Abstract
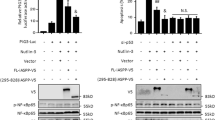
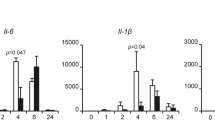
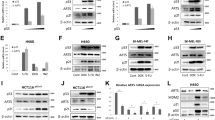
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), which exists as heterodimeric complexes composed of p50 and p65, has been shown to play an important role in cell survival processes. In the present study, we found for the first time that NF-κB has an ability to induce the ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of proapoptotic p73α. The activation of NF-κB in tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)-stimulated H1299 cells resulted in a significant reduction in the amounts of the endogenous p73α. Consistent with these results, TNF-α-mediated downregulation of p73α was observed in wild-type (WT) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) but not in p65-deficient MEFs. Ectopic expression of NF-κB decreased a half-life of p73α by increasing its ubiquitination levels, and thereby inhibiting the transcriptional activity as well as proapoptotic function of p73α, whereas NF-κB had undetectable effects on p53. Immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated that, under our experimental conditions, NF-κB does not bind to p73α in mammalian cultured cells. In contrast to WT p65, the COOH-terminal deletion mutant of p65 (p65ΔC) failed to reduce the expression levels of p73α, suggesting that NF-κB-mediated proteolytic degradation of p73α requires the transcriptional activity of NF-κB. Taken together, our present results imply that NF-κB-mediated degradation of proapoptotic p73 is a novel inhibitory mechanism of p73 that regulates cell survival and death.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CHX:
-
cycloheximide
- MEF:
-
mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
- Ub:
-
ubiquitin
References
Agami R, Blandino G, Oren M, Shaul Y . (1999). Nature 399: 809–813.
Balint E, Bates S, Vousden KH . (1999). Oncogene 18: 3923–3929.
Bayon Y, Ortiz MA, Lopez-hernandez FJ, Gao F, Karin M, Pfahl M et al. (2003). Mol Cell Biol 23: 1061–1074.
Beg AA, Baltimore D . (1996). Science 274: 782–784.
Beg AA, Sha WC, Bronson RT, Baltimore D . (1995). Nature 376: 167–170.
Bernassola F, Salomoni P, Oberst A, Di Como CJ, Pagano M, Melino G et al. (2004). J Exp Med 199: 1545–1557.
Bourdon JC, Fernandes K, Murray-Zmijewski F, Liu G, Diot A, Xirodimas DP et al. (2005). Genes Dev 19: 2122–2137.
Chang L, Kamata H, Solinas G, Luo JL, Maeda S, Venuprasad K et al. (2006). Cell 124: 601–613.
Flores ER, Tsai KY, Crowley D, Sengupta S, Yang A, McKeon F et al. (2002). Nature 416: 560–564.
Fontemaggi G, Gurtner A, Strano S, Higashi Y, Sacchi A, Piaggio G et al. (2001). Mol Cell Biol 21: 8461–8470.
Gong J, Costanzo A, Yang HQ, Melino G, Kaelin Jr WG, Levrero M et al. (1999). Nature 399: 806–809.
Gressner O, Schilling T, Lorenz K, Schulze Schleithoff E, Koch A, Schulze-Bergkamen H et al. (2005). EMBO J 24: 2458–2471.
Grob TJ, Novak U, Maisse C, Barcaroli D, Luthi AU, Pirnia F et al. (2001). Cell Death Differ 8: 1213–1223.
Huang TT, Wuerzberger-Davis SM, Seufzer BJ, Shumway SD, Kurama T, Boothman DA et al. (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 9501–9509.
Ikawa S, Nakagawara A, Ikawa Y . (1999). Cell Death Differ 6: 1154–1161.
Irwin MS, Kondo K, Marin MC, Cheng LS, Hahn WC, Kaelin Jr WG . (2003). Cancer Cell 3: 403–410.
Jost CA, Marin MC, Kaelin Jr WG . (1997). Nature 389: 191–194.
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A et al. (1997). Cell 90: 809–819.
Kawai H, Nie L, Yuan ZM . (2002). Mol Cell Biol 22: 6079–6088.
Kharbanda S, Ren R, Pandey P, Shafman TD, Feller SM, Weichselbaum RR et al. (1995). Nature 376: 785–788.
Kim JS, Lee JM, Chwae YJ, Kim YH, Lee JH, Kim K et al. (2004). Biochem Pharmacol 67: 1459–1468.
Kramer S, Ozaki T, Miyazaki K, Kato C, Hanamoto T, Nakagawara A . (2005). Oncogene 24: 938–944.
Lee CW, La Thangue NB . (1999). Oncogene 18: 4171–4181.
Leng RP, Lin Y, Ma W, Wu H, Lemmers B, Chung S et al. (2003). Cell 112: 779–791.
Lissy NA, Davis PK, Irwin M, Kaelin Jr WG, Dowdy SF . (2000). Nature 407: 642–645.
Mantovani F, Piazza S, Gostissa M, Strano S, Zacchi P, Mantovani R et al. (2004). Mol Cell 14: 625–636.
Melino G, De Laurenzi V, Vousden KH . (2002). Nat Rev Cancer 2: 605–615.
Muta T, Takeshige K . (2001). Eur J Biochem 268: 4580–4589.
Nakagawa T, Takahashi M, Ozaki T, Watanabe K, Todo S, Mizuguchi H et al. (2002). Mol Cell Biol 22: 2575–2585.
Pozniak CD, Radinovic S, Yang A, McKeon F, Kaplan DR, Miller FD . (2000). Science 289: 304–306.
Rossi M, De Laurenzi V, Munarriz E, Green DR, Liu YC, Vousden KH et al. (2005). EMBO J 24: 836–848.
Stiewe T, Putzer BM . (2002). Cell Death Differ 9: 237–245.
Stiewe T, Zimmermann S, Frilling A, Esche H, Putzer BM . (2002). Cancer Res 62: 3598–3602.
Strano S, Monti O, Pediconi N, Baccarini A, Fontemaggi G, Lapi E et al. (2005). Mol Cell 18: 447–459.
Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR, Verma IM . (1996). Science 274: 787–789.
Wan YY, DeGregori J . (2003). Immunity 18: 331–342.
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin ASJ . (1996). Science 274: 784–787.
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin SJ . (1998). Science 281: 1680–1683.
Yamagishi N, Miyakoshi J, Takebe H . (1997). Int J Radiat Biol 72: 157–162.
Yang A, Kaghad M, Wang Y, Gillett E, Fleming MD, Dotsch V et al. (1998). Mol Cell 2: 305–316.
Yang A, McKeon F . (2000). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1: 199–207.
Yang A, Walker N, Bronson R, Kaghad M, Oosterwegel M, Bonnin J et al. (2000). Nature 404: 99–103.
Yuan ZM, Shioya H, Ishiko T, Sun X, Gu J, Huang YY et al. (1999). Nature 399: 814–817.
Zaika AI, Slade N, Erster SH, Sansome C, Joseph TW, Pearl M et al. (2002). J Exp Med 196: 765–780.
Zeng X, Chen L, Jost CA, Maya R, Keller D, Wang X et al. (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: 3257–3266.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of our laboratory for helpful discussions. We also thank Y Nakamura for excellent technical assistance. We give special thanks to Dr M Karin for providing us with p65−/− MEF. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare for Third Term Comprehensive Control Research for Cancer, a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan, and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kikuchi, H., Ozaki, T., Furuya, K. et al. NF-κB regulates the stability and activity of p73 by inducing its proteolytic degradation through a ubiquitin-dependent proteasome pathway. Oncogene 25, 7608–7617 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209748
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209748
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Depletion of the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) sensitizes towards apoptosis via p53 and p73 posttranslational regulation
Oncogene (2013)
-
Regulation of p73 activity by post-translational modifications
Cell Death & Disease (2012)
-
Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in NB-4, an acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line, through up-regulation of p73 via suppression of nuclear factor kappa B-mediated inhibition of p73 transcription and prevention of NF-κB-mediated induction of XIAP, cIAP2, BCL-XL and survivin
Medical Oncology (2010)