeeswaran R, Jagadeesh S, Tretiakova MS, Nallasura V, Fox EA et al. (2005). Cancer Res 65: 1479–1488.
Ma PC, Kijima T, Maulik G, Fox EA, Sattler M, Griffin JD et al. (2003). Cancer Res 63: 6272–6281.
Mai M, Yokomizo A, Qian C, Yang P, Tindall DJ, Smith DI et al. (1998). Cancer Res 58: 2347–2349.
Makkinje A, Quinn DA, Chen A, Cadilla CL, Force T, Bonventre JV et al. (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 17838–17847.
Miettinen PJ, Berger JE, Meneses J, Phung Y, Pederson RA, Werb Z et al. (1995). Nature 376: 337–341.
Miettinen PJ, Warburton D, Bu D, Zhao JS, Berger JE, Minoo P et al. (1997). Dev Biol 186: 224–236.
Nomoto S, Haruki N, Kondo M, Konishi H, Takahashi T, Takahashi T et al. (1998). Cancer Res 58: 1380–1383.
Nomoto S, Haruki N, Tatematsu Y, Konishi H, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T et al. (2000). Genes Chromosomes Cancer 28: 342–346.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S et al. (2004). Science 304: 1497–1500.
Pante G, Thompson J, Lamballe F, Iwata T, Ferby I, Barr FA et al. (2005). J Cell Biol 171: 337–348.
Ragnarsson G, Eiriksdottir G, Johannsdottir JT, Jonasson JG, Egilsson V, Ingvarsson S . (1999). Br J Cancer 79: 1468–1474.
Sargent LM, Senft JR, Lowry DT, Jefferson AM, Tyson FL, Malkinson AM et al. (2002). Cancer Res 62: 1152–1157.
Stephens P, Hunter C, Bignell G, Edkins S, Davies H, Teague J et al. (2004). Nature 431: 525–526.
Thiagalingam S, Foy RL, Cheng KH, Lee HJ, Thiagalingam A, Ponte JF . (2002). Curr Opin Oncol 14: 65–72.
Tokuchi Y, Hashimoto T, Kobayashi M, Hayashi M, Nishida S, Imai K et al. (1999). Br J Cancer 80: 1623–1629.
Tsunoda T, Inokuchi J, Baba I, Okumura K, Naito S, Sasazuki T et al. (2002). Cancer Res 62: 5668–5671.
Virmani AK, Fong KM, Kodagoda D, McIntire D, Hung J, Tonk V et al. (1998). Genes Chromosomes Cancer 21: 308–319.
Wick M, Burger C, Funk M, Muller R . (1995). Exp Cell Res 219: 527–535.
Xu D, Makkinje A, Kyriakis JM . (2005a). J Biol Chem 280: 2924–2933.
Xu J, Keeton AB, Wu L, Franklin JL, Cao X, Messina JL . (2005b). Breast Cancer Res Treat 91: 207–215.
Yang A, Walker N, Bronson R, Kaghad M, Oosterwegel M, Bonnin J et al. (2000). Nature 404: 99–103.
Zhang YW, Su Y, Lanning N, Swiatek PJ, Bronson RT, Sigler R et al. (2005). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 11740–11745.
Zhang YW, Su Y, Volpert OV, Vande Woude GF . (2003). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 12718–12723.
Zochbauer-Muller S, Gazdar AF, Minna JD . (2002). Annu Rev Physiol 64: 681–708.
Acknowledgements
We thank Bryn Eagleson, Jason Martin, and Kellie Sisson for helping with the mice, Matt VanBrocklin and Han-Mo Koo for providing the lung cancer cell lines, Bree Berghuis and JC Goolsby for histological assistance, David Petillo for sequencing, Eric Kort for statistic analysis, David Nadziejka for technical editing of the manuscript, and Michelle Reed and Troy Carrigan for manuscript preparation. This work was supported by the Van Andel Foundation and in part by the Michigan Economic Development Corporation and Michigan Technology Tri-Corridor Grant MAMC 085P1000815.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YW., Staal, B., Su, Y. et al. Evidence that MIG-6 is a tumor-suppressor gene. Oncogene 26, 269–276 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209790
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209790
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Systematic Profiling of Mitogen-Inducible Gene 6 and Its Derived Peptides Binding to Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Bone Cancers at Molecular and Cellular Levels
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2024)
-
ARG1 Is a Potential Prognostic Marker in Metastatic Endometrial Cancer
Reproductive Sciences (2024)
-
High-throughput functional screen identifies YWHAZ as a key regulator of pancreatic cancer metastasis
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Overexpression of MIG-6 in the cartilage induces an osteoarthritis-like phenotype in mice
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2020)
-
MIG-6 negatively regulates STAT3 phosphorylation in uterine epithelial cells
Oncogene (2018)