Abstract
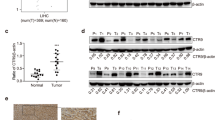
Cyr61 is a secreted, cysteine-rich, heparin-binding protein that mediates diverse functions including extracellular matrix formation, differentiation, cell proliferation, adhesion, migration, survival, as well as angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. In this study, we found that Cyr61 gene expression is significantly downregulated in the tumors of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. To elucidate its mechanism of gene regulation, we examined the promoter of Cyr61 which contains two long stretches of repeats, each comprising d(CA) dinucleotide repeats downstream of HNF3β- and ATF-binding sites. We hypothesized that the d(CA) repeats may play an important role in regulating Cyr61 promoter activity and performed promoter reporter assays to examine this. We found that a greater number of d(CA) repeats resulted in significantly lower promoter activity of the Cyr61 gene in the KB3-1 and HepG2 cell lines, but not in the MCF-7 cell line. In addition, the d(CA) repeats, but not other random sequences, were found to be important for Cyr61 promoter activity. We further demonstrate that the ATF- and HNF3β-binding sites upstream the d(CA) repeats positively and negatively modulate Cyr61 promoter activity, respectively. An examination of the d(CA) dinucleotide patterns in the Cyr61 promoter in HCC patients revealed that ∼32% of these patients exhibited either loss of heterozygosity or somatic mosaicism in either the tumors, adjacent normal liver tissues or both.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babic AM, Kireeva ML, Kolesnikova TV and Lau LF . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 6355–6360.
Borrmann L, Seebeck B, Rogalla P and Bullerdiek J . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 756–760.
Brigstock DR . (1999). Endocr. Rev., 20, 189–206.
Brigstock DR, Goldschmeding R, Katsube KI, Lam SC, Lau LF, Lyons K, Naus C, Perbal B, Riser B, Takigawa M and Yeger H . (2003). Mol. Pathol., 56, 127–128.
Chen BP, Liang G, Whelan J and Hai T . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 15819–15826.
Chen N, Chen CC and Lau LF . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 24953–24961.
Gebhardt F, Zanker KS and Brandt B . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 13176–13180.
Gehring M, Berthold F, Edler L, Schwab M and Amler LC . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 5366–5369.
Grzeszkiewicz TM, Kirschling DJ, Chen N and Lau LF . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 21943–21950.
Hainsworth PJ, Raphael KL, Stillwell RG, Bennett RC and Garson OM . (1992). Br. J. Cancer, 66, 131–135.
Hamada H, Seidman M, Howard BH and Gorman CM . (1984). Mol. Cell. Biol., 4, 2622–2630.
Hirasaki S, Koide N, Ujike K, Shinji T and Tsuji T . (2001). Hepatol. Res., 19, 294–305.
Huang TS, Lee CC, Chang AC, Lin S, Chao CC, Jou YS, Chu YW, Wu CW and Whang-Peng J . (2003). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 300, 901–907.
Jay P, Berge-Lefranc JL, Marsollier C, Mejean C, Taviaux S and Berta P . (1997). Oncogene, 14, 1753–1757.
Jedsadayanmata A, Chen CC, Kireeva ML, Lau LF and Lam SC . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 24321–24327.
Kireeva ML, Lam SC and Lau LF . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 3090–3096.
Latinkic BV, O'Brien TP and Lau LF . (1991). Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 3261–3267.
Lau LF and Lam SC . (1999). Exp. Cell Res., 248, 44–57.
Lee CG, Ramachandra M, Jeang KT, Martin MA, Pastan I and Gottesman MM . (2000). FASEB J., 14, 516–522.
Lee CG, Ren J, Cheong IS, Ban KH, Ooi LL, Yong Tan S, Kan A, Nuchprayoon I, Jin R, Lee KH, Choti M and Lee LA . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 2592–2603.
Menendez JA, Mehmi I, Griggs DW and Lupu R . (2003). Endocrine-Relat. Cancer, 10, 141–152.
Miyashita A, Crystal RG and Hay JG . (1995). Nucleic Acids Res., 23, 293–301.
Mori Y, Folco E and Koren G . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 27788–27796.
Naylor LH and Clark EM . (1990). Nucleic Acids Res., 18, 1595–1601.
O'Brien TP, Yang GP, Sanders L and Lau LF . (1990). Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 3569–3577.
Perbal B . (2001). Mol. Pathol., 54, 103–104.
Peters DG, Kassam A, St Jean PL, Yonas H and Ferrell RE . (1999). Stroke, 30, 2612–2616.
Pilarsky CP, Schmidt U, Eissrich C, Stade J, Froschermaier SE, Haase M, Faller G, Kirchner TW and Wirth MP . (1998). Prostate, 36, 85–91.
Rich A . (1993). Gene, 135, 99–109.
Rich A, Nordheim A and Wang AH . (1984). Annu. Rev. Biochem., 53, 791–846.
Rothenburg S, Koch-Nolte F, Rich A and Haag F . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 8985–8990.
Rotwein P, Pollock KM, Didier DK and Krivi GG . (1986). J. Biol. Chem., 261, 4828–4832.
Sampath D, Winneker RC and Zhang Z . (2001a). Endocrinology, 142, 2540–2548.
Sampath D, Zhu Y, Winneker RC and Zhang Z . (2001b). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 86, 1707–1715.
Schroth GP, Chou PJ and Ho PS . (1992). J. Biol. Chem., 267, 11846–11855.
Schutze N, Rucker N, Muller J, Adamski J and Jakob F . (2001). Mol. Pathol., 54, 170–175.
Schwartz T, Behlke J, Lowenhaupt K, Heinemann U and Rich A . (2001). Nat. Struct. Biol., 8, 761–765.
Schwartz T, Rould MA, Lowenhaupt K, Herbert A and Rich A . (1999). Science, 284, 1841–1845.
Shimajiri S, Arima N, Tanimoto A, Murata Y, Hamada T, Wang KY and Sasaguri Y . (1999). FEBS Lett., 455, 70–74.
Shin E, Fujita S, Takami K, Kurahashi H, Kurita Y, Kobayashi T, Mori T, Nishisho I and Takai S . (1993). Jpn. J. Cancer Res., 84, 402–408.
Simon D, Knowles BB and Weith A . (1991). Oncogene, 6, 765–770.
Tae HJ, Luo X and Kim KH . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 10475–10484.
Tong X, Xie D, O'Kelly J, Miller CW, Muller-Tidow C and Koeffler HP . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 47709–47714.
Tsai MS, Bogart DF, Castaneda JM, Li P and Lupu R . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 8178–8185.
Tsai MS, Hornby AE, Lakins J and Lupu R . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 5603–5607.
Wells RD . (1988). J. Biol. Chem., 263, 1095–1098.
Xie D, Miller CW, O'Kelly J, Nakachi K, Sakashita A, Said JW, Gornbein J and Koeffler HP . (2001a). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 14187–14194.
Xie D, Nakachi K, Wang H, Elashoff R and Koeffler HP . (2001b). Cancer Res., 61, 8917–8923.
Xu L, Hui L, Wang S, Gong J, Jin Y, Wang Y, Ji Y, Wu X, Han Z and Hu G . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 3176–3181.
Yang GP and Lau LF . (1991). Cell Growth Differ., 2, 351–357.
Yu H, Li BD, Smith M, Shi R, Berkel HJ and Kato I . (2001). Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 70, 117–122.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by block grants from the National Medical Research Council, Singapore and the SingHealth Cluster Research Fund through the National Cancer Center to CGL Lee and an academic research grant from the National University of Singapore to CGL Lee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Ren, J., Ooi, L. et al. Dinucleotide repeats negatively modulate the promoter activity of Cyr61 and is unstable in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Oncogene 24, 3999–4008 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208550
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208550
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ATF3 inhibits the tumorigenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via upregulation of CYR61 expression
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)
-
CCN1 promotes tumorigenicity through Rac1/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer
Tumor Biology (2012)
-
LIMD1 is more frequently altered than RB1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: clinical and prognostic implications
Molecular Cancer (2010)
-
The matricellular protein CCN1 induces fibroblast senescence and restricts fibrosis in cutaneous wound healing
Nature Cell Biology (2010)
-
Nucleotide sequence analyses of the MRP 1 gene in four populations suggest negative selection on its coding region
BMC Genomics (2006)