Abstract
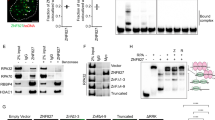
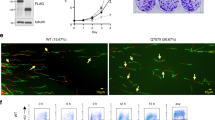
p53-binding protein 1 (53BP1) acts as an ‘adaptor/mediator’ for transducing DNA damage signals, especially following detection of DNA double-strand breaks. In an effort to broaden our understanding of the protein network surrounding 53BP1, we isolated possible 53BP1 binding partners by co-immunoprecipitation, and identified them via tandem mass spectrometric analysis. The 53BP1-associated proteins included RPA1 and RPA2, two components of the replication protein A (RPA) complex. The presence of RPA components in the immunoprecipitates was confirmed by immunoblotting, and we found that the association between 53BP1 and RPA2 was disrupted following DNA damage induced by treatment with camptothecin, a topoisomerase I inhibitor. To investigate the functional meaning of the 53BP1 and RPA interaction, we established U2OS osteosarcoma cell lines stably expressing dominant-negative fragments of 53BP1. We found that camptothecin-induced RPA2 phosphorylation was inhibited in these cells, and also following 53BP1 knockdown by siRNA transfection. On the cellular level, camptothecin-induced apoptosis was augmented in the dominant-negative cell lines, resulting in increased chemosensitivity to this drug. Taken together, these results suggest that 53BP1 is involved in DNA damage-induced RPA2 hyperphosphorylation, and inhibition of 53BP1 function may sensitize cancer cells to camptothecin treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson L, Henderson C and Adachi Y . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 1719–1729.
Carty MP, Zernik-Kobak M, McGrath S and Dixon K . (1994). EMBO J., 13, 2114–2123.
Din S, Brill SJ, Fairman MP and Stillman B . (1990). Genes Dev., 4, 968–977.
DiTullio Jr RA, Mochan TA, Venere M, Bartkova J, Sehested M, Bartek J and Halazonetis TD . (2002). Nat. Cell Biol., 4, 998–1002.
Emili A . (1998). Mol. Cell, 2, 183–189.
Fairman MP and Stillman B . (1988). EMBO J., 7, 1211–1218.
Fedier A, Steiner RA, Schwarz VA, Lenherr L, Haller U and Fink D . (2003). Int. J. Oncol., 22, 1169–1173.
Gately DP, Hittle JC, Chan GK and Yen TJ . (1998). Mol. Biol. Cell, 9, 2361–2374.
Goldberg M, Stucki M, Falck J, D’Amours D, Rahman D, Pappin D, Bartek J and Jackson SP . (2003). Nature, 421, 952–956.
Iftode C, Daniely Y and Borowiec JA . (1999). Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 34, 141–180.
Iwabuchi K, Bartel PL, Li B, Marraccino R and Fields S . (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 6098–6102.
Iwabuchi K, Li B, Massa HF, Trask BJ, Date T and Fields S . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 26061–26068.
Khanna KK and Jackson SP . (2001). Nat. Genet., 27, 247–254.
Kraakman-van der Zwet M, Overkamp WJ, Friedl AA, Klein B, Verhaegh GW, Jaspers NG, Midro AT, Eckardt-Schupp F, Lohman PH and Zdzienicka MZ . (1999). Mutat. Res., 434, 17–27.
Lee CH and Chung JH . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 30537–30541.
Liu VF and Weaver DT . (1993). Mol. Cell Biol., 13, 7222–7231.
Melo J and Toczyski D . (2002). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 14, 237–245.
Niu H, Erdjument-Bromage H, Pan ZQ, Lee SH, Tempst P and Hurwitz J . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 12634–12641.
Peng A and Chen PL . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 8873–8876.
Pizzolato JF and Saltz LB . (2003). Lancet, 361, 2235–2242.
Rappold I, Iwabuchi K, Date T and Chen J . (2001). J. Cell Biol., 153, 613–620.
Schultz LB, Chehab NH, Malikzay A and Halazonetis TD . (2000). J. Cell Biol., 151, 1381–1390.
Shao RG, Cao CX, Zhang H, Kohn KW, Wold MS and Pommier Y . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 1397–1406.
Smith PJ, Makinson TA and Watson JV . (1989). Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 55, 217–231.
Stewart GS, Wang B, Bignell CR, Taylor AM and Elledge SJ . (2003). Nature, 421, 961–966.
Sun Z, Hsiao J, Fay DS and Stern DF . (1998). Science, 281, 272–274.
Vialard JE, Gilbert CS, Green CM and Lowndes NF . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 5679–5688.
Wang B, Matsuoka S, Carpenter PB and Elledge SJ . (2002). Science, 298, 1435–1438.
Wang H, Guan J, Perrault AR, Wang Y and Iliakis G . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 8554–8563.
Wold MS . (1997). Annu. Rev. Biochem., 66, 61–92.
Wold MS and Kelly T . (1988). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 85, 2523–2527.
Xia Z, Morales JC, Dunphy WG and Carpenter PB . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 2708–2718.
Yarden RI, Pardo-Reoyo S, Sgagias M, Cowan KH and Brody LC . (2002). Nat. Genet., 30, 285–289.
Zernik-Kobak M, Vasunia K, Connelly M, Anderson CW and Dixon K . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 23896–23904.
Zhou BB and Elledge SJ . (2000). Nature, 408, 433–439.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research grants from the National Cancer Center (0110170 and 0410051) and by Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2001-041-D00238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, E., Kim, B., Lee, S. et al. 53BP1 is associated with replication protein A and is required for RPA2 hyperphosphorylation following DNA damage. Oncogene 24, 5423–5430 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208710
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208710
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prospective use of the single-mouse experimental design for the evaluation of PLX038A
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2020)
-
Plk1-mediated stabilization of 53BP1 through USP7 regulates centrosome positioning to maintain bipolarity
Oncogene (2017)
-
Control of gene editing by manipulation of DNA repair mechanisms
Mammalian Genome (2017)
-
RPA-coated single-stranded DNA as a platform for post-translational modifications in the DNA damage response
Cell Research (2015)
-
Immunoglobulin class-switch DNA recombination: induction, targeting and beyond
Nature Reviews Immunology (2012)