Abstract
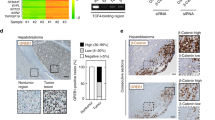
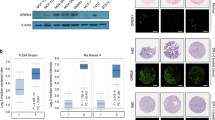
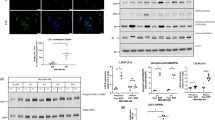
Liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) is a nuclear receptor previously known to have distinct functions during mouse development and essential roles in cholesterol homeostasis. Recently, a new role for LRH-1 has been discovered in tumor progression, giving LRH-1 potential transforming functions. In order to identify critical factors stimulating LRH-1 expression leading to deregulated cellular proliferation, we studied its expression and its regulation in several breast cancer cell lines. We observed that LRH-1 expression was increased in estrogen receptor (ER) α expressing cell lines, whereas weak-to-no expression was found in nonexpressing ERα cell lines. In MCF7, LRH-1 expression was highly induced after treatment with 17β-estradiol (E2). This transcriptional regulation was the result of a direct binding of the ER to the LRH-1 promoter, as demonstrated by gelshift and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. Interestingly, siRNA-mediated inactivation of LRH-1 decreased the E2-dependent proliferation of MCF7 cells. Finally, LRH-1 protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry in tumor cells of human mammary ductal carcinomas. Altogether, these data demonstrate that LRH-1 is transcriptionally regulated by the ER α and reinforce the hypothesis that LRH-1 could exert potential oncogenic effects during breast cancer formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S and Coombes RC . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 101–112.
Annicotte JS, Fayard E, Swift GH, Selander L, Edlund H, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Schoonjans K and Auwerx J . (2003). Mol. Cell Biol., 23, 6713–6724.
Bardin A, Boulle N, Lazennec G, Vignon F and Pujol P . (2004). Endocr. Relat. Cancer., 11, 537–551.
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby C, Brennan T, Wendling O, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Thomas W, Auwerx J and Schoonjans K . (2004). Mol. Cell., 15, 499–509.
Castoria G, Migliaccio A, Bilancio A, Di Domenico M, de Falco A, Lombardi M, Fiorentino R, Varricchio L, Barone MV and Auricchio F . (2001). EMBO. J., 20, 6050–6059.
Castro-Rivera E, Samudio I and Safe S . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 30853–30861.
Cicatiello L, Addeo R, Sasso A, Altucci L, Petrizzi VB, Borgo R, Cancemi M, Caporali S, Caristi S, Scafoglio C, Teti D, Bresciani F, Perillo B and Weisz A . (2004). Mol. Cell Biol., 24, 7260–7274.
Clyne CD, Speed CJ, Zhou J and Simpson ER . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 20591–20597.
Committee NRN . (1999). Cell, 97, 161–163.
Falender AE, Lanz R, Malenfant D, Belanger L and Richards JS . (2003). Endocrinology, 144, 3598–3610.
Fayard E, Auwerx J and Schoonjans K . (2004). Trends Cell Biol., 14, 250–260.
Hinshelwood MM, Repa JJ, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Mangelsdorf DJ and Mendelson CR . (2003). Mol. Cell Endocrinol., 207, 39–45.
Krylova IN, Sablin EP, Moore J, Xu RX, Waitt GM, Mackay JA, Juzumiene D, Bynum JM, Madauss K, Montana V, Lebedeva L, Suzawa M, Williams JD, Williams SP, Guy RK, Thornton JW, Fletterick RJ, Willson TM and Ingraham HA . (2005). Cell, 120, 343–355.
Lazennec G, Bresson D, Lucas A, Chauveau C and Vignon F . (2001). Endocrinology, 142, 4120–4130.
McMahon C, Suthiphongchai T, DiRenzo J and Ewen ME . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 5382–5387.
Neuman E, Ladha MH, Lin N, Upton TM, Miller SJ, DiRenzo J, Pestell RG, Hinds PW, Dowdy SF, Brown M and Ewen ME . (1997). Mol. Cell Biol., 17, 5338–5347.
Pare JF, Malenfant D, Courtemanche C, Jacob-Wagner M, Roy S, Allard D and Belanger L . (2004). J. Biol. Chem., 279, 21206–21216.
Planas-Silva MD and Weinberg RA . (1997). Mol. Cell Biol., 17, 4059–4069.
Prall OW, Sarcevic B, Musgrove EA, Watts CK and Sutherland RL . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 10882–10894.
Sabbah M, Courilleau D, Mester J and Redeuilh G . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 11217–11222.
Sablin EP, Krylova IN, Fletterick RJ and Ingraham HA . (2003). Mol. Cell., 11, 1575–1585.
Schoonjans K, Dubuquoy L, Mebis J, Fayard E, Wendling O, Haby C, Geboes K and Auwerx J . (2005). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA.
Zhou J, Suzuki T, Kovacic A, Saito R, Miki Y, Ishida T, Moriya T, Simpson ER, Sasano H and Clyne CD . (2005). Cancer Res., 65, 657–663.
Zwijsen RM, Buckle RS, Hijmans EM, Loomans CJ and Bernards R . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 3488–3498.
Zwijsen RM, Wientjens E, Klompmaker R, van der Sman J, Bernards R and Michalides RJ . (1997). Cell, 88, 405–415.
Acknowledgements
Helpful discussions with Dr M Esslimani-Sahla and members of the Fajas lab are greatly appreciated. We thank Fanja Rabeolina for excellent technical help and the Vector Core of the University Hospital of Nantes for the production of adenovirus. This work was supported by grants from INSERM, CHU de Montpellier, Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer, and Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale. JSA is supported by post-doctoral fellowships from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (2004) and the INSERM (2005). CC is supported by a post-doctoral fellowship from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer. This work is dedicated to the memory of the coauthor F Vignon, deceased while the manuscript was in preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Annicotte, JS., Chavey, C., Servant, N. et al. The nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 is an estrogen receptor target gene. Oncogene 24, 8167–8175 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208950
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208950
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Liver receptor homolog-1: structures, related diseases, and drug discovery
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2024)
-
Expression of NR5A2, NUP153, HNF4A, USP15 and FNDC3B is consistent with their use as novel biomarkers for bovine mammary stem/progenitor cells
Journal of Molecular Histology (2021)
-
Exploiting vulnerabilities of cancer by targeting nuclear receptors of stromal cells in tumor microenvironment
Molecular Cancer (2019)
-
Regulation of liver receptor homologue-1 by DDB2 E3 ligase activity is critical for hepatic glucose metabolism
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
LRH1 enhances cell resistance to chemotherapy by transcriptionally activating MDC1 expression and attenuating DNA damage in human breast cancer
Oncogene (2018)