Abstract
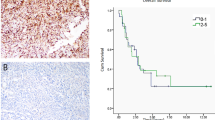
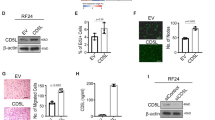
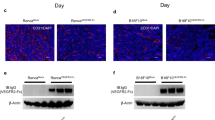
In vivo neuroblastoma (NB) xenograft model, resistant to the DNA-topoisomerase I inhibitor irinotecan (CPT-11), has been established to study resistance mechanisms acquired in a therapeutic setting. Common mechanisms of resistance were not involved in this resistance. Thus, we compared the gene expression profiles of sensitive, resistant, and reverted tumors using cDNA expression arrays. Expression of selected transcripts was confirmed by quantitative real-time PCR. We found that pleiotrophin (PTN), a heparin-binding growth factor, was the only gene significantly affected: PTN gene expression was downregulated in all resistant tumors (8–14-fold) as compared to sensitive tumors, and was increased (2–4-fold) in all reverted tumors as compared to resistant tumors. PTN thus appeared to be a likely candidate gene associated with resistance to CPT-11 in this in vivo model. To investigate the direct implication of PTN in NB, we transfected two NB cell lines with RNA interferences in order to silence PTN. PTN failed to demonstrate implication in resistance to CPT-11 in vitro but could influence sensitivity to CPT-11 exclusively through an in vivo mechanism. Indeed, vasculature was significantly enhanced in resistant NB xenografts compared to sensitive and reverted xenografts, and we suggest that PTN is acting in our resistant in vivo NB model as an angiostatic factor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NB:
-
neuroblastoma
- PTN:
-
pleiotrophin
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
- pRS:
-
pRetroSuper
- MDR:
-
multidrug resistance
- MRP:
-
multidrug resistance-associated protein
- BCRP:
-
breast cancer resistance protein
References
Blaney S, Berg SL, Pratt C, Weitman S, Sullivan J, Luchtman-Jones L et al. (2001). Clin Cancer Res 7: 32–37.
Bourhis J, Benard J, Hartmann O, Boccon-Gibod L, Lemerle J, Riou G . (1989). J Natl Cancer Inst 81: 1401–1405.
Bowden ET, Stoica GE, Wellstein A . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 35862–35868.
Brodeur GM, Seeger RC, Schwab M, Varmus HE, Bishop JM . (1984). Science 224: 1121–1124.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . (2002). Science 296: 550–553.
Calvet L, Santos A, Valent A, Terrier-Lacombe MJ, Opolon P, Merlin JL et al. (2004). Br J Cancer 91: 1205–1212.
Chauhan AK, Li YS, Deuel TF . (1993). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 679–682.
Choudhuri R, Zhang HT, Donnini S, Ziche M, Bicknell R . (1997). Cancer Res 57: 1814–1819.
Corbley MJ . (1997). J Biol Chem 272: 24696–24702.
Courty J, Dauchel MC, Caruelle D, Perderiset M, Barritault D . (1991). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 180: 145–151.
Czubayko F, Schulte AM, Berchem GJ, Wellstein A . (1996). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 14753–14758.
Deuel TF, Zhang N, Yeh HJ, Silos-Santiago I, Wang ZY . (2002). Arch Biochem Biophys 397: 162–171.
Elie N, Plancoulaine B, Signolle JP, Herlin P . (2003). Cytometry A 56: 37–45.
Fang W, Hartmann N, Chow DT, Riegel AT, Wellstein A . (1992). J Biol Chem 267: 25889–25897.
Fong CT, Dracopoli NC, White PS, Merrill PT, Griffith RC, Housman DE et al. (1989). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 3753–3757.
Furman WL, Stewart CF, Poquette CA, Pratt CB, Santana VM, Zamboni WC et al. (1999). J Clin Oncol 17: 1815–1824.
Hayashi Y, Kanda N, Inaba T, Hanada R, Nagahara N, Muchi H et al. (1989). Cancer 63: 126–132.
Herbst RS, Takeuchi H, Teicher BA . (1998). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 41: 497–504.
Heroult M, Bernard-Pierrot I, Delbe J, Hamma-Kourbali Y, Katsoris P, Barritault D et al. (2004). Oncogene 23: 1745–1753.
Jain RK . (2005). Science 307: 58–62.
Kadomatsu K, Muramatsu T . (2004). Cancer Lett 204: 127–143.
Kim NT, Elie N, Plancoulaine B, Herlin P, Coster M . (2003). Anal Cell Pathol 25: 63–75.
Komuro H, Li P, Tsuchida Y, Yokomori K, Nakajima K, Aoyama T et al. (1994). Med Pediatr Oncol 23: 487–492.
Laaroubi K, Delbe J, Vacherot F, Desgranges P, Tardieu M, Jaye M et al. (1994). Growth Factors 10: 89–98.
Li XG, Haluska Jr P, Hsiang YH, Bharti A, Kufe DW, Rubin EH . (1996). Ann NY Acad Sci 803: 111–127.
Li YS, Milner PG, Chauhan AK, Watson MA, Hoffman RM, Kodner CM et al. (1990). Science 250: 1690–1694.
Liu R, Page C, Beidler DR, Wicha MS, Nunez G . (1999). Am J Pathol 155: 1861–1867.
Lock RB, Stribinskiene L . (1996). Cancer Res 56: 4006–4012.
Look AT, Hayes FA, Shuster JJ, Douglass EC, Castleberry RP, Bowman LC et al. (1991). J Clin Oncol 9: 581–591.
Milner PG, Li YS, Hoffman RM, Kodner CM, Siegel NR, Deuel TF . (1989). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 165: 1096–1103.
Nakagawara A, Milbrandt J, Muramatsu T, Deuel TF, Zhao H, Cnaan A et al. (1995). Cancer Res 55: 1792–1797.
Papadimitriou E, Polykratis A, Courty J, Koolwijk P, Heroult M, Katsoris P . (2001). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 282: 306–313.
Polykratis A, Delbe J, Courty J, Papadimitriou E, Katsoris P . (2004). Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36: 1954–1966.
Rauvala H . (1989). EMBO J 8: 2933–2941.
Ries LAG, Smith MA, Gurney JG, Linet M, Tamra T, Young JL et al. (1999). Cancer Incidence and Survival Among Children and Adolescents: United States SEER Program 1975–1995. National Cancer institut, SEER Program.
Rubin EH, Li TK, Duann P, Liu LF . (1996). Cancer Treat Res 87: 243–260.
Schmitt CA, Rosenthal CT, Lowe SW . (2000). Nat Med 6: 1029–1035.
Teicher BA, Dupuis NP, Robinson MF, Emi Y, Goff DA . (1995). Oncol Res 7: 237–243.
Teicher BA, Herman TS, Holden SA, Wang YY, Pfeffer MR, Crawford JW et al. (1990). Science 247: 1457–1461.
Thompson J, Zamboni WC, Cheshire PJ, Lutz L, Luo X, Li Y et al. (1997a). Clin Cancer Res 3: 423–431.
Thompson J, Zamboni WC, Cheshire PJ, Richmond L, Luo X, Houghton JA et al. (1997b). Anticancer Drugs 8: 313–322.
Vassal G, Doz F, Frappaz D, Gentet JC, Pichon F, Chastagner P et al. (2002). Med Pediatr Oncol (Int Soc Pediatr Oncol, Meet) 39: 257.
Vassal G, Doz F, Frappaz D, Imadalou K, Sicard E, Santos A et al. (2003). J Clin Oncol 21: 3844–3852.
Vassal G, Pondarre C, Cappelli C, Terrier-Lacombe MJ, Boland I, Morizet J et al. (1997). Eur J Cancer 33: 2011–2015.
Vassal G, Terrier-Lacombe MJ, Bissery MC, Venuat AM, Gyergyay F, Benard J et al. (1996). Br J Cancer 74: 537–545.
Wildiers H, Guetens G, De Boeck G, Verbeken E, Landuyt B, Landuyt W et al. (2003). Br J Cancer 88: 1979–1986.
Acknowledgements
We thank Patrice Ardouin and the staff in the Animal Experimentation Unit, Institut Gustave-Roussy, for the care of the animals; Dr Marjorie Flahaut, Dr Roland Meier and Katya Auderset for excellent technical support from Department of Pediatric Oncology Research, CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland; Elisabeth Connault from Institut Gustave-Roussy for excellent technical support and Lorna Saint-Ange from Institut Gustave-Roussy for editing the manuscript. We thank the Ligue National Contre le Cancer and the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calvet, L., Geoerger, B., Regairaz, M. et al. Pleiotrophin, a candidate gene for poor tumor vasculature and in vivo neuroblastoma sensitivity to irinotecan. Oncogene 25, 3150–3159 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209348
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209348
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pleiotrophin is a potential colorectal cancer prognostic factor that promotes VEGF expression and induces angiogenesis in colorectal cancer
International Journal of Colorectal Disease (2012)
-
Early evaluation of the effects of chemotherapy with longitudinal FDG small-animal PET in human testicular cancer xenografts: early flare response does not reflect refractory disease
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2009)
-
Usefulness of Automatic Quantification of Immunochemical Staining on Whole Tumor Sections for Correlation with Oncological Small Animal PET Studies: An Example with Cell Proliferation, Glucose Transporter 1 and FDG
Molecular Imaging and Biology (2008)