Abstract
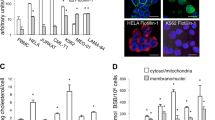
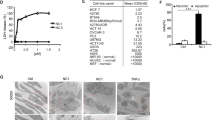
Apoptin, a chicken anemia virus-derived protein, selectively induces apoptosis in transformed but not in normal cells, thus making it a promising candidate as a novel anticancer therapeutic. The mechanism of apoptin-induced apoptosis is largely unknown. Here, we report that contrary to previous assumptions, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL inhibit apoptin-induced cell death in several tumor cell lines. In contrast, deficiency of Bax conferred resistance, whereas Bax expression sensitized cells to apoptin-induced death. Cell death induction by apoptin was associated with cytochrome c release from mitochondria as well as with caspase-3 and -7 activation. Benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone, a broad spectrum caspase inhibitor, was highly protective against apoptin-induced cell death. Apoptosis induced by apoptin required Apaf-1, as immortalized Apaf-1-deficient fibroblasts as well as tumor cells devoid of Apaf-1 were strongly protected. Thus, our data indicate that apoptin-induced apoptosis is not only Bcl-2- and caspase dependent, but also engages an Apaf-1 apoptosome-mediated mitochondrial death pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMC:
-
7-aminomethyl-4-coumarin
- CAV:
-
chicken anemia virus
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- HUVEC:
-
human umbilical vein endothelial cell
- zVAD-fmk:
-
benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone
References
Adair BM . (2000). Dev Comp Immunol 24: 247–255.
Almazan G, McKay R . (1992). Brain Res 579: 234–245.
Antonsson B, Martinou JC . (2000). Exp Cell Res 256: 50–57.
Bitzer M, Armeanu S, Prinz F, Ungerechts G, Wybranietz W, Spiegel M et al. (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 29817–29824.
Bouillet P, Strasser A . (2002). J Cell Sci 115: 1567–1574.
Cecconi F, Alvarez Bolado G, Meyer BI, Roth KA, Gruss P . (1998). Cell 94: 727–737.
Danen-Van Oorschot AA, Fischer DF, Grimbergen JM, Klein B, Zhuang S, Falkenburg JH et al. (1997). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 5843–5847.
Danen-Van Oorschot AA, van der Eb AJ, Noteborn MH . (1999). Adv Exp Med Biol 457: 245–249.
Danen-van Oorschot AA, van der Eb AJ, Noteborn MH . (2000). J Virol 74: 7072–7078.
Danen-Van Oorschot AA, Zhang YH, Leliveld SR, Rohn JL, Seelen MC, Bolk MW et al. (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 27729–27736.
Daniel PT, Schulze-Osthoff K, Belka C, Guner D . (2003). Essays Biochem 39: 73–88.
Essmann F, Bantel H, Totzke G, Engels IH, Sinha B, Schulze-Osthoff K et al. (2003). Cell Death Differ 10: 1260–1272.
Everett H, McFadden G . (2001). Virology 288: 1–7.
Fischer U, Janicke RU, Schulze-Osthoff K . (2003). Cell Death Differ 10: 76–100.
Fischer U, Schulze-Osthoff K . (2005). Pharmacol Rev 57: 187–215.
Ghavami S, Kerkhoff C, Los M, Hashemi M, Sorg C, Karami-Tehrani F . (2004). J Leukoc Biol 76: 169–175.
Gillissen B, Essmann F, Graupner V, Starck L, Radetzki S, Dorken B et al. (2003). EMBO J 22: 3580–3590.
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ . (1999). Genes Dev 13: 1899–1911.
Guelen L, Paterson H, Gaken J, Meyers M, Farzaneh F, Tavassoli M . (2004). Oncogene 23: 1153–1165.
Hamilton A, Piccart M . (2000). Ann Oncol 11: 647–663.
Haraguchi M, Torii S, Matsuzawa S, Xie Z, Kitada S, Krajewski S et al. (2000). J Exp Med 191: 1709–1720.
Jaattela M, Benedict M, Tewari M, Shayman JA, Dixit VM . (1995). Oncogene 10: 2297–2305.
Kane DJ, Ord T, Anton R, Bredesen DE . (1995). J Neurosci Res 40: 269–275.
Lamkanfi M, Declercq W, Depuydt B, Kalai M, Saelens X, Vandenabeele P . (2002) In: Los M, Walczak H (eds). Caspases – Their Role in Cell Death and Cell Survival. Kluwer Academic Press: New York.
Lassus P, Opitz-Araya X, Lazebnik Y . (2002). Science 297: 1352–1354.
Los M, Mozoluk M, Ferrari D, Stepczynska A, Stroh C, Renz A et al. (2002). Mol Biol Cell 13: 978–988.
Los M, Wesselborg S, Schulze Osthoff K . (1999). Immunity 10: 629–639.
Marsden VS, O'Connor L, O'Reilly LA, Silke J, Metcalf D, Ekert PG et al. (2002). Nature 419: 634–637.
Marsden VS, Strasser A . (2003). Annu Rev Immunol 21: 71–105.
McDonnell TJ, Deane N, Platt FM, Nunez G, Jaeger U, McKearn JP et al. (1989). Cell 57: 79–88.
Noteborn MH, Todd D, Verschueren CA, de Gauw HW, Curran WL, Veldkamp S et al. (1994). J Virol 68: 346–351.
Noteborn MH, Zhang YH, van der Eb AJ . (1998). Mutat Res 400: 447–455.
Oro C, Jans DA . (2004). Curr Drug Targets 5: 179–190.
Poon IK, Oro C, Dias MM, Zhang JP, Jans DA . (2005). J Virol 79: 1339–1341.
Poppe M, Reimertz C, Dussmann H, Krohn AJ, Luetjens CM, Bockelmann D et al. (2001). J Neurosci 21: 4551–4563.
Rampino N, Yamamoto H, Ionov Y, Li Y, Sawai H, Reed JC et al. (1997). Science 275: 967–969.
Reed JC, Green DR . (2002). Mol Cell 9: 1–3.
Rohn JL, Zhang YH, Aalbers RI, Otto N, Den Hertog J, Henriquez NV et al. (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 50820–50827.
Schoop RA, Kooistra K, Baatenburg De Jong RJ, Noteborn MH . (2004). Int J Cancer 109: 38–42.
Schulze-Osthoff K, Ferrari D, Los M, Wesselborg S, Peter ME . (1998). Eur J Biochem 254: 439–459.
Schwerk C, Schulze-Osthoff K . (2005). Mol Cell 19: 1–13.
Somai S, Chaouat M, Jacob D, Perrot JY, Rostene W, Forgez P et al. (2003). Int J Cancer 105: 607–612.
Strasser A, O'Connor L, Dixit VM . (2000). Annu Rev Biochem 69: 217–245.
Stroh C, Schulze-Osthoff K . (1998). Cell Death Differ 5: 997–1000.
Suzuki M, Youle RJ, Tjandra N . (2000). Cell 103: 645–654.
Tavassoli M, Guelen L, Luxon BA, Gaken J . (2005). Apoptosis 10: 717–724.
Teodoro JG, Heilman DW, Parker AE, Green MR . (2004). Genes Dev 18: 1952–1957.
Thomson BJ . (2001). Int J Exp Pathol 82: 65–76.
Wadia JS, Wagner MV, Ezhevsky SA, Dowdy SF . (2004). J Virol 78: 6077–6078.
Zhang YH, Leliveld SR, Kooistra K, Molenaar C, Rohn JL, Tanke HJ et al. (2003). Exp Cell Res 289: 36–46.
Zheng TS, Flavell RA . (2000). Exp Cell Res 256: 67–73.
Zhuang SM, Shvarts A, Jochemsen AG, van Oorschot AA, van der Eb AJ, Noteborn MH . (1995). Carcinogenesis 16: 2939–2944.
Acknowledgements
This work was in part supported by grants from the ‘Deutsche Krebshilfe' and the DFG. ML is supported by CIHR ‘Canada Research Chair’ and MHRC programs. SM acknowledges the generous support from CCMF. We are grateful to Drs J Prehn, RU Jänicke, F Prinz, F Cecconi, M Jäättela, LC Murphy for providing cell lines, expertise and reagents. We are in debt also to A Kemp and A Kania for help with experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burek, M., Maddika, S., Burek, C. et al. Apoptin-induced cell death is modulated by Bcl-2 family members and is Apaf-1 dependent. Oncogene 25, 2213–2222 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209258
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209258
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A novel anti-CD22 scFv–apoptin fusion protein induces apoptosis in malignant B-cells
AMB Express (2017)
-
The chimeric multi-domain proteins mediating specific DNA transfer for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment
Cancer Cell International (2016)
-
Creation of an apoptin-derived peptide that interacts with SH3 domains and inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion
Tumor Biology (2016)
-
Viral genes as oncolytic agents for cancer therapy
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
-
Apoptin selectively induces the apoptosis of tumor cells by suppressing the transcription of HSP70
Tumor Biology (2013)