Abstract
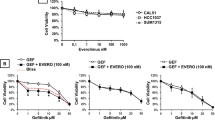
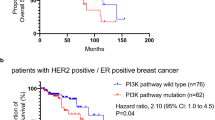
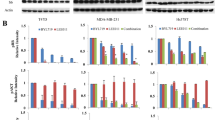
Mutational inactivation or deletion of the phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN)/MMAC1/TEP gene in human cancer cells leads to a constitutively active status of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in the cells and has been linked to the lack of responses of the cells to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-targeted therapeutics. Akt is strongly inhibited by perifosine, an orally active alkyl-lysophospholipid currently being evaluated as an anti-cancer agent in phase 1 and 2 clinical trials. To determine whether perifosine may enhance the antitumor activity of the anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab/C225 in PTEN-deficient cancer cells, we exposed MDA468 breast cancer cells (which contain mutated PTEN gene) and PC3 prostate cancer cells (in which the PTEN gene is deleted) to perifosine and cetuximab, alone and in combination. Treatment of the cells with perifosine reduced baseline levels of phosphorylated Akt, phosphorylated p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and p38MAPK, and increased baseline levels of phosphorylated stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK)/c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK). A 72-h exposure of the MDA468 and PC3 cells to perifosine alone resulted in cell death in a dose-dependent manner, which was enhanced by cetuximab. Addition of subtoxic doses of perifosine to cetuximab treatment also enhanced the cetuximab-induced growth inhibition. The combination treatment enhanced the inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt, p44/42MAPK and p38MAPK, but offset the phosphorylation of SAPK/JNK that was activated by perifosine treatment alone. Taken together, the data showed that perifosine enhances the antitumor activity of cetuximab in PTEN-deficient cancer cells. Further evaluation of the combination treatment in preclinical and clinical studies is warranted.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- PTEN:
-
phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10
- PI3-K:
-
phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PIP:
-
phosphatidylinositol phosphate
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- SAPK:
-
stress-activated protein kinase
- JNK:
-
c-jun NH2-terminal kinase
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
References
Aikin R, Maysinger D, Rosenberg L . (2004). Endocrinology 145: 4522–4531.
Barthwal MK, Sathyanarayana P, Kundu CN, Rana B, Pradeep A, Sharma C et al. (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 3897–3902.
Bianco R, Shin I, Ritter CA, Yakes FM, Basso A, Rosen N et al. (2003). Oncogene 22: 2812–2822.
Clive S, Gardiner J, Leonard RC . (1999). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44 (Suppl): S29–S30.
Clive S, Leonard RC . (1997). Lancet 349: 621–622.
Crul M, Rosing H, de Klerk GJ, Dubbelman R, Traiser M, Reichert S et al. (2002). Eur J Cancer 38: 1615–1621.
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A et al. (2004). N Engl J Med 351: 337–345.
De Siervi A, Marinissen M, Diggs J, Wang XF, Pages G, Senderowicz A . (2004). Cancer Res 64: 743–750.
Dummer R, Roger J, Vogt T, Becker J, Hefner H, Sindermann H et al. (1992). Prog Exp Tumor Res 34: 160–169.
Fry MJ . (2001). Breast Cancer Res 3: 304–312.
Goldstein NI, Prewett M, Zuklys K, Rockwell P, Mendelsohn J . (1995). Clin Cancer Res 1: 1311–1318.
Gonzalez I, Tripathi G, Carter EJ, Cobb LJ, Salih DA, Lovett FA et al. (2004). Mol Cell Biol 24: 3607–3622.
Gratton JP, Morales-Ruiz M, Kureishi Y, Fulton D, Walsh K, Sessa WC . (2001). J Biol Chem 276: 30359–30365.
Hilgard P, Klenner T, Stekar J, Nossner G, Kutscher B, Engel J . (1997). Eur J Cancer 33: 442–446.
Hilgard P, Klenner T, Stekar J, Unger C . (1993). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 32: 90–95.
Jin W, Wu L, Liang K, Liu B, Lu Y, Fan Z . (2003). Br J Cancer 89: 185–191.
Kim AH, Khursigara G, Sun X, Franke TF, Chao MV . (2001). Mol Cell Biol 21: 893–901.
Kim AH, Yano H, Cho H, Meyer D, Monks B, Margolis B et al. (2002). Neuron 35: 697–709.
Knuefermann C, Lu Y, Liu B, Jin W, Liang K, Wu L et al. (2003). Oncogene 22: 3205–3212.
Kondapaka SB, Singh SS, Dasmahapatra GP, Sausville EA, Roy KK . (2003). Mol Cancer Ther 2: 1093–1103.
Li DM, Sun H . (1997). Cancer Res 57: 2124–2129.
Li J, Simpson L, Takahashi M, Miliaresis C, Myers MP, Tonks N et al. (1998). Cancer Res 58: 5667–5672.
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose S, Wang SI et al. (1997). Science 275: 1943–1947.
Liang K, Lu Y, Jin W, Ang KK, Milas L, Fan Z . (2003). Mol Cancer Ther 2: 1113–1120.
Liu B, Fang M, Schmidt M, Lu Y, Mendelsohn J, Fan Z . (2000). Br J Cancer 82: 1991–1999.
Lu Y, Lin YZ, LaPushin R, Cuevas B, Fang X, Yu SX et al. (1999). Oncogene 18: 7034–7045.
Lu Y, Wang H, Mills GB . (2003). Rev Clin Exp Hematol 7: 205–228.
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J . (2000). Oncogene 19: 6550–6565.
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J . (2003). J Clin Oncol 21: 2787–2799.
Park HS, Kim MS, Huh SH, Park J, Chung J, Kang SS et al. (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 2573–2578.
Podsypanina K, Ellenson LH, Nemes A, Gu J, Tamura M, Yamada KM et al. (1999). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 1563–1568.
Prewett M, Rockwell P, Rockwell RF, Giorgio NA, Mendelsohn J, Scher HI et al. (1996). J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol 19: 419–427.
Ruiter GA, Verheij M, Zerp SF, Moolenaar WH, van Blitterswijk WJ . (2002). Int J Cancer 102: 343–350.
Ruiter GA, Zerp SF, Bartelink H, van Blitterswijk WJ, Verheij M . (1999). Cancer Res 59: 2457–2463.
Ruiter GA, Zerp SF, Bartelink H, van Blitterswijk WJ, Verheij M . (2003). Anticancer Drugs 14: 167–173.
She QB, Solit D, Basso A, Moasser MM . (2003). Clin Cancer Res 9: 4340–4346.
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de laPompa JL, Brothers GM, Mirtsos C, Sasaki T et al. (1998). Cell 95: 29–39.
Steck PA, Pershouse MA, Jasser SA, Yung WK, Lin H, Ligon AH et al. (1997). Nat Genet 15: 356–362.
Sun H, Lesche R, Li DM, Liliental J, Zhang H, Gao J et al. (1999). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 6199–6204.
Teng DH, Hu R, Lin H, Davis T, Iliev D, Frye C et al. (1997). Cancer Res 57: 5221–5225.
Terwogt JM, Mandjes IA, Sindermann H, Beijnen JH, Bokkel Huinink WW . (1999). Br J Cancer 79: 1158–1161.
Unger C, Sindermann H, Peukert M, Hilgard P, Engel J, Eibl H . (1992). Prog Exp Tumor Res 34: 153–159.
Van Ummersen L, Binger K, Volkman J, Marnocha R, Tutsch K, Kolesar J et al. (2004). Clin Cancer Res 10: 7450–7456.
Verweij J, Gandia D, Planting AS, Stoter G, Armand JP . (1993). Eur J Cancer 29A: 778–779.
Verweij J, Planting A, van der BM, Stoter G . (1992). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 118: 606–608.
Vlietstra RJ, van Alewijk DC, Hermans KG, van Steenbrugge GJ, Trapman J . (1998). Cancer Res 58: 2720–2723.
Wu X, Senechal K, Neshat MS, Whang YE, Sawyers CL . (1998). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15587–15591.
Zhou X, Lu X, Richard C, Xiong W, Litchfield DW, Bittman R et al. (1996). J Clin Invest 98: 937–944.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Maosheng Huang of the Department of Epidemiology of MD Anderson Cancer Center for assistance with the statistical analyses. This work was supported in part by a generous grant from the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (New York, NY, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Luwor, R., Lu, Y. et al. Enhancement of antitumor activity of the anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab/C225 by perifosine in PTEN-deficient cancer cells. Oncogene 25, 525–535 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209075
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209075
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Phospho-Akt overexpression is prognostic and can be used to tailor the synergistic interaction of Akt inhibitors with gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2017)
-
Proteome and Acetylome Analysis Identifies Novel Pathways and Targets Regulated by Perifosine in Neuroblastoma
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Combination treatment with perifosine and MEK-162 demonstrates synergism against lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
Tumor Biology (2015)
-
The short chain cell-permeable ceramide (C6) restores cell apoptosis and perifosine sensitivity in cultured glioblastoma cells
Molecular Biology Reports (2013)
-
The alkylphospholipid, perifosine, radiosensitizes prostate cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo
Radiation Oncology (2011)