Abstract
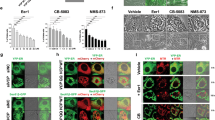
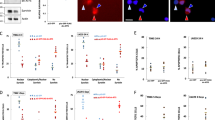
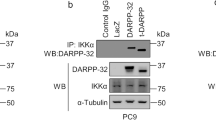
The Fhit tumor suppressor binds and hydrolyses diadenosine polyphosphates and the Fhit–substrate complex has been proposed as a proapoptotic effector, as determined by infection of susceptible cancer cells with adenoviruses carrying wild-type fragile histidine triad (FHIT) or catalytic site mutants. The highly conserved Fhit tyrosine 114 (Y114), within the unstructured loop C-terminal of the catalytic site, can be phosphorylated by Src family tyrosine kinases, although endogenous phospho-Fhit is rarely detected. To explore the importance of Y114 and identify Fhit-mediated signaling events, wild-type and Y114 mutant FHIT-expressing adenoviruses were introduced into two human lung cancer cell lines. Caspase-dependent apoptosis was effectively induced only by wild-type but not Y114 mutant Fhit proteins. By expression profiling of FHIT versus mutant FHIT-infected cells, we found that survivin, an Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (IAP) family member, was significantly decreased by wild-type Fhit. In addition, Fhit inhibited activity of Akt, a key effector in the phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase (PI3K) pathway; loss of endogenous Fhit expression caused increased Akt activity in vitro and in vivo, and overexpression of constitutively active Akt inhibited Fhit-induced apoptosis. The results indicate that the Fhit Y114 residue plays a critical role in Fhit-induced apoptosis, occurring through inactivation of the PI3K-Akt-survivin signal pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 October 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02472-x
References
Altieri DC . (2003). Nat Rev Cancer 3: 46–54.
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC . (1997). Nat Med 3: 917–921.
Barnes LD, Garrison PN, Siprashvili Z, Guranowski A, Robinson AK, Ingram SW et al. (1996). Biochemistry 35: 11529–11535.
Brenner C, Pace HC, Garrison PN, Robinson AK, Rosler A, Liu XH et al. (1997). Protein Eng 10: 1461–1463.
Croce CM, Sozzi G, Huebner K . (1999). J Clin Oncol 17: 1618–1624.
Dan HC, Jiang K, Coppola D, Hamilton A, Nicosia SV, Sebti SM et al. (2004). Oncogene 23: 706–715.
Dumon KR, Ishii H, Fong LY, Zanesi N, Fidanza V, Mancini R et al. (2001b). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 3346–3351.
Dumon KR, Ishii H, Vecchione A, Trapasso F, Baldassarre G, Chakrani F et al. (2001a). Cancer Res 61: 4827–4836.
Fong LY, Fidanza V, Zanesi N, Lock LF, Siracusa LD, Mancini R et al. (2000). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 4742–4747.
Fornaro M, Plescia J, Chheang S, Tallini G, Zhu Y-M, King M et al. (2003). J Biol Chem 50: 50402–50411.
Fujishita T, Doi Y, Sonoshita M, Hiai H, Oshima M, Huebner K et al. (2004). Br J Cancer 91: 1571–1574.
Garrison PN, Robinson A, Pekarsky Y, Croce CM, Barnes LD . (2005). Biochemistry 44: 6286–6292.
Hao XP, Willis JE, Pretlow TG, Rao JS, MacLennan GT, Talbot IC et al. (2000). Cancer Res 60: 18–21.
Hu B, Han SY, Wang X, Ottey M, Dicker A, Huebner K et al. (2005). J Cell Physiol 202: 518–523.
Huebner K, Croce CM . (2003). Br J Cancer 88: 1501–1506.
Huebner K, Garrison PN, Barnes LD, Croce CM . (1998). Annu Rev Genet 32: 7–31.
Iliopoulos D, Guler G, Han SY, Johnston D, Druck T, McCorkell KA et al. (2005). Oncogene 24: 1625–1633.
Ishii H, Dumon KR, Vecchione A, Trapasso F, Mimori K, Alder H et al. (2001). Cancer Res 61: 1578–1584.
Ji L, Fang B, Yen N, Fong K, Minna FJ, Roth JA . (1999). Cancer Res 59: 3333–3339.
Junttila TT, Laato M, Vahlberg T, Soderstrom KO, Visakorpi T, Isola J et al. (2003). Clin Cancer Res 9: 5346–5357.
Kato H, Semba S, Miskad UA, Seo Y, Kasuga M, Yokozaki H . (2004). Clin Cancer Res 10: 7318–7328.
Kuroki T, Trapasso F, Yendamuri S, Matsuyama A, Alder H, Mori M et al. (2003). Cancer Res 63: 3724–3728.
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J, Tognin S, Marchisio PC et al. (1998). Nature 396: 580–584.
Lu Y, Yu Q, Liu JH, Zhang J, Wang H, Koul D et al. (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 40057–40066.
Mao L, Lee JS, Kurie JM, Fan YH, Lippman SM, Lee JJ et al. (1997). J Natl Cancer Inst 89: 857–862.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Poulaki V, Schlossman R, Akiyama M, Chauhan D et al. (2002). Oncogene 21: 5673–5683.
Mori M, Mimori K, Shiraishi T, Alder H, Inoue H, Tanaka Y et al. (2000). Cancer Res 60: 1177–1182.
Nishizaki M, Sasaki J, Fang B, Atkinson EN, Minna JD, Roth JA et al. (2004). Cancer Res 64: 5745–5752.
Ohta M, Inoue H, Cotticelli MG, Kastury K, Baffa R, Palazzo J et al. (1996). Cell 84: 587–597.
Ottey M, Han SY, Druck T, Barnoski BL, McCorkell KA, Croce CM et al. (2004). Br J Cancer 91: 1669–1677.
Pace HC, Garrison PN, Robinson AK, Barnes LD, Draganescu A, Rosler A et al. (1998). Proc Natl Sci USA 95: 5484–5489.
Papapetropoulos A, Fultin D, Mahbouby K, Kalb RG, O'Connoy DS, Li F et al. (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 9102–9105.
Pekarsky Y, Garrison PN, Palamarchuk A, Zanesi N, Aqeilan RI, Huebner K et al. (2004). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 3775–3779.
Pekarsky Y, Koval A, Hallas C, Bichi R, Tresini M, Malstrom S et al. (2000). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 3028–3033.
Roz L, Gramegna M, Ishii H, Croce CM, Sozzi G . (2002). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 3615–3620.
Semba S, Itoh N, Ito M, Youssef EM, Harada M, Moriya T et al. (2002). Clin Cancer Res 8: 3824–3831.
Sevignani C, Calin GA, Cesari R, Sarti M, Ishii H, Yendamuri S et al. (2003). Cancer Res 63: 1183–1187.
Shi Y, Zou M, Farid NR, Paterson MC . (2000). Biochem J 352: 443–448.
Siprashvili Z, Sozzi G, Barnes LD, McCue P, Robinson AK, Eryomin V et al. (1997). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 13771–13776.
Sozzi G, Veronese ML, Negrini M, Baffa R, Cotticelli MG, Inoue H et al. (1996). Cell 85: 17–26.
Trapasso F, Krakowiak A, Cesari R, Arkles J, Yendamuri S, Ishii H et al. (2003). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 1592–1597.
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G . (2001). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 5116–5121.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL . (2002). Nat Rev Cancer 2: 489–501.
Zanesi N, Fidanza V, Fong LY, Mancini R, Druck T, Valtieri M et al. (2001). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 10250–10255.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by USPHS grants from the National Cancer Institure, P01 CA77738 (K Huebner) and P01 CA78890 (CM Croce), State of Pennsylvania Tobacco Settlement funds, funds from the Breast Cancer Program of US DOD, BC043090 (D Iliopoulos) and NIH training Grant T32-HLO7780 (KA McCorkell).
We thank Dr Shuang-Yin Han, for assistance in preparation of the recombinant adenoviral vectors, Drs Chang-Gong Liu and Xiuping Liu for assistance with microarray analysis, Drs Masaki Mori and Koshi Mimori for contribution of the esophageal cancer cell lines and Angela Robinson for expert assistance with preparation of purified Fhit proteins.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information accompanies the paper on Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
The original online version of this article was revised: The GFP blot images for Figure 1A, b, in this article have been removed because the original data are no longer available, thus these images cannot be validated.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semba, S., Trapasso, F., Fabbri, M. et al. Fhit modulation of the Akt-survivin pathway in lung cancer cells: Fhit-tyrosine 114 (Y114) is essential. Oncogene 25, 2860–2872 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209323
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209323
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Germinal epimutation of Fragile Histidine Triad (FHIT) gene is associated with progression to acute and chronic adult T-cell leukemia diseases
Molecular Cancer (2021)
-
Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Survivin Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
FHIT loss confers cisplatin resistance in lung cancer via the AKT/NF-κB/Slug-mediated PUMA reduction
Oncogene (2015)
-
Transcriptional regulation of the survivin gene
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
Activation state-dependent interaction between Gαq subunits and the Fhit tumor suppressor
Cell Communication and Signaling (2013)