Abstract
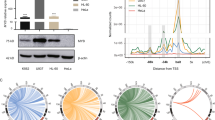
The retroviral oncogene v-myb encodes a transcription factor (v-Myb) that disrupts myelomonocytic differentiation and transforms myelomonocytic cells. It is thought that the biological effects of v-Myb are caused by deregulation of specific target genes. The CCAAT box/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBPβ), a member of the basic region-leucine zipper (bzip) class of transcription factors, which itself plays an important role during myelomonocytic differentiation, has previously been shown to be regulated by Myb. Here we have addressed the mechanism by which v-Myb affects C/EBPβ expression. We have employed the mapping of DNase I hypersensitive sites (DHSs) in chromatin as a tool to detect in vivo target sites of v-Myb. Our data identify a DHS downstream of the C/EBPβ gene that appears to be specific for v-myb-transformed myeloblasts. We have confirmed by chromatin immunoprecipitation that v-Myb is bound to this region in vivo. Furthermore, we have found that ectopic expression of v-Myb in a myelomonocytic cell line is able to induce a DHS downstream of the C/EBPβ gene, showing for the first time that v-Myb can affect chromatin structure. Reporter gene experiments demonstrate that the downstream DHS acts as a Myb-dependent enhancing element in transiently as well as in stably transfected myelomonocytic cells. Previous work has shown that v-Myb acts on the C/EBPβ promoter; it now appears that Myb stimulates C/EBPβ expression by acting on the promoter as well as on an enhancer of the C/EBPβ gene. Interestingly, the mechanisms by which Myb acts on both elements differ; while Myb activation of the promoter requires the cooperation with C/EBPβ, activation of the enhancer by Myb is independent of C/EBPβ. Apart from the identification of a novel Myb-dependent enhancer, our work demonstrates the potential of chromatin structure analysis for the identification of Myb target sites.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Isshiki H, Sugita T, Tanabe O, Kinoshita S, Nishio Y, Nakajima T, Hirano T and Kishimoto T . (1990). EMBO J., 9, 1897–1906.
Biedenkapp H, Borgmeyer U, Sippel AE and Klempnauer K-H . (1988). Nature, 355, 835–837.
Britos-Bray M and Friedman AD . 1997. Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 5127–5135.
Burk O and Klempnauer K-H . (1991). EMBO J., 10, 3713–3719.
Burk O, Mink S, Ringwald M and Klempnauer K-H . (1993). EMBO J., 12, 2027–2038.
Burk O, Worpenberg S, Haenig B and Klempnauer K-H . (1997). EMBO J., 16, 1371–1380.
Calkhoven CF, Müller C and Leutz A . (2000). Genes Dev., 14, 1920–1932.
Cao Z, Umek RM and McKnight SL . (1991). Genes Dev., 5, 1538–1552.
Chang CJ, Shen BJ and Lee SC . (1995). DNA Cell Biol., 14, 529–537.
Chumakov AM, Grillier I, Chumakova E, Chih D, Slater J and Koeffler PH . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 1375–1386.
Darlington GJ, Ross SE and MacDougald OA . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 30057–30060.
Ess KC, Whitaker TL, Cost GJ, Witte DP, Hutton JJ and Aronow BJ . (1995). Mol. Cell. Biol., 15, 5707–5715.
Frampton J, Ramqvist T and Graf T . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 2720–2731.
Hernandez-Munain C and Krangel MS . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 473–483.
Himly M, Foster DN, Bottoli I, Iacovoni JS and Vogt PK . (1998). Virology, 248, 295–304.
Hogg A, Schirm S, Nakagoshi H, Bartley P, Ishii S, Bishop JM and Gonda TJ . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 2885–2898.
Ibanez CE and Lipsick JS . (1990). Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 2285–2293.
Introna M, Golay J, Frampton J, Nakano T, Ness SA and Graf T . (1990). Cell, 63, 1287–1297.
Katz S, Kowenz LE, Müller C, Meese K, Ness SA and Leutz A . (1993). EMBO J., 12, 1321–1332.
Kintscher J, Miethe J and Klempnauer K-H . (2003). DNA Cell Biol., 22, 201–208.
Klempnauer K-H, Arnold H and Biedenkapp H . (1989). Genes Dev., 3, 1582–1589.
Klempnauer K-H, Bonifer C and Sippel AE . (1986). EMBO J., 5, 1903–1911.
Kowenz-Leutz E, Herr P, Niss K and Leutz A . (1997). Cell, 91, 185–195.
Lekstrom-Himes J and Xanthopoulos KG . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 28545–28548.
Lin WC, Shen BJ, Tsay YG, Yen HC, Lee SC and Chang CJ . (2002). DNA Cell Biol., 21, 551–560.
Lipsick JS and Wang DM . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 3047–3055.
Metz R and Ziff E . (1991). Genes Dev., 5, 1754–1766.
Mink S, Haenig B and Klempnauer K-H . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 6609–6617.
Mink S, Jaswal S, Burk O and Klempnauer K-H . (1999). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1447, 175–184.
Mink S, Kerber U and Klempnauer K-H . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 1316–1325.
Moscovici C, Moscovici MG, Jiminez H, Lai MMC, Hayman MJ and Vogt PK . (1977). Cell, 11, 95–103.
Nakajima T, Kinoshita S, Sasagawa T, Sasaki K, Narito M, Kishimoto T and Akira S . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 2207–2211.
Natsuka S, Akira S, Nishio Y, Hashimoto S, Sugita T, Isshiki H and Kishimoto T . (1992). Blood, 79, 460–466.
Ness SA . (1996). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1288, F123–F139.
Ness SA, Kowenz-Leutz E, Casini T, Graf T and Leutz A . (1993). Genes Dev., 7, 749–759.
Ness SA, Marknell A and Graf T . (1989). Cell, 59, 1115–1125.
Niehof M, Kubicka S, Zender L, Manns MP and Trautwein C . (2001a). J. Mol. Biol., 309, 855–868.
Niehof M, Manns MP and Trautwein C . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 3600–3613.
Niehof M, Streetz K, Rakemann T, Dischoff SC, Manns MP, Horn F and Trautwein C . (2001b). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 9016–9027.
Oelgeschläger M, Nuchprayoon I, Lüscher B and Friedman AD . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 4717–4725.
Oh I-H and Reddy EP . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 3017–3033.
Poli V, Mancini FP and Cortese R . (1990). Cell, 63, 643–653.
Reizis B and Leder P . (2001). J. Exp. Med., 194, 979–990.
Rushton JJ, Davis LM, Lei W, Mo X, Leutz A and Ness SA . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 308–313.
Schlichter U, Burk O, Worpenberg S and Klempnauer K-H . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 231–239.
Scott LM, Civin CI, Rorth P and Friedman AD . (1992). Blood, 80, 1725–1735.
Sippel AE, Saueressig H, Huber MC, Hoefer HC, Stief A, Borgmeyer U and Bonifer C . (1996). Methods Enzymol., 274, 233–246.
Sleeman JP . (1993). Oncogene, 8, 1931–1941.
Sterneck E, Muller C, Katz S and Leutz A . (1992). EMBO J., 11, 115–126.
Tahirov TH, Sato K, Ichikawa-Iwata E, Sasaki M, Inoue-Bungo T, Shiina M, Kimura K, Takata S, Fujikawa A, Morii H, Kumasaka T, Yamamoto M, Ishii S and Ogata K . (2002). Cell, 108, 57–70.
Taylor D, Badiani P and Weston K . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 2732–2744.
Trautwein C, Caelles C, van der Geer P, Hunter T, Karin M and Chojkier M . (1993). Nature, 364, 544–547.
Wegner M, Cao Z and Rosenfeld MG . (1992). Science, 256, 370–373.
Weston K . (1998). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 8, 76–81.
Weston K and Bishop JM . (1989). Cell, 58, 85–93.
Worpenberg S, Burk O and Klempnauer K-H . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 213–221.
Yamanaka R, Lekstrom-Himes J, Barlow C, Wynshaw-Boris A and Xanthopoulos KG . (1998). Int. J. Mol. Med., 1, 213–221.
Yeh W-C, Cao Z, Classon M and McKnight SL . (1995). Genes Dev., 9, 168–181.
Acknowledgements
We thank A Brehmer-Fastnacht for expert technical assistance and the members of our group for discussions. This work was supported by the DFG (SFB 293 and Kl 461/10-1). VY was supported by a fellowship from the Ministry of University Affairs, Thailand. DB was supported by the Studienstiftung des Deutschen Volkes and the Fonds der chemischen Industrie, which is financed, in part, by the BMBF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kintscher, J., Yamkamon, V., Braas, D. et al. Identification of a Myb-responsive enhancer of the chicken C/EBPβ gene. Oncogene 23, 5807–5814 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207722
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207722