Abstract
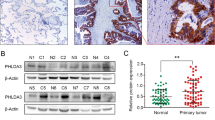
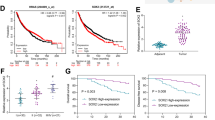
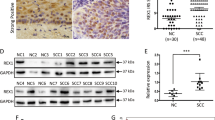
By using microarray and an invasion/metastasis lung cell line model, we identified the DnaJ-like heat shock protein 40, HLJ1, and found that the expression of HLJ1 correlates negatively with cancer cell invasion ability. Overexpression of HLJ1 can suppress cancer cell invasion in vitro. We further characterize the putative promoter region and investigate the transcriptional regulations of human HLJ1. A serial deletion of the 1.2 kb at the 5′-flanking region of the human HLJ1 gene was subcloned into a vector containing reporter gene and transfected into human lung adenocarcinoma cell line CL1-0, followed by luciferase activity assay. The results indicated that the region from –232 to +176 could drive the basal transcriptional activity of the HLJ1 gene. Sequence analysis of the HLJ1 gene promoter region showed absence of a TATA box, but identified an inverted CCAAT box and four YY1 transcriptional factor-binding sites, which may be important in the regulation of HLJ1 expression. Co-transfection of the YY1 and HLJ1 basal promoter regions, site-directed mutagenesis, and electrophoretic mobility shift assay confirmed that YY1 could upregulate HLJ1 basal promoter activity. Furthermore, we also demonstrated that overexpression of YY1 in CL1-0 cells can increase HLJ1 expression and reduce cell invasive capability. The reduction of cancer cell invasive ability is, at least in part, through upregulation of E-cadherin expression. The increase in HLJ1 and E-cadherin expression, as well as the suppression of invasion ability, can be reversed specifically by HLJ1 siRNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austen M, Cerni C, Luscher-Firzlaff JM and Luscher B . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 511–520.
Azizkhan JC, Jensen DE, Pierce AJ and Wade M . (1993). Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr., 3, 229–254.
Berx G, Becker KF, Hofler H and Van Roy F . (1998). Hum. Mutat., 12, 226–237.
Birch M, Mitchell S and Hart IR . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 6660–6667.
Bird AP . (1986). Nature, 321, 209–213.
Bremnes RM, Veve R, Hirsch FR and Franklin WA . (2002). Lung Cancer, 36, 115–124.
Bukholm IK, Nesland JM, Karesen R, Jacobsen U and Borresen-Dale AL . (1998). J. Pathol., 185, 262–266.
Caroline J and Richard IM . (2000). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 92, 1564–1572.
Chen JJW, Peck K, Hong TM, Yang SC, Sher YP, Shih JY, Wu R, Cheng JL, Roffler SR, Wu CW and Yang PC . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 5223–5230.
Chen JJW, Yao PL, Yuan A, Hong TM, Shun CT, Kuo ML, Lee YC and Yang PC . (2003). Clin. Cancer Res., 9, 729–737.
Chen HW, Chien CT, Yu SL, Lee YT and Chen WJ . (2002). Br. J. Pharmacol., 137, 771–781.
Chu YW, Yang PC, Yang SC, Shyu YC, Hendrix MJC, Wu R and Wu CW . (1997). Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 17, 353–360.
Craig EA, Weissman JS and Horwich AL . (1994). Cell, 78, 365–372.
Ficzycz A and Ovsenek N . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 8382–8387.
Galvin KM and Shi Y . (1997). Mol. Cell Biol., 17, 3723–3732.
Georgopoulos C . (1992). Trends Biochem. Sci., 17, 295–299.
Gottesman S, Wickner S and Maurizi MR . (1997). Genes Dev., 11, 815–823.
Guo B, Aslam F, van Wijnen AJ, Roberts SGE, Frenkel B, Green MR, Deluca H, Lian JB, Stein GS and Stein JL . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 121–126.
Hajra KM, Chen DY and Fearon ER . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 1613–1618.
Hariharan N, Kelley DE and Perry RP . (1991). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 88, 9799–9803.
Hamajima F, Hasegawa T, Nakashima I and Isobe KI . (2002). J. Cell. Biochem., 84, 401–404.
Hartl FU . (1996). Nature, 381, 571–580.
Hattori H, Liu YC, Tohnai I, Ueda M, Kaneda T, Kobayashi T, Tanabe K and Ohtsuka K . (1992). Cell Struct. Funct., 17, 77–86.
Hehlgans T and Strominger JL . (1995). J. Immunol., 154, 5181–5187.
Heinemeyer T, Chen X, Karas H, Kel AE, Kel OV, Liebich I, Meinhardt T, Reuter I, Schacherer F and Wingender E . (1999). Nucleic Acids Res., 27, 318–322.
Hendric JP and Hartl FU . (1993). Annu. Rev. Biochem., 62, 349–384.
Hirohashi S . (1998). Am. J. Pathol., 153, 333–339.
Hoe KL, Won M, Chung KS, Jang YJ, Lee SB, Kim DU, Lee JW, Yun JH and Yoo HS . (1998). Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1383, 4–8.
Lee JS, Galvin KM, See RH, Eckner R, Livingston D, Moran E and Shi Y . (1995). Genes Dev., 9, 1188–1198.
Li WW, Hsiung Y, Wong V, Galvin K, Zhou Y, Shi Y and Lee AS . (1997a). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 61–68.
Li WW, Hsiung Y, Zhou Y, Roy B and Lee AS . (1997b). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 54–60.
Liotta LA, Steeg PS and Stetler-Stevenson WG . (1991). Cell, 64, 327–336.
Lu S-Y, Rodriguez M and Liao WS-L . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 6253–6263.
Mantovani R . (1998). Nucleic Acids Res., 26, 1135–1143.
Matz M, Shagin D, Bogdanova E, Britanova O, Lukyanov S, Diatchenko L and Chenchik A . (1999). Nucleic Acids Res., 27, 1558–1560.
Meier VS and Groner B . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 128–137.
Natesan S and Gilman MZ . (1993). Genes Dev., 7, 2497–2509.
Ohtsuka K . (1993). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 197, 235–240.
Ohtsuka K and Hata M . (2000). Cell Stress Chaperones., 5, 98–112.
Prestridge DS . (1991). CABIOS, 7, 203–206.
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E and Werner T (MatInd and MatInspector) (1995). Nucleic Acids Res., 23, 4878–4884.
Riggs KJ, Saleque S, Wong KK, Merrell KT, Lee JS, Shi Y and Calame K . (1993). Mol. Cell. Biol., 13, 7487–7495.
Seto E, Shi Y and Shenk T . (1991). Nature, 354, 241–245.
Shi Y, Lee JS and Galvin KM . (1997). Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1332, F49–F66.
Shi Y, Seto E, Chang LS and Shenk T . (1991). Cell, 67, 377–388.
Shih JY, Yang SC, Hong TM, Yuan A, Chen JJW, Yu CJ, Chang YL, Lee YC, Peck K, Wu CW and Yang PC . (2001). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 93, 1392–1400.
Sreenath T, Matrisian LM, Stetler-Stevenson W, Gattoni-Celli S and Pozzatti RO . (1992). Cancer Res., 52, 4942–4947.
Takeichi M . (1991). Science, 251, 1451–1455.
Thomas MJ and Seto E . (1999). Gene, 236, 197–208.
Uleminckx K, Vackat L, Mareel M, Fiers W and Von Roy F . (1991). Cell, 66, 107–119.
Usheva A and Shenk T . (1994). Cell, 76, 1115–1121.
Welch WJ . (1992). Physiol. Rev., 72, 1063–1081.
Yao YL, Yang WM and Seto E . (2001). Mol. Cell Biol., 21, 5979–5991.
Zhou Q and Engel DA . (1995). J. Virol., 69, 7402–7409.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Council and National Health Research Institutes of the Republic of China through the National Research Program for Genomic Medicine grants (NSC91-3112-P-005-008-Y, NHRI92A1-NSCLC09-5, and NHRI93A1-NSCLC09-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, CC., Tsai, MF., Hong, TM. et al. The transcriptional factor YY1 upregulates the novel invasion suppressor HLJ1 expression and inhibits cancer cell invasion. Oncogene 24, 4081–4093 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208573
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208573
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Heat shock protein paradigms in cancer progression: future therapeutic perspectives
3 Biotech (2024)
-
MicroRNAs as the critical regulators of Doxorubicin resistance in breast tumor cells
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
DNAJB9 suppresses the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by promoting FBXO45-mediated degradation of ZEB1
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
MicroRNA-140 impedes DNA repair by targeting FEN1 and enhances chemotherapeutic response in breast cancer
Oncogene (2020)
-
Pulmonary administration of curcumin inhibits B16F10 melanoma lung metastasis and invasion in mice
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2018)