Abstract
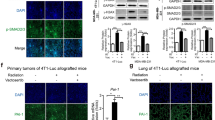
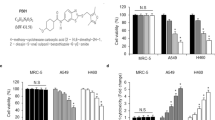
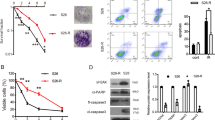
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) has been implicated as a promising anticancer agent by inhibiting cell growth and inducing apoptosis in certain types of cancer cells. This study explored the antimetastasis property of arsenic, drew potential link between arsenic use and radiotherapy, and uncovered the specific mechanisms underlying these remarkable responses. Using gelatin invasion assay and intravasation assay, we report the novel finding that low-dose ATO (1 μ M) reduced the intrinsic migration ability of HeLa cells and significantly inhibited radiation-promoted tumor invasive potential of CaSki cells without inducing apoptotic cell death. Using the murine Lewis lung carcinoma model, the control animals and ATO treatment animals (1 mg/kg i.p., twice weekly) displayed similar in vivo growth kinetics, whereas the radiation (30 Gy in one fraction) and concurrent treatment groups showed considerable growth inhibition. Importantly, although concurrent treatment did not enhance the effectiveness of radiation therapy to the primary tumor, further examination of the lungs revealed that all animals succumbed to radiation-accelerated lung metastases could be effectively treated by combination of ATO and radiation. Radiation-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expression was significantly inhibited by ATO using sequential analysis of the expression of MMPs in xenografts. Supporting this observation, ATO directly downregulates radiation-induced MMP-9 mRNA expression by inhibiting nuclear factor κB activity in human cervical cancer cells. In sum, concurrent arsenic–radiation therapy not only achieves local tumor control but also inhibits distant metastasis. Experimental results of this study highlight a novel strategy in cancer treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanzar WE, Brambila EM, Diwan BA, Webber MM and Waalkes MP . (2002). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 94, 1888–1891.
Azria D, Larbouret C, Robert B, Culine S, Ychou M, Verrelle P, Dubois JB and Pelegrin A . (2003). Bull Cancer, 90 (Spec No.), S202–S212.
Baker AH, Edwards DR and Murphy G . (2002). J. Cell Sci., 115, 3719–3727.
Camphausen K, Moses MA, Beecken WD, Khan MK, Folkman J and O'Reilly MS . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 2207–2211.
Chambers AF and Matrisian LM . (1997). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 89, 1260–1270.
Chambers AF, Groom AC and MacDonald IC . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 563–572.
Choy H, Akerley W, Safran H, Graziano S, Chung C, Williams T, Cole B and Kennedy T . (1998). J. Clin. Oncol., 16, 3316–3322.
Choy H and Kim DW . (2003). Semin. Oncol., 30, 3–10.
Christofori G and Semb H . (1999). Trends Biochem. Sci., 24, 73–76.
Chun YJ, Park IC, Park MJ, Woo SH, Hong SI, Chung HY, Kim TH, Lee YS, Rhee CH and Lee SJ . (2002). FEBS Lett., 519, 195–200.
Criswell T, Leskov K, Miyamoto S, Luo G and Boothman DA . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 5813–5827.
Didelot C, Barberi-Heyob M, Bianchi A, Becuwe P, Mirjolet JF, Dauca M and Merlin JL . (2001). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 51, 1354–1360.
Egeblad M and Werb Z . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 161–174.
Eichholtz-Wirth H and Sagan D . (2000). Apoptosis, 5, 255–263.
Folkman J . (2002). Semin. Oncol., 29, 15–18.
Forastiere AA, Goepfert H, Maor M, Pajak TF, Weber R, Morrison W, Glisson B, Trotti A, Ridge JA, Chao C, Peters G, Lee DJ, Leaf A, Ensley J and Cooper J . (2003). N. Engl. J. Med., 349, 2091–2098.
Ghosh S, May MJ and Kopp EB . (1998). Annu. Rev. Immunol., 16, 225–260.
Gorski DH, Mauceri HJ, Salloum RM, Halpern A, Seetharam S and Weichselbaum RR . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 308–311.
Hughes MF . (2002). Toxicol. Lett., 133, 1–16.
Inanami O, Sugihara K, Okui T, Hayashi M, Tsujitani M and Kuwabara M . (2002). Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 78, 267–274.
Isaac N, Panzarella T, Lau A, Mayers C, Kirkbride P, Tannock IF and Vallis KA . (2002). Cancer, 95, 696–703.
Itoh T, Tanioka M, Matsuda H, Nishimoto H, Yoshioka T, Suzuki R and Uehira M . (1999). Clin. Exp. Metast., 17, 177–181.
Kapahi P, Takahashi T, Natoli G, Adams SR, Chen Y, Tsien RY and Karin M . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 36062–36066.
Kato T, Duffey DC, Ondrey FG, Dong G, Chen Z, Cook JA, Mitchell JB and Van Waes C . (2000). Head Neck, 22, 748–759.
Kim J, Yu W, Kovalski K and Ossowski L . (1998). Cell, 94, 353–362.
Kondraganti S, Mohanam S, Chintala SK, Kin Y, Jasti SL, Nirmala C, Lakka SS, Adachi Y, Kyritsis AP, Ali-Osman F, Sawaya R, Fuller GN and Rao JS . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 6851–6855.
Kwong YL and Todd D . (1997). Blood, 89, 3487–3488.
Lew YS, Kolozsvary A, Brown SL and Kim JH . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 4202–4205.
Liebmann J, Cook JA, Fisher J, Teague D and Mitchell JB . (1994). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 86, 441–446.
Lukashev ME and Werb Z . (1998). Trends Cell Biol., 8, 437–441.
Mathas S, Lietz A, Janz M, Hinz M, Jundt F, Scheidereit C, Bommert K and Dorken B . (2003). Blood, 102, 1028–1034.
McGinn CJ, Shewach DS and Lawrence TS . (1996). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 88, 1193–1203.
Miller Jr WH, Schipper HM, Lee JS, Singer J and Waxman S . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 3893–3903.
Miyamoto S, Yano K, Sugimoto S, Ishii G, Hasebe T, Endoh Y, Kodama K, Goya M, Chiba T and Ochiai A . (2004). Cancer Res., 64, 665–671.
Murgo AJ . (2001). Oncologist, 6 (Suppl 2), 22–28.
Overall CM and Lopez-Otin C . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 657–672.
Qian LW, Mizumoto K, Urashima T, Nagai E, Maehara N, Sato N, Nakajima M and Tanaka M . (2002). Clin. Cancer Res., 8, 1223–1227.
Rose PG, Bundy BN, Watkins EB, Thigpen JT, Deppe G, Maiman MA, Clarke-Pearson DL and Insalaco S . (1999). N. Engl. J. Med., 340, 1144–1153.
Russo SM, Tepper JE, Baldwin Jr AS, Liu R, Adams J, Elliott P and Cusack Jr JC . (2001). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 50, 183–193.
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM, Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, Chen Y, Zhou L, Fang ZW, Wang YT, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, Chen SJ, Chen Z and Wang ZY . (1997). Blood, 89, 3354–3360.
Sienel W, Hellers J, Morresi-Hauf A, Lichtinghagen R, Mutschler W, Jochum M, Klein C, Passlick B and Pantel K . (2003). Int. J. Cancer, 103, 647–651.
Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang ZG, Jhanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ, Corso D, DeBlasio A, Gabrilove J, Scheinberg DA, Pandolfi PP and Warrell Jr RP . (1998). N. Engl. J. Med., 339, 1341–1348.
Sporn MB . (1996). Lancet, 347, 1377–1381.
Sternlicht MD and Werb Z . (2001). Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 17, 463–516.
Strand S, Vollmer P, van den Abeelen L, Gottfried D, Alla V, Heid H, Kuball J, Theobald M, Galle PR and Strand D . (2004). Oncogene, 23, 3732–3736.
Tanioka Y, Yoshida T, Yagawa T, Saiki Y, Takeo S, Harada T, Okazawa T, Yanai H and Okita K . (2003). Br. J. Cancer, 89, 2116–2121.
van Kempen LC and Coussens LM . (2002). Cancer Cell, 2, 251–252.
Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, Van Antwerp D and Miyamoto S . (1995). Genes Dev., 9, 2723–2735.
Wei LH, Kuo ML, Chen CA, Chou CH, Cheng WF, Chang MC, Su JL and Hsieh CY . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 5799–5809.
Wick W, Wick A, Schulz JB, Dichgans J, Rodemann HP and Weller M . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 1915–1919.
Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Rimner A, Dichgans J and Wick W . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 2744–2750.
Yamagishi N, Miyakoshi J and Takebe H . (1997). Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 72, 157–162.
Yang CR, Wilson-Van Patten C, Planchon SM, Wuerzberger-Davis SM, Davis TW, Cuthill S, Miyamoto S and Boothman DA . (2000). FASEB J., 14, 379–390.
Yu Q and Stamenkovic I . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 35–48.
Zhou D, Yu T, Chen G, Brown SA, Yu Z, Mattson MP and Thompson JS . (2001). Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 77, 763–772.
Zucker S and Vacirca J . (2004). Cancer Metast. Rev., 23, 101–117.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Yung-Ming Jeng (Department of Pathology, National Taiwan University Hospital) for review of histological work presented in this study and Julie Yu for carefully reading the manuscript. This work was supported by grant from National Taiwan University Hospital 92-S016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, LH., Lai, KP., Chen, CA. et al. Arsenic trioxide prevents radiation-enhanced tumor invasiveness and inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 through downregulation of nuclear factor κB. Oncogene 24, 390–398 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208192
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208192
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A candidate for lung cancer treatment: arsenic trioxide
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2019)
-
Toxicology of arsenic in fish and aquatic systems
Environmental Chemistry Letters (2017)
-
Matrix metalloproteinases in tumorigenesis: an evolving paradigm
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2011)
-
Effects of irradiation on tumor cell survival, invasion and angiogenesis
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2010)
-
Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in NB-4, an acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line, through up-regulation of p73 via suppression of nuclear factor kappa B-mediated inhibition of p73 transcription and prevention of NF-κB-mediated induction of XIAP, cIAP2, BCL-XL and survivin
Medical Oncology (2010)