Abstract
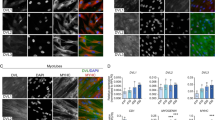
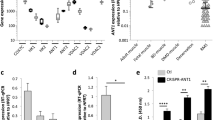
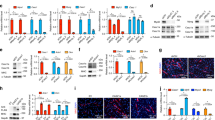
The membrane-anchored MMP-regulator RECK is down regulated in many solid tumors; the extent of RECK down regulation correlates with poor prognosis. Forced expression of RECK in tumor cells results in suppression of angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Studies on the roles and the mechanisms of regulation of the RECK gene during normal development may therefore yield important insights into how the malignant behaviors of tumor cells arise and how they can be controlled. Our previous studies indicate that mice lacking RECK die around E10.5 with reduced tissue integrity. In the present study, we have found that in later stage wild-type embryos, RECK is abundantly expressed in skeletal muscles, especially in the areas where the myoblast differentiation factor MRF4 is expressed. Consistent with this finding, the RECK-promoter is activated by MRF4 in cultured cells. In contrast, a myoblast determination factor MyoD suppresses the RECK-promoter. Myoblastic cells lacking RECK expression give rise to myotubes at higher efficiency than the cells expressing RECK, indicating that RECK suppresses myotube formation. These findings suggest that MyoD down regulates RECK to facilitate myotube formation, whereas MRF4 up regulates RECK to promote other aspects of myogenesis that require extracellular matrix integrity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biesiada E, Hamamori Y, Kedes L and Sartorelli V . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 2577–2584.
Birk DE and Mayne R . (1997). Eur. J. Cell Biol., 72, 352–361.
Blau HM, Pavlath GK, Hardeman EC, Chiu CP, Silberstein L, Webster SG, Miller SC and Webster C . (1985). Science, 230, 758–766.
Braun T, Bober E, Winter B, Rosenthal N and Arnold HH . (1990). EMBO J., 9, 821–831.
Braun T, Buschhausen-Denker G, Bober E, Tannich E and Arnold HH . (1989). EMBO J., 8, 701–709.
Buckingham M, Bajard L, Chang T, Daubas P, Hadchouel J, Meilhac S, Montarras D, Rocancourt D and Relaix F . (2003). J. Anat., 202, 59–68.
Caron NJ, Asselin I, Morel G and Tremblay JP . (1999). Cell Transplant., 8, 465–476.
Chang T, Primig M, Hadchouel J, Tajbakhsh S, Rocancourt D, Fernandez A, Kappler R, Scherthan H and Buckingham M . (2004). Dev. Biol., 269, 595–608.
Chen EH and Olson EN . (2004). Trends Cell Biol., 14, 352–460.
Chin JR and Werb Z . (1997). Development, 124, 1519–1530.
Couch CB and Strittmatter WJ . (1983). Cell, 32, 257–265.
Davis RL, Weintraub H and Lassar AB . (1987). Cell, 51, 987–1000.
Edmondson DG and Olson EN . (1989). Genes Dev., 3, 628–640.
El Fahime E, Torrente Y, Caron NJ, Bresolin MD and Tremblay JP . (2000). Exp. Cell Res., 258, 279–287.
Ferguson JW, Thoma BS, Mikesh MF, Kramer RH, Bennett KL, Purchio A, Bellard BJ and LeBaron RG . (2003). Cell Tissue Res., 313, 93–105.
Fomin M, Nomokonova N and Arnold H-H . (2004). Dev. Biol., 272, 498–509.
Horsley V and Pavlath GK . (2004). Cells Tissues Organs, 176, 67–78.
Kassar-Duchossoy L, Gayraud-Morel B, Gomes D, Rocancourt D, Buckingham M, Shinin V and Tajbakhsh S . (2004). Nature, 431, 466–471.
Lewis MP, Tippett HL, Sinanan AC, Morgan MJ and Hunt NP . (2000). J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil., 21, 223–233.
Miner JH and Wold B . (1990). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 1089–1093.
Novitch BG, Mulligan GJ, Jacks T and Lassar AB . (1996). J. Cell Biol., 135, 441–456.
Oh J, Takahashi R, Adachi E, Kondo S, Kuratomi S, Noma A, Alexander DB, Motoda H, Okada A, Seiki M, Itoh T, Itohara S, Takahashi C and Noda M . (2004). Oncogene, 23, 5041–5048.
Oh J, Takahashi R, Kondo S, Mizoguchi A, Adachi E, Sasahara RM, Nishimura S, Imamura Y, Kitayama H, Alexander DB, Ide C, Horan T, Arakawa T, Yoshida S, Mishikawa S, Itoh Y, Seiki M, Takahashi C and Noda M . (2001). Cell, 107, 789–800.
Osses N and Brandan E . (2002). Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 282, C383–C394.
Rhodes SJ and Konieczny SF . (1989). Genes Dev., 3, 2050–2061.
Sasahara RM, Takahashi C and Noda M . (1999). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 264, 668–675.
Schollmeyer JE . (2003). Exp. Cell Res., 162, 411–422.
Takahashi C, Sheng Z, Horan TP, Kitayama H, Maki M, Hitomi K, Kitaura Y, Takai S, Sasahara RM, Horimoto A, Ikawa Y, Ratzkin BJ, Arakawa T and Noda M . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 13221–13226.
Tidball JG . (1994). Dev. Biol., 163, 447–456.
Vinals F, Fandos C, Santalucia T, Ferre J, Testar X, Palacin M and Zorzano A . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 12913–12921.
Yaffe D and Saxel O . (1977). Nature, 270, 725–727.
Yagami-Hiromasa T, Sato T, Kurisaki T, Kamijo K, Nabeshima Y and Fujisawa-Sehara A . (1995). Nature, 377, 652–656.
Zhu Z and Miller JB . (1997). Dev. Dyn., 209, 233–241.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Shigeyoshi Itohara and Motoharu Seiki for providing MMP-deficient mice, Drs Harold Weintraub, Stephen F Konieczny, Jeong Yoon, Yoichi Nabeshima, and Woodring E Wright for providing MRF cDNAs, and Ms Mari Kojima for the advise on histological techniques. This work was supported by grants from MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Echizenya, M., Kondo, S., Takahashi, R. et al. The membrane-anchored MMP-regulator RECK is a target of myogenic regulatory factors. Oncogene 24, 5850–5857 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208733
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208733
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Impact of Reck expression and promoter activity in neuronal in vitro differentiation
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)
-
E-cadherin–downregulation and RECK-upregulation are coupled in the non-malignant epithelial cell line MCF10A but not in multiple carcinoma-derived cell lines
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Estrogen suppresses expression of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) within the mouse uterus
Endocrine (2012)
-
A systematic analysis of the skeletal muscle miRNA transcriptome of chicken varieties with divergent skeletal muscle growth identifies novel miRNAs and differentially expressed miRNAs
BMC Genomics (2011)
-
Involvement of the Reck tumor suppressor protein in maternal and embryonic vascular remodeling in mice
BMC Developmental Biology (2010)