Abstract
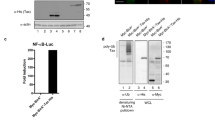
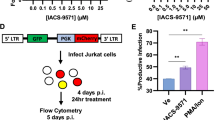
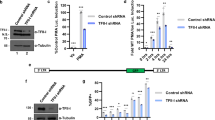
Disruption of transcriptional control of cellular genes by human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV-1) is thought to be associated, at least in part, with the development of adult T-cell leukemia. It has been reported that activating protein-1 (AP-1) is dysregulated by HTLV-1 infection. HTLV-1-encoded Tax elevates AP-1 activity through the induction of AP-1 family member gene expression, including c-Jun, JunD, c-Fos, and Fra-1. However, the precise mechanism by which HTLV-1 regulates AP-1 activity remains to be addressed. Recently, a novel viral protein named HTLV-1 basic leucine-zipper factor, HBZ, has been shown to interact with c-Jun and repress c-Jun-mediated transcription by abrogating its DNA-binding activity. In the course of investigating HBZ function, we found that HBZ reduced the steady-state levels of c-Jun, and the levels were restored by treatment with a proteasome inhibitor. Together, this indicates that HBZ promotes c-Jun degradation through a proteasome-dependent pathway. Furthermore, HBZ deletion mutants revealed that both the N-terminal and leucine-zipper region of HBZ were required for the elimination of c-Jun. These results suggest dual effects of HBZ on the suppression of AP-1 activity by inhibiting c-Jun function, which may contribute to the dysregulation of cell proliferation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi T and Shimotohno K . (1993). J. Virol., 67, 1211–1217.
Albrecht B and Lairmore MD . (2002). Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 66, 396–406, table of contents.
Basbous J, Arpin C, Gaudray G, Piechaczyk M, Devaux C and Mesnard JM . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 43620–43627.
Curtiss VE, Smilde R and McGuire KL . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 3567–3575.
Derijard B, Hibi M, Wu IH, Barrett T, Su B, Deng T, Karin M and Davis RJ . (1994). Cell, 76, 1025–1037.
Fu W, Shah SR, Jiang H, Hilt DC, Dave HP and Joshi JB . (1997). J. Neurovirol., 3, 16–27.
Fujii M, Niki T, Mori T, Matsuda T, Matsui M, Nomura N and Seiki M . (1991). Oncogene, 6, 1023–1029.
Fujii M, Sassone-Corsi P and Verma IM . (1988). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 85, 8526–8530.
Gaudray G, Gachon F, Basbous J, Biard-Piechaczyk M, Devaux C and Mesnard JM . (2002). J. Virol., 76, 12813–12822.
Grassmann R, Berchtold S, Radant I, Alt M, Fleckenstein B, Sodroski JG, Haseltine WA and Ramstedt U . (1992). J. Virol., 66, 4570–4575.
Hooper WC, Rudolph DL, Lairmore MD and Lal RB . (1991). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 181, 976–980.
Huibregtse JM, Scheffner M and Howley PM . (1991). EMBO J., 10, 4129–4135.
Iwai K, Mori N, Oie M, Yamamoto N and Fujii M . (2001). Virology, 279, 38–46.
Larocca D, Chao LA, Seto MH and Brunck TK . (1989). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 163, 1006–1013.
Mori N, Fujii M, Iwai K, Ikeda S, Yamasaki Y, Hata T, Yamada Y, Tanaka Y, Tomonaga M and Yamamoto N . (2000). Blood, 95, 3915–3921.
Mori N, Mukaida N, Ballard DW, Matsushima K and Yamamoto N . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 3993–4000.
Mukaida N, Morita M, Ishikawa Y, Rice N, Okamoto S, Kasahara T and Matsushima K . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 13289–13295.
Pozzatti R, Vogel J and Jay G . (1990). Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 413–417.
Querido E, Blanchette P, Yan Q, Kamura T, Morrison M, Boivin D, Kaelin WG, Conaway RC, Conaway JW and Branton PE . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 3104–3117.
Scheffner M, Huibregtse JM, Vierstra RD and Howley PM . (1993). Cell, 75, 495–505.
Stopak K, de Noronha C, Yonemoto W and Greene WC . (2003). Mol. Cell., 12, 591–601.
Tanaka A, Takahashi C, Yamaoka S, Nosaka T, Maki M and Hatanaka M . (1990). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 1071–1075.
Thebault S, Basbous J, Hivin P, Devaux C and Mesnard JM . (2004). FEBS Lett., 562, 165–170.
Treier M, Staszewski LM and Bohmann D . (1994). Cell, 78, 787–798.
Uchijima M, Sato H, Fujii M and Seiki M . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 14946–14950.
Uchiyama T . (1997). Annu. Rev. Immunol., 15, 15–37.
Yamagata T, Mitani K, Ueno H, Kanda Y, Yazaki Y and Hirai H . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 4272–4281.
Yamaoka S, Inoue H, Sakurai M, Sugiyama T, Hazama M, Yamada T and Hatanaka M . (1996). EMBO J., 15, 873–887.
Yu X, Yu Y, Liu B, Luo K, Kong W, Mao P and Yu XF . (2003). Science, 302, 1056–1060.
Zimmermann H, Degenkolbe R, Bernard HU and O'Connor MJ . (1999). J. Virol., 73, 6209–6219.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs N Mukaida and M Hatanaka for p2 × AP-1-Luc and pH2R-Tax, respectively. We also thank members of the Laboratory of Human Tumor Viruses for helpful advice and discussion. This work was supported by grants-in-aid for cancer research and for the second-term comprehensive 10-year strategy for cancer control from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, and grants-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, and grants-in-aid of research for the future from the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science. JM was supported by the 21st Century COE Program of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to Graduate School of Biostudies and Institute for Virus Research, Kyoto University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, J., Ohshima, T., Isono, O. et al. HTLV-1 HBZ suppresses AP-1 activity by impairing both the DNA-binding ability and the stability of c-Jun protein. Oncogene 24, 1001–1010 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208297
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208297
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multifaceted functions and roles of HBZ in HTLV-1 pathogenesis
Retrovirology (2016)
-
HTLV-1 subgroups associated with the risk of HAM/TSP are related to viral and host gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, independent of the transactivation functions of the viral factors
Journal of NeuroVirology (2016)
-
HTLV-1 HBZ positively regulates the mTOR signaling pathway via inhibition of GADD34 activity in the cytoplasm
Oncogene (2014)
-
Development of T cell lymphoma in HTLV-1 bZIP factor and Tax double transgenic mice
Archives of Virology (2014)
-
HTLV-1 bZIP factor supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells through suppression of C/EBPα signaling
Retrovirology (2013)