Abstract
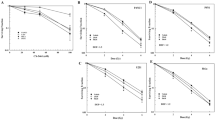
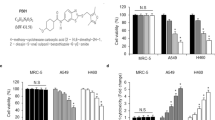
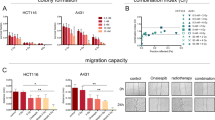
Survivin and XIAP are members of inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) family. They are upregulated in various malignancies. Inactivation of these molecules has resulted in chemosensitization. The purpose of this study was to determine whether inhibition of survivin, XIAP, or both enhances radiotherapy in a lung cancer model. Transient transfection of H460 cells with antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) against either molecule has specifically reduced their expression, by Western analysis. Results from 3-(4,5-methylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide and clonogenic assays suggest that inhibition of survivin or XIAP greatly decreased cell survival following irradiation. A significantly increased number of apoptotic cells were detected when H460 cells were treated with either antisurvivin, anti-XIAP or both ASOs (P=0.03, 0.0003 and 0.01, respectively) plus irradiation. H460 xenografts that were treated with ASOs plus radiotherapy demonstrated growth delay beyond 15 days. Growth delay in the groups of combined treatment was greater than that in other groups. However, treatment with ASOs alone did not affect tumor growth delay in mice, but decreased the survival of H460 cells in culture. Antisense treatment did not cause any mortality or weight loss during the 32 days of study. These data suggest that inhibition of survivin or XIAP radiosensitizes H460 lung cancer cells by upregulating apoptosis and downregulating cell survival. Combination of radiotherapy and inhibition of survivin and XIAP through the antisense approach results in improved tumor control by radiotherapy in a mouse model of lung cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HUVEC:
-
human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
- IAP:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis
- ASO:
-
antisense oligonucleotides
- XIAP:
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
References
Adams RR, Carmena M and Earnshaw WC . (2001). Trends Cell Biol., 11, 49–54.
Altieri DC . (2003). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 3, 46–54.
Bao R, Connolly DC, Murphy M, Green J, Weinstein JK, Pisarcik DA and Hamilton TC . (2002). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 94, 522–528.
Blanc-Brude OP, Mesri M, Wall NR, Plescia J, Dohi T and Altieri DC . (2003). Clin. Cancer Res., 9, 2683–2692.
Edwards E, Geng L, Tan J, Onishko H, Donnelly E and Hallahan DE . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 4671–4677.
Ferreira CG, van der Valk P, Span SW, Ludwig I, Smit EF, Kruyt FA, Pinedo HM, van Tinteren H and Giaccone G . (2001). Clin. Cancer Res., 7, 2468–2474.
Geng L, Donnelly E, McMahon G, Lin PC, Sierra-Rivera E, Oshinka H and Hallahan DE . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 2413–2419.
Harfouche R, Hassessian HM, Guo Y, Faivre V, Srikant CB, Yancopoulos GD and Hussain SN . (2002). Microvasc. Res., 64, 135–147.
Hofmann HS, Simm A, Hammer A, Silber RE and Bartling B . (2002). J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol., 128, 554–560.
Holcik M, Gibson H and Korneluk RG . (2001). Apoptosis, 6, 253–261.
Holcik M, Yeh C, Korneluk RG and Chow T . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 4174–4177.
Hu Y, Cherton-Horvat G, Dragowska V, Baird S, Korneluk RG, Durkin JP, Mayer LD and LaCasse EC . (2003). Clin. Cancer Res., 9, 2826–2836.
Ikehara M, Oshita F, Kameda Y, Ito H, Ohgane N, Suzuki R, Saito H, Yamada K, Noda K and Mitsuda A . (2002). Oncol. Rep., 9, 835–838.
Jansen B and Zangemeister-Wittke U . (2002). Lancet Oncol., 3, 672–683.
Kallio MJ, Nieminen M and Eriksson JE . (2001). FASEB J., 15, 2721–2723.
Lu B, Mu Y, Cao C, Zeng F, Schneider S, Tan J, Price J, Chen J, Freeman M and Hallahan DE . (2004). Cancer Res., 64, 2840–2845.
Mesri M, Morales-Ruiz M, Ackermann EJ, Bennett CF, Pober JS, Sessa WC and Altieri DC . (2001). Am. J. Pathol., 158, 1757–1765.
Monzo M, Rosell R, Felip E, Astudillo J, Sanchez JJ, Maestre J, Martin C, Font A, Barnadas A and Abad A . (1999). J. Clin. Oncol., 17, 2100–2104.
O'Connor DS, Schechner JS, Adida C, Mesri M, Rothermel AL, Li F, Nath AK, Pober JS and Altieri DC . (2000). Am. J. Pathol., 156, 393–398.
Olie RA, Simoes-Wust AP, Baumann B, Leech SH, Fabbro D, Stahel RA and Zangemeister-Wittke U . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 2805–2809.
Papapetropoulos A, Fulton D, Mahboubi K, Kalb RG, O'Connor DS, Li F, Altieri DC and Sessa WC . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 9102–9105.
Pennati M, Binda M, Colella G, Folini M, Citti L, Villa R, Daidone MG and Zaffaroni N . (2003). J. Invest. Dermatol., 120, 648–654.
Rodel C, Haas J, Groth A, Grabenbauer GG, Sauer R and Rodel F . (2003). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 55, 1341–1347.
Salvesen GS and Duckett CS . (2002). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 3, 401–410.
Schimmer AD, Welsh K, Pinilla C, Wang Z, Krajewska M, Bonneau M J, Pedersen IM, Kitada S, Scott FL, Bailly-Maitre B, Glinsky G, Scudiero D, Sausville E, Salvesen G, Nefzi A, Ostresh JM, Houghten RA and Reed JC . (2004). Cancer Cell, 5, 25–35.
Tran J, Master Z, Yu JL, Rak J, Dumont DJ and Kerbel RS . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 4349–4354.
Tran J, Rak J, Sheehan C, Saibil SD, LaCasse E, Korneluk RG and Kerbel RS . (1999). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 264, 781–788.
Uren AG, Wong L, Pakusch M, Fowler KJ, Burrows FJ, Vaux DL and Choo KH . (2000). Curr. Biol., 10, 1319–1328.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Vanderbilt Discovery Grant and Vanderbilt Physician Scientist Grant, NIH grants R01-CA58508, R01-CA88076, R01-CA89674 and the Vanderbilt Lung Cancer SPORE, P50-CA90949.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, C., Mu, Y., Hallahan, D. et al. XIAP and survivin as therapeutic targets for radiation sensitization in preclinical models of lung cancer. Oncogene 23, 7047–7052 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207929
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207929
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Apoptosis Detection Methods in Diagnosis of Cancer and Their Potential Role in Treatment: Advantages and Disadvantages: a Review
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer (2021)
-
Inhibition of Notch and HIF enhances the antitumor effect of radiation in Notch expressing lung cancer
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2017)
-
The paradox role of caspase cascade in ionizing radiation therapy
Journal of Biomedical Science (2016)
-
The X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein is an independent prognostic marker for rectal adenocarcinoma after preoperative chemoradiotherapy
Virchows Archiv (2016)
-
Targeting IAP proteins in combination with radiotherapy
Radiation Oncology (2015)