Abstract
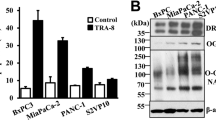
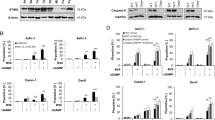
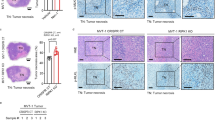
Recently, we identified Insulinoma–Glucagonoma clone 20 (IG20) that can render cells more susceptible to tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)-induced apoptosis. In addition, it can slow cell proliferation, and enhance drug- and radiation-induced cell death. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) can selectively induce apoptosis in some cancer cells and render others susceptible to cotreatment with drugs and irradiation, with little or no effect on most normal cells. In this study, we investigated the potential of IG20 to enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis and found that it can render cells more susceptible to TRAIL treatment through enhanced activation of caspases. Further, we showed that this effect can be suppressed by caspase inhibitors, p35 and CrmA, and a dominant-negative Fas-associated death domain-containing protein (DN-FADD). Results from colocalization and immunoprecipitation studies showed that IG20 can interact with TRAIL death receptors (DR), DR4 and DR5 and increase recruitment of FADD and caspase-8 into the TRAIL death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). These results indicate that IG20 is a novel protein that can enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis by facilitating DISC formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Zoubi AM, Efimova EV, Kaithamana S, Martinez O, El-Idrissi Mel-A, Dogan RE and Prabhakar BS . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 47202–47211.
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM . (1999). Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol., 11, 255–260.
Beidler DR, Tewari M, Friesen PD, Poirier G and Dixit VM . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 16526–16528.
Bodmer JL, Holler N, Reynard S, Vinciguerra P, Schneider P, Juo P, Blenis J and Tschopp J . (2000). Nat. Cell Biol., 2, 241–243.
Brown TL and Howe PH . (1998). Curr. Biol., 8, R191.
Bump NJ, Hackett M, Hugunin M, Seshagiri S, Brady K, Chen P, Ferenz C, Franklin S, Ghayur T, Li P, Licari P, Mankovich J, Shi L, Greenberg AH, Miller LK and Wong WW . (1995). Science, 269, 1885–1888.
Chow VT and Lee SS . (1996). DNA Seq., 6, 263–273.
Chow VT, Lim KM and Lim D . (1998). Genome, 41, 543–552.
Coppola T, Perret-Menoud V, Gattesco S, Magnin S, Pombo I, Blank U and Regazzi R . (2002). Biochem. J., 362, 273–279.
Cunningham SJ . (1996). Cloning and Characterization of a Novel cDNA Isolated from Human Beta Cells. Doctoral dissertation, University of Texas Medical Branch, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences at Galveston.
Degli-Esposti MA, Smolak PJ, Walczak H, Waugh J, Huang CP, DuBose RF, Goodwin RG and Smith CA . (1997). J. Exp. Med., 186, 1165–1170.
Deng Y, Lin Y and Wu X . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 33–45.
Efimova EV, Al-Zoubi AM, Martinez O, Kaithamana S, Lu SF, Arima T and Prabhakar BS . (2004). Oncogene, 23, 1076–1087.
Efimova EV, Martinez O, Lokshin A, Arima T and Prabhakar BS . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 8768–8776.
Goto Y, De Silva MG, Toscani A, Prabhakar BS, Notkins AL and Lan MS . (1992). J. Biol. Chem., 267, 15252–15257.
Griffith TS, Wiley SR, Kubin MZ, Sedger LM, Maliszewski CR and Fanger NA . (1999). J. Exp. Med., 189, 1343–1353.
Jo M, Kim TH, Seol DW, Esplen JE, Dorko K, Billiar TR and Strom SC . (2000). Nat. Med., 6, 564–567.
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR . (1972). Br. J. Cancer, 26, 239–257.
Kim K, Fisher MJ, Xu S and El-Deiry WS . (2000). Clin. Cancer Res., 6, 335–346.
Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Behrmann I, Germer M, Pawlita M, Krammer PH and Peter ME . (1995). EMBO J., 14, 5579–5588.
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ and Ashkenazi A . (2000). Immunity, 12, 611–620.
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Tinel A, LeBlanc H, Virmani A, Schow P, Gazdar A, Blenis J, Arnott D and Ashkenazi A . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 46639–46646.
Kuang AA, Diehl GE, Zhang J and Winoto A . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 25065–25068.
LeBlanc H, Lawrence D, Varfolomeev E, Totpal K, Morlan J, Schow P, Fong S, Schwall R, Sinicropi D and Ashkenazi A . (2002). Nat. Med., 8, 274–281.
Leverkus M, Neumann M, Mengling T, Rauch CT, Brocker EB, Krammer PH and Walczak H . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 553–559.
Lim KM and Chow VT . (2002). Mol. Carcinogen., 35, 110–126.
Lim KM, Yeo WS and Cho VT . (2004). Int. J. Cancer, 109, 24–37.
Miyazaki T and Reed JC . (2001). Nat. Immunol., 2, 493–500.
Neznanov N, Chumakov KP, Ullrich A, Agol VI and Gudkov AV . (2002). Med. Sci. Monit., 8, 391–396.
Ozoren N and El-Deiry WS . (2002). Neoplasia, 4, 551–557.
Pan G, Ni J, Wei YF, Yu G, Gentz R and Dixit VM . (1997). Science, 277, 815–818.
Pan G, Ni J, Yu G, Wei YF and Dixit VM . (1998). FEBS Lett., 424, 41–45.
Ravi R, Bedi GC, Engstrom LW, Zeng Q, Mookerjee B, Gelinas C, Fuchs EJ and Bedi A . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, 409–416.
Ray CA, Black RA, Kronheim SR, Greenstreet TA, Sleath PR, Salvesen GS and Pickup DJ . (1992). Cell, 69, 597–604.
Sarker M, Ruiz-Ruiz C, Robledo G and Lopez-Rivas A . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 4323–4327.
Schievella AR, Chen JH, Graham JR and Lin LL . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 12069–12075.
Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM, Gurney A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Ramakrishnan L, Gray CL, Baker K, Wood WI, Goddard AD, Godowski P and Ashkenazi A . (1997). Science, 277, 818–821.
Sprick MR, Rieser E, Stahl H, Grosse-Wilde A, Weigand MA and Walczak H . (2002). EMBO J., 21, 4520–4530.
Sprick MR, Weigand MA, Rieser E, Rauch CT, Juo P, Blenis J, Krammer PH and Walczak H . (2000). Immunity, 12, 599–609.
Suliman A, Lam A, Datta R and Srivastava RK . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 2122–2133.
Takai Y, Sasaki T, Shirataki H and Nakanishi H . (1996). Genes Cells, 1, 615–632.
Tanaka M, Miyoshi J, Ishizaki H, Togawa A, Ohnishi K, Endo K, Matsubara K, Mizoguchi A, Nagano T, Sato M, Sasaki T and Takai Y . (2001). Mol. Biol. Cell, 12, 1421–1430.
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y . (1998). Science, 281, 1312–1316.
Wada M, Nakanishi H, Satoh A, Hirano H, Obaishi H, Matsuura Y and Takai Y . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 3875–3878.
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, Smith C, Smolak P, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT, Schuh JC and Lynch DH . (1999). Nat. Med., 5, 157–163.
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA and Goodwin RG . (1995). Immunity, 3, 673–682.
Yamada H, Tada-Oikawa S, Uchida A and Kawanishi S . (1999). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 265, 130–133.
Zhou Q, Snipas S, Orth K, Muzio M, Dixit VM and Salvesen GS . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 7797–7800.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Vishva M Dixit for the DR4 Flag construct, Dr WS El-Deiry for the DR5-Myc construct, Dr Marcus Peter for the C-15 reagent, Dr Tom Hope and Dr David McDonald, for their help with the deconvolution microscopy, Dr Shashi Kaithamana for the IG20-GFP construct, Dr Prasad Kanteti and Dr David Ucker for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramaswamy, M., Efimova, E., Martinez, O. et al. IG20 (MADD splice variant-5), a proapoptotic protein, interacts with DR4/DR5 and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis by increasing recruitment of FADD and caspase-8 to the DISC. Oncogene 23, 6083–6094 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207804
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207804
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vemurafenib may overcome TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) resistance in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells
Endocrine (2020)
-
Alternative splicing as a biomarker and potential target for drug discovery
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2015)
-
Arf and Rho GAP adapter protein ARAP1 participates in the mobilization of TRAIL-R1/DR4 to the plasma membrane
Apoptosis (2008)
-
Alteration of apoptotic signaling molecules as a function of time after radiation in human neuroblastoma cells
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2008)
-
Elevated expression of genes assigned to NF-κB and apoptotic pathways in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts following mechanical stretch
Cell and Tissue Research (2007)